CME Structure and Configuration
These sections explain the primary concepts of CME configuration.
CME Directories and Files
-
The CME is located in this directory on the Security Management or Multi-Domain Security Management Server:
/opt/CPcme/ -
To execute the configuration tool for autoscaling solutions (such as Azure VMSS, AWS
 Amazon® Web Services. Public cloud platform that offers global compute, storage, database, application and other cloud services. ASG, GCP
Amazon® Web Services. Public cloud platform that offers global compute, storage, database, application and other cloud services. ASG, GCP See 'Google Cloud Platform'. MIG, OCI Instance Pool), run this command in Expert mode:
See 'Google Cloud Platform'. MIG, OCI Instance Pool), run this command in Expert mode:autoprov_cfgA more detailed description of
autoprov_cfgis provided in Configuring CME using the autoprov_cfg Command Line Configuration Tool (not recommended). -
Run this command in Expert mode to execute the command line configurations menu:
cme_menuFor each CME feature that requires the CME Menu, see the specific instructions in the related chapter.
-
Configuration tool for AWS Transit Gateway:
tgw_menuFor a more detailed description of the
tgw-menufeatures, see Configuring the tgw_menu.
About CME Service Commands
After a successful installation, CME runs the 'cme' service.
|
Function |
Run this Command |
|---|---|
|
Stop the service |
|
|
Start the service |
|
|
Restart the service |
|
|
Test the service |
|
|
Get the status of the service |
|
Locating the Configuration Files
CME's primary configuration file is autoprovision.json, and CME maintains backup files for it:
-
autoprovision.json.bak - when there is a configuration change.
-
autoprovision.json.bak_schema - when CME schema version is updated - See Schema section.
To find the CME configuration files, use one of these directories:
-
On a Multi-Domain Security Management Server:
$MDSDIR/conf
The configuration files are synchronized between the primary and secondary servers in a Management High Availability environment.
The CME Logs
The CME log files are:
-
Primary CME Service log:
/var/log/CPcme/cme.log* -
CME command line menu log:
/var/log/CPcme/cme_menu.log
More logs used by Check Point Support:
-
rest_infra.log -
cme_api.log -
gunicorn_server.log -
diagnostics.log
See CME Log Collector.
CME Authentication
This section describes the necessary steps for CME authentication with different public cloud platforms.
AWS
Refer to sk130372 > 3. Creating an AWS IAM User and IAM Role section.
AWS Controller (account) connects to these URLs:
-
https://ec2.<region_code>.amazonaws.com
-
https://elasticloadbalancing.<region_code>.amazonaws.com
For example, https://ec2.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/.
Azure
For authentication with Azure, you can use Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) or Azure Identity and Access Management (IAM).
Option 1: Create a Microsoft Entra ID and Service Principal
With the Microsoft Entra ID and Service Principal, the Check Point Security Management Server![]() Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. monitors the creation and status of the VMSS, so it can complete the provision of these Security Gateways.
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. monitors the creation and status of the VMSS, so it can complete the provision of these Security Gateways.
|
|
Note - Grant the Service Principal at least "Managed Application Contributor", "Storage Account Contributor", "Network Contributor", and "Virtual Machine Contributor" permissions to the Azure subscription. For any extra permissions needed, see the official Microsoft documentation for guidance. |
-
Connect to portal.azure.com.
-
Click Microsoft Entra ID.
-
Click +Add > App registration. The Register an application screen opens
-
Create new registration:
-
Select a meaningful Name.
-
Supported account types - Select Accounts in this organizational directory only (Single tenant).
-
Redirect URL - Select Web, and type https://localhost/vmss-name - instead of vmss-name. It can be any name.
-
Click Register. The new application is created.
-
In the new application screen, on the left menu pane, click Manage > Certificates and secrets.
-
In the Client Secrets tab, click + New Client Secret.
-
Add the duration for the key.
-
Click Add.
-
Backup the key. You cannot look at the key later. Save it now.
-
After you create the application, write down these values to use in the "Configure the Check Point Security Management Server" step.
-
Application ID
client_id -
Key value
client_secret -
Tenant ID
directory (tenant) ID
Permissions:
Give the Microsoft Entra ID application a minimum role of Reader to the VMSS and the VNET as explained here.
Option 2: Configure Azure IAM on the Security Management Server
To enable the system-assigned managed identity for the Security Management Server Virtual Machine, do these steps:
-
Connect to portal.azure.com.
-
Go to the desired VM and open its settings.
-
In the left pane, go to "Security" > "Identity".
-
Under “System assigned”, switch "Status" to "On".
-
Save the changes.
Permissions:
Assign a managed identity access to the Security Management Server with a minimum role of Reader to the VMSS and the VNET as explained here.
