032
ENTERPRISE SECURITY BLUEPRINT
CONTROL LAYER
02
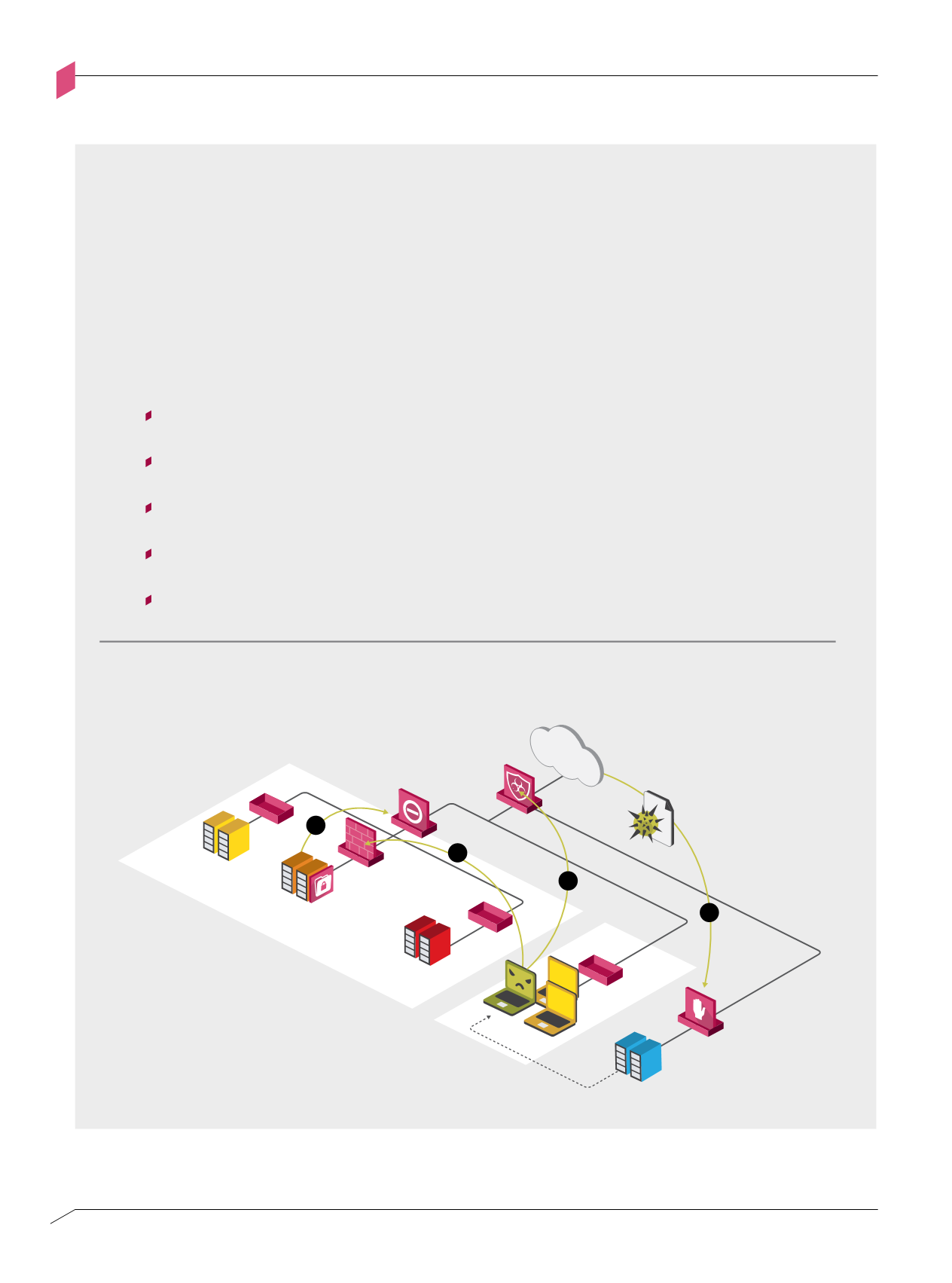
Although the RSA security team had threat intelligence and analytics controls implemented and were able
to detect the attack while it was in progress, they lacked suitable preventive controls to block the attackers
from achieving their goals once inside the network. In this attack, the intrusion kill chain
1
corresponded
to a series of interactions. In a well-segmented enterprise, these interactions would cross multiple segment
boundaries and enforcement points such as Internet to DMZ, DMZ to Internal Server segment, and
Internal Server segment to Access Network. Each of these enforcement points represents an opportunity
for detecting and blocking attacks via a combination of different security control logic types.
The RSA attack could have been disrupted at several points along the intrusion kill chain:
Pre-infection Threat Prevention –
The email attachment could have been
quarantined and tested to ascertain that it posed no threat to the organization
Post-infection Threat Prevention –
The Poison Ivy RAT is a well-known malicious
application that should have been blocked from connecting to its C&C servers
Inbound Access Control –
The infected endpoint should have been blocked from
accessing RSA’s “crown jewels”
Outbound Access Control –
Data exfiltration could have been blocked by using a
data loss prevention security control at the organizational perimeter
Data Protection -
Sensitive information should have been stored in encrypted form
Protection strategies for disrupting the RSA intrusion kill chain
Figure 2-F
Figure 2-f: Protection strategies for disrupting the RSA intrusion kill chain
DATA CENTER
DMZ
LAN
DEPARTMENTAL
SERVERS
SENSITIVE
SERVERS
INTERNAL
SERVERS
INTERNET
Outbound
Access Control
Inbound
Access Control
DATA PROTECTION
Post-infection
Threat Prevention
Pre-infection
Threat Prevention
1
4
3
2
1
Intrusion kill chain is a concept labeled by Lockheed Martin to describe an attacker methodology as a series of sequential steps, including
reconnaissance, weaponization, delivery, exploitation, installation, command and control (C2), and actions on objectives.


