022
ENTERPRISE SECURITY BLUEPRINT
CONTROL LAYER
02
Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is obtained using external and internal sources of threat data. Ideally
these sources should include public security intelligence, such as Computer Emergency
Readiness Teams (CERTs) and Computer Security Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs),
various security analysts, security product vendors and other organizations within the
security community. In addition to such external sources, threat intelligence is generated
within the enterprise through malware research, sandboxing techniques and data analysis of
security events collected from enforcement points.
Threat intelligence describes threat agents, their intended targets, attack campaigns, and
known Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs). Using threat intelligence, the threat
prevention controls translate the security Big Data into actionable intelligence in the
form of indicators and attack descriptions. Those indicators are the logic from which the
enforcement layers execute enforcement decisions and allow organizations to anticipate
attacks before they unfold and to recognize their significance when detected in the network.
Threat
Intelligence is
generated using
external and
internal sources
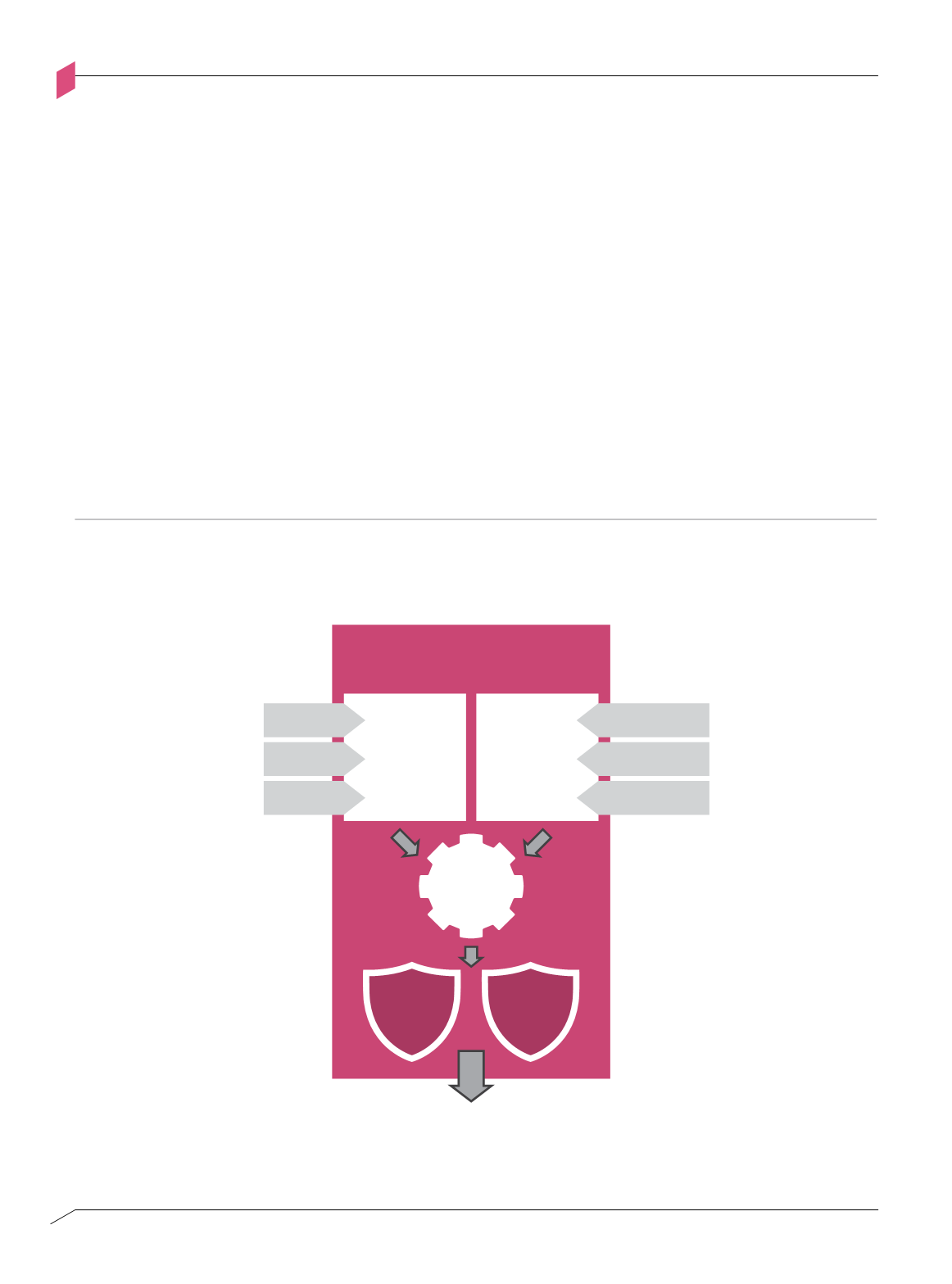
Threat intelligence analysis process
Figure 2-B
Threat
Indicators
Context &
Metadata
Threat Intelligence
External
Sources
Internal
Sources
Security Protections
Security
Analysts
CERTs
Security
Community
Malware
Research
Sandboxing
Security
Events Analysis
Big Data
Analysis
Figure 2-b:
reat Intelligence Analysis Process