Azure Controller (account) connects to these URLs:
-
AzureCloud
-
https://core.windows.net
-
https://management.azure.com
-
https://login.microsoftonline.com
-
-
AzureChinaCloud
-
https://login.chinacloudapi.cn
-
https://management.chinacloudapi.cn
-
https://core.chinacloudapi.cn
-
-
AzureUSGovernment
-
https://login.microsoftonline.us
-
https://management.usgovcloudapi.net
-
https://core.usgovcloudapi.net
-
GCP
Create a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Service Account
The Check Point Security Management Server uses the GCP Service account to monitor the creation and status of the autoscaling Managed Instance Group. This lets the Security Management Server complete provisioning of these Security Gateways.
To create a GCP service account:
-
Go to https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/creating-managing-service-accounts.
Use these parameters:
Name:
check-point-autoprovisionRole:
Compute Engine \ Compute Viewer -
Click Create Key > JSON (as the key type). A JSON file is downloaded to your computer.

Note - This JSON file is later used as the credentials file in CME Structure and Configuration.
Permissions:
"Compute viewer"
GCP Controller (account) connects to this URL:
https://www.googleapis.com/
OCI
To add user permissions:
-
Create a group with required permissions:
-
Go to Identity & Security > Identity > Domains.
-
Select the user domain.
-
On the left pane, click Groups.
-
Click Create Group and follow the steps to create a group with autoscale permissions.
-
After creating the group, go to Identity & Security > Identity > Policies.
-
Create a new policy with these permissions (replace <domain>, <group_name>, and <compartment_name> with corresponding names):
Allow group <domain>/<group_name> to manage instance-family in compartment <compartment_name>
Allow group <domain>/<group_name> to inspect vnic-attachments in compartment <compartment_name>
Allow group <domain>/<group_name> to manage virtual-network-family in compartment <compartment_name>
Allow group <domain>/<group_name> to inspect instance-pools in compartment <compartment_name>
-
-
Assign a user to the group:
-
Go to Identity & Security > Identity > Domains.
-
Select the user domain.
-
In the Identity domain menu at the left, click Groups.
-
Select the group with autoscale permissions (created in Step 1).
-
Click Assign user to groups.
-
Select the user from the list and click Add.
-
To generate an API signing key pair:
Refer to the OCI documentation for the most up-to-date instructions.
After you have generated the API signing key pair and downloaded the private API key, write down these values (you will need them later for the Security Management Server configuration step):
-
user: The OCID (Oracle Cloud
 Oracle Cloud is a cloud computing service offered by Oracle Corporation. It provides servers, storage, networks, applications, and services through a global network of Oracle Corporation-managed data centers. Identifier) of the user.
Oracle Cloud is a cloud computing service offered by Oracle Corporation. It provides servers, storage, networks, applications, and services through a global network of Oracle Corporation-managed data centers. Identifier) of the user. -
tenancy: The OCID of your tenancy.
-
key: The contents of the private API key (it starts with “
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----" and ends with “-----END PRIVATE KEY-----").
Configuring CME in SmartConsole (recommended)
CME is integrated into SmartConsole![]() Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on., Web SmartConsole, and Smart-1 Cloud starting from:
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on., Web SmartConsole, and Smart-1 Cloud starting from:
-
R82.10 SmartConsole Releases Build 82.10.9900.408
-
R82 SmartConsole Releases Build 1055
-
R81.20 SmartConsole Releases Build 663
-
Web SmartConsole Take 128
-
CME Take 297
This integration facilitates cloud-native connectivity between Check PointCloudGuard Network solutions and various cloud platforms.
To configure CME controllers (accounts) and create configuration templates with SmartConsole, go to Manage & Settings > CloudGuard Network.
|
|
Note - If you already have a CME configuration on the Security Management Server that was added with If they are not, you can associate them by running this command on the Security Management Server:
|
Add an account
-
To add the first account for the cloud provider, on the corresponding cloud provider tile, click Add account.

Note - To add more accounts, click the Edit button at the right, above the cloud provider tiles. The CME Overview page opens. Then click the
 icon above the Accounts table.
icon above the Accounts table.The CME Account window opens.
-
Give the account a name.
-
In the Platform drop-down list, select AWS, GCP, or Azure.
-
Enter the parameters.
-
Click OK to save the changes.
Parameters for AWS
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Access Key ID |
AWS Access Key ID. This parameter is mandatory unless you select Role Authentication (IAM). |
|
Secret Access Key |
AWS Secret Key. This parameter is mandatory unless you select Role Authentication (IAM). |
|
Role Authentication (IAM) |
This option is available only in on-premises Security Management Server deployments. It is not available in Smart-1 Cloud. |
|
Regions |
The AWS regions in which the Security Gateways are being deployed. |
|
STS Role |
The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of an IAM role to assume. |
|
STS External ID |
An optional STS External ID to use when assuming an IAM role in the account. |
|
Scan Gateway Load Balancer subnets |
Enable to scan Gateway Load Balancer subnets. |
|
Synchronize VPN |
Enable to synchronize VPN. |
|
Sub Accounts |
Add new sub accounts or configure properties of existing sub accounts. The sub-account name must be unique. Enter STS Role or STS External ID. |
Parameters for Azure
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Application ID |
The service principal’s application ID in UUID format. |
|
Client Secret |
The service principal's client secret value. |
|
Directory ID |
The service principal's Directory ID in UUID format. |
| Subscription ID |
The subscription ID where the VMSS resides in UUID format. |
|
Azure Environment |
Select the environment in the drop-down list. The default value is "Azure Cloud". |
Parameters for GCP
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Service Account Key Authentication |
Upload a public service account key file in JSON format. |
|
|
Important - Before adding a GCP account, you must change the default Security Management Server name ("MGMT") to the name in all lowercase letters because of the GCP platform limitation. |
Edit an account
-
To edit an account, click the Edit button at the right, above the cloud provider tiles.
