014
ENFORCEMENT LAYER
01
ENTERPRISE SECURITY BLUEPRINT
Software-defined Networking (SDN)
In traditional network infrastructures, networking and network security functions – such
as routers, switches, firewalls and IPS – are implemented as physical appliances or devices.
Networking flows are determined by network topology, with each individual network
device making local decisions about the best way to move a packet along to its destination.
But with the emergence of cloud-based virtualized server and network environments, the
ability to quickly deploy new applications without complex network changes has become a
standard requirement. SDN is an emerging network architecture where network control is
decoupled from the network infrastructure.
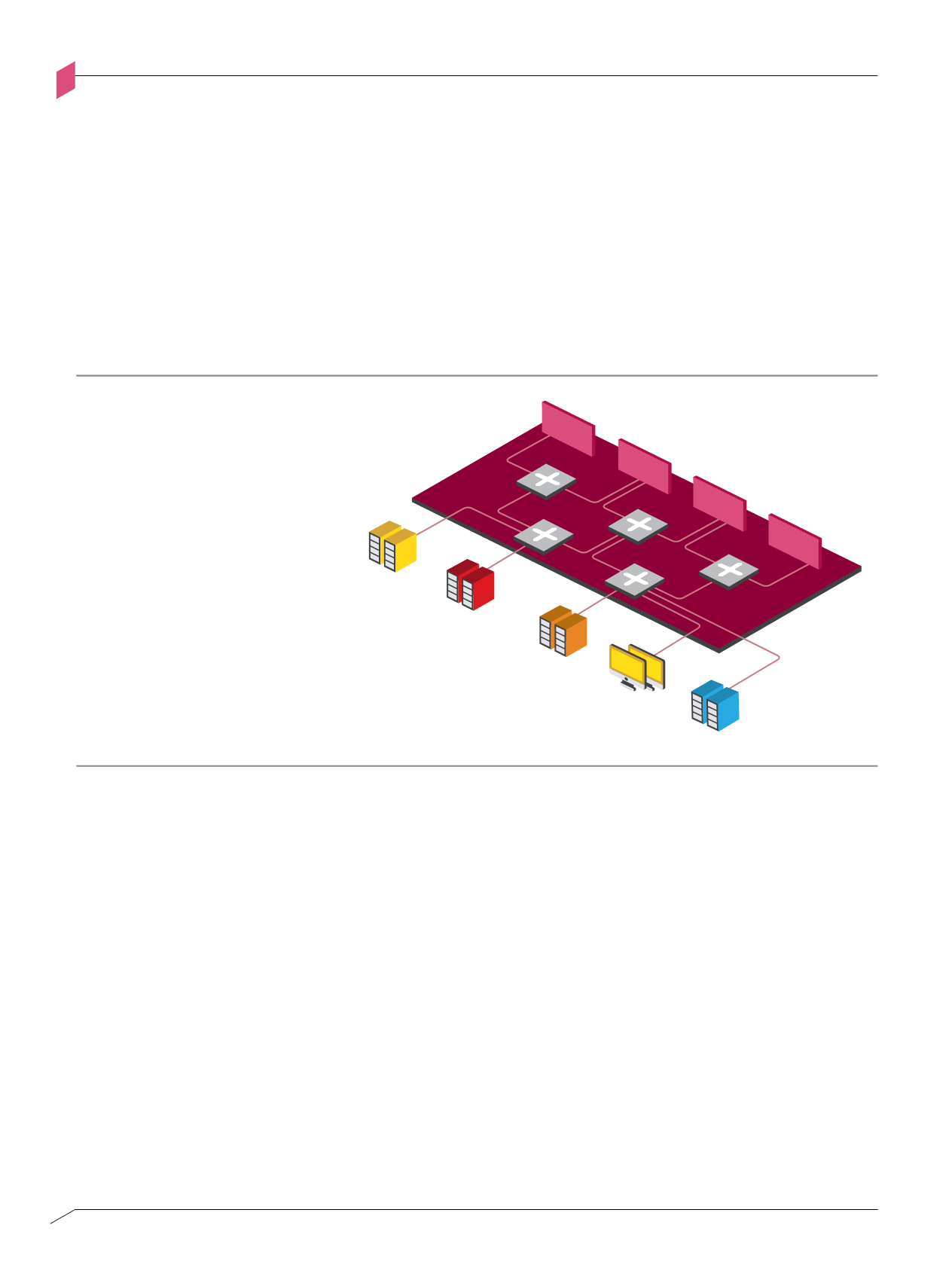
By integrating the SDP Enforcement Layer with the SDN Infrastructure Layer as depicted
above in Figure 1-F, the SDN switches are enlisted as simple enforcement points whose
security roles are to offload the appropriate flows and sub-flows to the appropriate SDP
segment enforcement points.
Figure 1-G below shows the integration between the SDP and SDN architectures. The
SDP Management Layer orchestrates this integration by using SDN application APIs (1)
and by coordinating network and security policies between the SDP and SDN control
layers (2). Network flows are then programmed by the SDP/SDN Control Layer to pass
through centralized physical or virtual SDP enforcement points (3). This ensures that all
inter-segment interactions are continuously mediated by enlisting the SDN switches as
simple enforcement points whose security role is to offload the appropriate flows and sub-
flows to the appropriate segment enforcement points.
Figure 1-f: So ware-de ned Networking (SDN) Enforcement Layer
DMZ
LAN
SENSITIVE
SERVERS
INTERNAL
SERVERS
DEPARTMENTAL
SERVERS
Enforcement Layer
Enforcement
Point
Enforcement
Point
Enforcement
Point
Enforcement
Point
SDN Switch
SDN Switch
SDN Switch
SDN Switch
SDN Switch
Software-defined Networking
(SDN) Enforcement Layer
Figure 1-F