The CME Overview window opens.
-
In the Accounts table, select the account you want to edit and click the "pencil" icon in the toolbar above the table.
The CME Account window opens.
-
Edit the parameters.
-
Click OK to save the changes.
Add a Security Gateway configuration template
-
To add the first Security Gateway
 Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. configuration template to the cloud provider account, on the corresponding cloud provider tile, click Add template.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. configuration template to the cloud provider account, on the corresponding cloud provider tile, click Add template.
Note - To add more templates, click the Edit button at the right, above the cloud provider tiles. The CME Overview page opens. Then click the
 icon above the Gateway Templates table.
icon above the Gateway Templates table.The CME Template window opens.
-
Give the Security Gateway configuration template a name.

Important - This name must be the same that you used in the configuration of your CloudGuard Network Security solution.
-
Open Gateway Settings. In the Account drop-down list, select the applicable Account.
-
Select the Security Gateway version.
-
Enter a one-time password.
-
Confirm the one-time password.
-
On the Network Security and Threat Prevention tabs, select the checkboxes for the blades you want to enable on the Security Gateway.
-
Open CME Attributes to select the policy to install on the Security Gateway. You can also specify a name of the rule
 Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. section in the Access and NAT layers in the policy, where to insert the automatically generated rules.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. section in the Access and NAT layers in the policy, where to insert the automatically generated rules.
Note - To add support for AWS Transit Gateways to the AWS account, configure the below parameters in CME Attributes.
Parameters for AWS Transit Gateway
Parameter
Description
VPN Domain
A VPN Domain.
VPN Community
A VPN Star community where the VPN Gateway is the center.
TGW Static Routes
Enter network addresses (CIDR) to create a static route on each Gateway of the Transit Gateway auto-scaling group.
TGW Static Spokes
Spoke CIDR is learned from the TGW over BGP and is re-advertised by the Gateways of the TGW auto-scaling group to the AWS TGW.
For more information on AWS Transit Gateway, refer to CloudGuard Network for AWS Transit Gateway Deployment Guide.

Note - To add IPv6 support to the Azure account, select the IPv6 checkbox in CME Attributes.
-
Provide the repository script name and parameters if necessary.

Note - For more information on repository scripts and their usage, refer to R82 Quantum Security Management Administration Guide > Managing Gateways > Running Scripts.
-
Click Logs to add log servers.
-
Click NAT to select which settings to use for communication with the Security Management Server or log servers when they are behind NAT or in the public cloud.

Note - This section is enabled only for the R82 version of Security Gateway.
-
Click OK to save the changes.
Edit a Security Gateway configuration template
-
To edit a Security Gateway configuration template, click the Edit button at the right, above the cloud provider tiles.
The CME Overview window opens.
-
In the Accounts table, select the account which templates you want to edit.
-
In the Gateway Templates table, select the template you want to edit and click the "pencil" icon in the toolbar above the table.
The CME Template window opens.
-
Edit the parameters.
-
Click OK to save the changes.
Advanced settings
To open the Advanced Settings window, click the Advanced link at the right, above the cloud provider tiles.
In this section, you can:
-
Change the Security Management Server name.

Important - If you change the Security Management Server name, you must change it also in the configuration of your CloudGuard Network Security solution.

Important - You must change the default Security Management Server name ("MGMT") to the name in all lowercase letters before adding a GCP account (because of the GCP platform limitation).
-
Change the Delay Cycle value (the waiting time after each poll cycle).
-
Download logs with information about CME operations and API calls.
Configuring CME using CME Management API (recommended)
We recommend using CME Management API to configure CME.
CME API Documentation:
-
SwaggerHub: CME API
-
Postman Collection: CME API Postman collection
Prerequisites:
-
CME Take 139 or higher installed on the Security Management Server.
-
Management API version 1.8 or higher installed on the Security Management Server (see the Check Point Management API Reference (at the top, select the correct version) ).
Configuring Delay using CME API
CME API uses a "delay_cycle" parameter to set the sleep time (in seconds) between CME iterations.
The default "delay_cycle" value is 30 seconds.
To see the current "delay_cycle" value with CME API:
Send a GET request:
|
GET https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/generalConfiguration/delayCycle |
Response example:
|
|
To set the "delay_cycle" value with CME API:
Send a PUT request:
|
PUT https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/generalConfiguration/delayCycle |
Request body parameters:
|
Object |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Time (in seconds) to wait after each poll cycle. |
Example:
PUT request:
|
PUT https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/generalConfiguration/delayCycle
Body:
|
Configuring Management using CME API
To see the current Management configuration with CME API:
Send a GET request:
|
GET https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/management |
Response example:
|
|
To edit the Management configuration with CME API:
Send a PUT request:
|
PUT https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/management |
Request body parameters:
|
Object |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The name of the management server. |
|
|
The name of the script which is located at $FWDIR/conf/cme. |
|
|
The management's domain name in the MDS environment. |
Example:
PUT request:
|
PUT https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/management
Body:
|
Configuring Accounts (CME Controllers) with CME API
To connect to your cloud account and automatically provision Security Gateways deployed in the account, the Security Management Server needs cloud-specific information, including authorization settings.
To see all current accounts (controllers) used by the Security Management Server connected to the cloud environments:
Send a GET request:
|
GET https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/accounts |
Response example:
|
|
To see details of a specific account (controller) used by the Security Management Server connected to the cloud environments:
Send a GET request:
|
GET https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/accounts/accountName |
Response example:
|
|
To configure CME Azure account (controller) on the Security Management Server:
-
With Microsoft Entra ID and Service Principal:
Send a POST request:
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/accounts/azure
Request body parameters:
Parameter Name
Description
nameAzure account name.
subscriptionAzure subscription ID.
directory_idThe Azure Active Directory tenant ID.
application_idThe service principal's client ID value.
client_secretThe service principal's client secret value.
deletion_toleranceThe number of cycles until a Gateway object in SmartConsole is deleted.
This operation returns
"status-code": 200. -
With Azure IAM (starting from CME API v1.2.3):
Prerequisite: Security Management Server virtual machine is using a system-assigned managed identity.
Send a POST request:
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/accounts/azure
Request body parameters:
Parameter Name
Description
nameAzure account name.
subscriptionAzure subscription ID.
iamEnable/disable IAM. Must be set to
true.deletion_toleranceThe number of cycles until a Gateway object in SmartConsole is deleted.
domainSpecify the domain name or the domain UID that manages this controller.
This parameter is mandatory for Multi-Domain Security Management Server environments with more than one domain configured.
environmentAn optional attribute that specifies Azure's environment type.
The possible values are:
AzureCloud (default)
AzureChinaCloud
AzureUSGovernment
This operation returns
"status-code": 200.
To configure CME AWS account (controller) on the Security Management Server:
Send a POST request:
|
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/accounts/aws |
Request body parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Your AWS account name. |
|
|
A comma-separated list of AWS regions where the gateways are deployed. For example: eu-west-1,us-east-1,eu-central-1. |
|
|
The number of cycles until a Gateway object in SmartConsole is deleted. |
|
|
The path to a text file with the AWS credentials. |
|
|
AWS Access Key ID |
|
|
AWS Secret Key |
|
|
The STS Role ARN of a role to assume. |
|
|
An optional STS External ID to use when assuming a role in the account. |
|
|
Set "true" to scan gateways with AWS TGW. |
|
|
Set "true" to scan VPN with the AWS TGW solution. |
|
|
Set true to scan load balancers' access and NAT rules with the AWS TGW solution. |
|
|
An optional comma-separated list of communities which are allowed for VPN connections that this controller discovers. If this attribute is missing or its value is an empty list, any community may be joined by VPN connections that belong to this controller. This is useful to prevent an automatic addition of VPN connections to a community based on the customer gateway public IP address. |
|
|
Set "true" to scan subnets with the AWS GWLB solution. |
|
|
Set "true" to scan IPv6 subnets with the AWS GWLB solution. |
|
|
A list of sub-accounts with their configuration parameters. |
This operation returns "status-code": 200.
To configure CME GCP account (controller) on the Security Management Server:
Send a POST request:
|
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/accounts/gcp |
Request body parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Your GCP account name. |
||
|
|
The ID of the GCP project where to scan for VM instances. |
||
|
|
The number of cycles until a Gateway object in SmartConsole is deleted. |
||
|
|
The path to a text file with the GCP credentials. The credentials file should be placed on the Security Management Server under the following path:
|
||
|
|
The base64-encoded string that represent the content of the credentials file. |
||
|
|
The account's domain name in the Multi-Domain Security Management Server (MDS) environment. To delete it, insert the |
This operation returns "status-code": 200.
To configure CME OCI account (controller) on the Security Management Server:
Send a POST request:
|
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.3/accounts/oci |
Request body parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Your OCI account name. |
||
|
|
The OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier) of the compartment. For example: " |
||
|
|
An OCI region. For example: “ |
||
|
|
The domain for the OCI realm. For example, "oraclecloud.com". |
||
|
|
The base64-encoded string with OCI credentials. For example: “
|
This operation returns "status-code": 200.
Configuring Templates (gateway-configurations) with CME API
Information required to automatically provision Security Gateways, such as what policy to install and which Software Blades to enable, is placed in a configuration template in the CME configuration.
We recommend configuring templates (gateway-configurations) with CME API.
To see all current templates (gateway-configurations) that you can apply on Security Gateways:
Send a GET request:
|
GET https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/gwConfigurations |
Response example:
|
|
To see details of a specific template (gateway-configuration):
Send a GET request:
|
GET https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/gwConfigurations/templateName |
Response example:
|
|
To configure CME Azure template (gateway-configuration) on the Security Management Server:
Send a POST request:
|
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/gwConfigurations/azure |
Request body parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Unique configuration template name for identification. |
|
|
The Security Gateway version. |
|
|
Key for trusted communication between Security Management Server and Security Gateway. A base64-encoded string, the decoded string have to be between 8 and 30 alphanumeric characters. |
|
|
Policy name to be installed on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
Azure account to associate with the Security Gateway Configuration. |
|
|
Blades to activate/deactivate on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
Identity Awareness |
|
|
A name or UID of a script that exists in the scripts repository on the Security Management Server. |
|
|
Enable XFF headers in HTTP / HTTPS requests. |
|
|
Name of a rule section in the Access and NAT layers in the policy, where to insert the automatically generated rules. |
|
|
Color of the Security Gateway objects in SmartConsole. |
|
|
"Gateway behind NAT" communications settings with the Check Point Servers(Management, Multi-Domain, Log Servers). |
|
|
Enable IPv6 for Azure VMSS. |
|
|
Names of Primary Log Servers to which logs are sent. |
|
|
Names of Backup Log Servers to which logs are sent when Primary Log Servers are not available. |
|
|
Names of Alert Log Servers to which alerts are sent. |
This operation returns "status-code": 200.
To configure CME AWS template (gateway-configuration) on the Security Management Server:
Send a POST request:
|
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/gwConfigurations/aws |
Request body parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Unique configuration template name for identification. |
|
|
The Security Gateway version. |
|
|
Key for trusted communication between Security Management Server and Security Gateway. A base64-encoded string, the decoded string have to be between 8 and 30 alphanumeric characters. |
|
|
Policy name to be installed on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
AWS account to associate with the Security Gateway Configuration. |
|
|
Blades to activate/deactivate on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
Identity Awareness settings that can be configured on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
A name or UID of a script that exists in the scripts repository on the Security Management Server. |
|
|
Enable XFF headers in HTTP / HTTPS requests. |
|
|
Name of a rule section in the Access and NAT layers in the policy, where to insert the automatically generated rules. |
|
|
Color of the Security Gateway objects in SmartConsole. |
|
|
"Gateway behind NAT" communications settings with the Check Point Servers(Management, Multi-Domain, Log Servers). |
|
|
The VPN domain for the VPN gateway. |
|
|
A star community in which to place the VPN gateway as center. |
|
|
The deployment type of the CloudGuard Security Gateways. |
|
|
Comma separated list of cidrs, for each cidr a static route will be created on each gateway of the TGW auto scaling group. |
|
|
Comma separated list of spoke cidrs, each spoke cidr that was learned from the TGW over bgp will be re-advertised by the gateways of the TGW auto scaling group to the AWS TGW. |
|
|
Names of Primary Log Servers to which logs are sent. |
|
|
Names of Backup Log Servers to which logs are sent when Primary Log Servers are not available. |
|
|
Names of Alert Log Servers to which alerts are sent. |
This operation returns "status-code": 200.
To configure CME GCP template (gateway-configuration) on the Security Management Server:
Send a POST request:
|
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.3/gwConfigurations/gcp |
Request body parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Unique configuration template name for identification. |
|
|
The Security Gateway version. |
|
|
Key for trusted communication between Security Management Server and Security Gateway. A base64-encoded string, the decoded string have to be between 8 and 30 alphanumeric characters. |
|
|
Policy name to be installed on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
GCP account to associate with the Security Gateway Configuration. |
|
|
Blades to activate/deactivate on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
Identity Awareness settings that can be configured on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
A name or UID of a script that exists in the scripts repository on the Security Management Server. |
|
|
Enable XFF headers in HTTP / HTTPS requests. |
|
|
Name of a rule section in the Access and NAT layers in the policy, where to insert the automatically generated rules. |
|
|
Color of the Security Gateway objects in SmartConsole. |
|
|
"Gateway behind NAT" communications settings with the Check Point Servers(Management, Multi-Domain, Log Servers). |
|
|
Names of Primary Log Servers to which logs are sent. |
|
|
Names of Backup Log Servers to which logs are sent when Primary Log Servers are not available. |
|
|
Names of Alert Log Servers to which alerts are sent. |
This operation returns "status-code": 200.
To configure CME OCI template (gateway-configuration) on the Security Management Server:
Send a POST request:
|
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.3/gwConfigurations/oci |
Request body parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Unique configuration template name for identification. |
|
|
The Security Gateway version. |
|
|
Key for trusted communication between Security Management Server and Security Gateway. A base64-encoded string, the decoded string have to be between 8 and 30 alphanumeric characters. |
|
|
Policy name to be installed on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
OCI account to associate with the Security Gateway Configuration. |
|
|
Blades to activate/deactivate on the Security Gateway. |
|
|
A name or UID of a script that exists in the scripts repository on the Security Management Server. |
|
|
Enable XFF headers in HTTP / HTTPS requests. |
|
|
Name of a rule section in the Access and NAT layers in the policy, where to insert the automatically generated rules. |
|
|
Color of the Security Gateway objects in SmartConsole. |
|
|
"Gateway behind NAT" communications settings with the Check Point Servers(Management, Multi-Domain, Log Servers). |
|
|
Names of Primary Log Servers to which logs are sent. |
|
|
Names of Backup Log Servers to which logs are sent when Primary Log Servers are not available. |
|
|
Names of Alert Log Servers to which alerts are sent. |
This operation returns "status-code": 200.
Configuring Identity Sharing using CME API
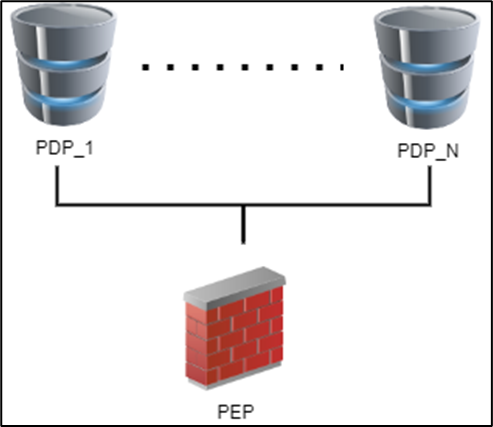
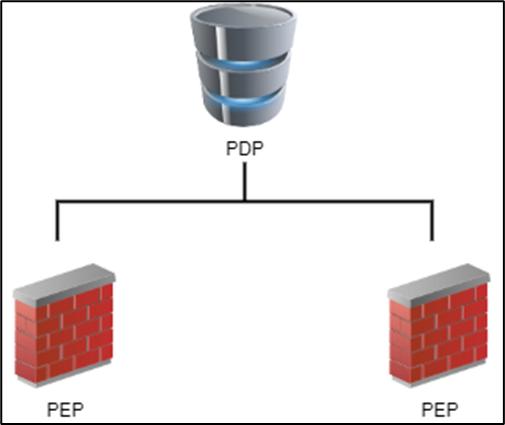
Identity Sharing lets Identity AwarenessSecurity Gateways configured as Policy Decision Points (PDPs) retrieve identity information and share it with other Security Gateways acting as Policy Enforcement Points (PEPs). This feature reduces load on identity sources and enhances system performance.
Examples of Identity Sharing topologies:
Configuring Identity Sharing
Starting from CME API v1.2.2, you can set up Identity Sharing for the Auto Scaling instances to let them receive identities from configured PDPSecurity Gateways. This feature is part of the Identity Awareness settings.
Prerequisites:
-
Set up static Identity AwarenessSecurity Gateways as PDPs to share identities. For more information, see the Identity Sharing documentation.
-
Configure Auto Scaling instances template to receive identities from those PDPSecurity Gateways.
-
Make sure the PDPSecurity Gateways and Auto Scaling Security Gateway instances exist in the same domain for Multi-Domain Security Management deployments.
To configure Identity Sharing using CME API:
Send a POST request:
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.2/gwConfigurations/<azure/gcp/aws>
Request body parameters for Identity Sharing:
|
Object |
Description |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
A container object that holds blades configuration parameters.
|
||||||
|
|
A container object that holds configuration parameters of the Identity Awareness blade.
|
|
|
Note - Enabling the Identity Awareness blade without setting the Identity Awareness Settings automatically enables the Web API identity source for the CloudGuard Controller ( |
Example:
POST request:
|
URL: POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.2/gwConfigurations/<azure/gcp/aws>
Body:
|
Configuring CME using the autoprov_cfg Command Line Configuration Tool (not recommended)
-
The
autoprov_cfgis a command-line tool to configure autoscaling solutions, such as AzureVMSS, AWS ASG, GCPMIG, OCI Instance Pool. -
Refer to the specific solutions administration guide for specific information about how to use
autoprov_cfg. -
For instructions about how to use the
autoprov_cfg, run:autoprov_cfg -h -
Commands summary:
Command Description initInitialize auto-provision with Management, a Configuration Template, and a Controller (account) configuration
showShow all or specific configuration settings
add-
Add a new Configuration Template or a Controller
-
Add a new configuration to the Management or to a Configuration Template or a Controller
setSet values in an existing configuration of Management, Configuration Template or a Controller
delete-
Remove a Configuration Template or a Controller
-
Remove a configuration from the Management or from a Configuration Template or a Controller
-vShow the version of CME
-hShows specific help documentation

Important - If you have an existing configuration, running the
autoprov_cfg initcommand will override it.To add one more auto-provisioned environment, use the
autoprov_cfg addcommand instead ofautoprov_cfg init. -
-
Specific help documentation is available for each option that you select.
For example, this command shows the available initialization parameters for AWS and their definition:
autoprov_cfg init AWS -h
Schema
-
Starting from CME Take 212, the CME configuration has a schema version.
-
This attribute ensures that only compatible CME runs with the given CME configuration.
-
CME does not run when the schema version in the CME configuration is not compatible.
-
Example scenarios that can cause incompatibility:
-
Revert to the older CME Take.
-
Upgrade - export configuration and importing it on a machine with an older CME Take.
-
High Availability Management/Multi Domain servers where the CME on the two members is not from the same take.
-
-
CME adds/updates a schema version parameter automatically and stores a backup of the previous configuration file in the
autoprovision.json.bak_schemafile. -
To show the current schema version value, look for the schema value in the CME configuration:
autoprov_cfg show all -
This is a read-only parameter.
-
This attribute ensures that only compatible CME runs with the given CME configuration.
Delay
-
The delay parameter sets the sleep time between CME iterations.
-
The default delay value is 30 seconds.
-
To see the current delay value, look for the delay value in the CME configuration:
autoprov_cfg show all -
To edit the delay configuration, run:
autoprov_cfg set delay <NEW_TIME_IN_SEC>
Management
-
There is one Management configuration for CME.
-
The Management configuration applies to each controller and each template.
To see the current Management configurations, run:
autoprov_cfg show managementTo edit the management configurations, run:
autoprov_cfg set management -h
Management Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
Description |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
MANAGEMENT-NAME |
The name of this CME management configuration. This name must match the management name configured for each deployed scale set.
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
DOMAIN: |
The domain name or the domain UID that manage CME. This parameter is mandatory for Multi-Domain Security Management Server environments when one domain manages CME. If more than one domain manages CME, you must remove this parameter and configure it in the controller part, as explained below in the controller section. |
||||||||||||||
|
|
SCRIPT FULL PATH |
This parameter lets you set a custom script to execute on the Management Server in these scenarios:
In each of these scenarios, CME runs the script with different arguments, as listed in the table below:
You can download an example of the Custom Management Script from here. To add parameters to the script, see |
Controllers (accounts)
-
To connect to your cloud account and automatically provision Security Gateways deployed in the account, the Security Management Server needs cloud-specific information, such as credentials and regions.
This information is related to a controller in the CME configuration.
-
To configure and manage controllers using CME API, refer to this chapter: Configuring Accounts (CME Controllers) with CME API.
-
To see the current controllers used by the Management Server connected to the cloud environments, run:
autoprov_cfg show controllers -
To add a new controller to an existing CME configuration, run:
autoprov_cfg add controller {AWS,Azure,GCP,NSX,Nutanix,OCI} -
To show the command help message, run:
autoprov_cfg add controller -h
|
|
|
Controllers (accounts) - General Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
CONTROLLER-NAME |
The name of the cloud environment controller. The name must be unique. |
|
|
DELETION-TOLERANCE |
The number of cycles until a Gateway object in SmartConsole is deleted. |
|
|
CONTROLLER TEMPLATES |
An optional list of templates that are linked to this specific controller. This parameter is mandatory for Multi-Domain Security Management Server environments with more than one domain configured. for example, TEMPLATE1-NAME TEMPLATE2-NAME |
|
|
CONTROLLER DOMAIN |
Specify the domain name or the domain UID that manages this controller. This parameter is mandatory for Multi-Domain Security Management Server environments with more than one domain configured. |
Controllers (accounts) - Parameters for AWS only
| Parameter | Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
REGIONS |
A comma-separated list of AWS regions where the gateways are deployed. For example: eu-west-1,us-east-1,eu-central-1 |
|
|
AWS ACCESS KEY |
AWS Access Key ID |
|
|
AWS SECRET KEY |
AWS Secret Key |
|
|
- |
Use this flag to specify if you use an IAM role profile |
|
|
AWS CREDENTIALS FILE PATH |
The path to a text file with the AWS credentials |
|
|
STS ROLE |
The STS Role ARN of a role to assume |
|
|
STS EXTERNAL ID |
An optional STS External ID to use when assuming a role in the account |
|
|
SUB-CREDENTIALS NAME |
Sub account name. The name must be unique |
|
|
AWS SUB-CREDENTIALS ACCESS KEY |
AWS Access Key ID for the sub-account |
|
-ssk |
AWS SUB-CREDENTIALS SECRET KEY |
AWS Secret Key for a sub-account |
|
|
AWS SUB-CREDENTIALS FILE PATH |
The path to a text file containing AWS credentials for a sub-account |
|
|
- |
Use this flag to specify whether to use an IAM role profile for a sub-account |
|
|
AWS SUB-CREDENTIALS STS ROLE |
STS Role ARN of a role to assume for a sub-account |
|
|
AWS SUB-CREDENTIALS STS EXTERNAL ID |
An optional STS External ID to use when assuming a role in this sub-account |
|
|
COMMUNITIES |
An optional comma-separated list of communities which are allowed for VPN connections that this controller discovers. If this attribute is missing or its value is an empty list, any community may be joined by VPN connections that belong to this controller. This is useful to prevent an automatic addition of VPN connections to a community based on the customer gateway public IP address. |
|
|
- |
Use this flag to enable the auto-provisioning of VPN objects |
|
|
- |
Use this flag to enable the auto-provisioning of load balancer Access and NAT rules |
|
|
- |
Use this flag to enable scan subnets with Centralized GWLB solution |
Controllers (accounts) - Parameters for Azure only
| Parameter | Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
SUBSCRIPTION ID |
The Azure subscription ID |
|
|
- |
An optional attribute that specifies Azure's environment type. The possible values are:
|
|
|
TENANT ID |
The Azure Active Directory tenant ID. |
|
|
CLIENT ID |
The service principal's client ID value. |
|
|
CLIENT SECRET |
The service principal's client secret value. |
Controllers (accounts) - Parameters for NSX only
| Parameter | Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
NSX FINGERPRINT |
NSX-T manager fingerprint |
|
|
NSX MANAGER PASSWORD |
NSX-T manager password |
|
|
NSX MANAGER USERNAME |
NSX-T manager username |
|
|
NSX MANAGER HOST |
NSX-T manager host IP |
|
|
NSX SERVICE MANAGER PASSWORD |
NSX service manager password |
|
|
NSX AD AUTH |
NSX-T manager ad auth |
Controllers (accounts) - Parameters for Nutanix only
| Parameter | Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
NUTANIX PRISM FINGERPRINT |
|
|
|
NUTANIX PRISM PASSWORD |
Nutanix Prism password |
|
|
NUTANIX PRISM USERNAME |
Nutanix Prism username |
|
|
NUTANIX PRISM IP |
Nutanix Prism IP |
Controllers (accounts) - Parameters for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) only
| Parameter | Value |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
OCI-COMPARTMENT |
The OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier) of the compartment. For example: " |
||
|
|
OCI-REGION |
An OCI region. For example: “ |
||
|
|
OCI-REALM-DOMAIN |
The domain for the OCI realm. For example, "oraclecloud.com". |
||
|
|
OCI-CREDENTIALS-DATA |
The base64-encoded string with OCI credentials. For example: “
|
Controllers (accounts) - Parameters for GCP only
| Parameter | Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
GCP-PROJECT |
The GCP project ID of the project in which you deploy the CloudGuard Security Gateways. For example, " |
|
|
GCP-SERVICE-ACCOUNT-KEY |
Full path to GCP Service Account key file. The file must be in $FWDIR/conf and only have admin read permissions. For example, $FWDIR/conf/ACME-Production13cebb.json. |
|
|
GCP-SERVICE-ACCOUNT-DATA |
The content of GCP service account data encoded in base64. |
Configuration Templates (gateway-configurations)
-
Information required to automatically provision Security Gateways, such as what policy to install and which Software Blades to enable, is placed in a configuration template in the CME configuration.
-
To see the current configuration templates that you can apply on Security Gateways, run:
autoprov_cfg show templates -
To add a new configuration template to an existing CME configuration, run the command:
autoprov_cfg add template -tn <CONFIGURATION-TEMPLATE-NAME> -otp <SIC-KEY> -ver <VERSION> -po <POLICY-NAME>
Configuring Name Prefix for Provisioned Gateways
By default, CME provisions the gateway objects using these naming conventions:
-
AWS:
<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<INSTANCE-ID>--<REGION-NAME> -
Azure:
<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<SCALE-SET-INSTANCE-NAME>--<RESOURCE-GROUP-NAME> -
GCP:
<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<MANAGED-INSTANCE-GROUP-NAME> -
Nutanix:
<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<VM-NAME> -
NSX-T:
<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<VM-NAME> -
OCI:
<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<INSTANCE-POOL-NAME>
To add the template name as a name prefix (that comes before the controller name), run:
|
|
To add a unique name as a name prefix (that comes before the controller name), run:
|
|
|
|
Note - Currently, the Automatic HF deployment does not support name-prefix. |
Configuring Network Group
CME automatically creates and updates a network group object with all the provisioned scale-set instances in the Security Management Server or Multi-Domain Security Management Server.
Network group object naming convention in the Security Management Server or Multi-Domain Security Management Server by cloud providers:
-
General: CME_<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<PLATFORM-UNIQUE-IDENTIFIER>
-
AWS: CME_<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<INSTANCE-ID>--<REGION-NAME>
-
GCP: CME_<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<MANAGED-INSTANCE-GROUP-NAME>
-
Azure: CME_<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<SCALE-SET-NAME>--<RESOURCE-GROUP-NAME>
-
Nutanix: CME_<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<NETWORK-FUNCTION-PROVIDER>
-
NSX-T: CME_<CONTROLLER-NAME>--<REGISTERED-SERVICE-NAME>
-
OCI: CME_<CONTROLLER_NAME>--<INSTANCE-POOL-NAME>
|
|
Notes:
|
You can use the Network Group object in these policies and policy columns:
-
Access Control rule columns:
-
Source
-
Destination
-
Install On
-
-
NAT rule columns:
-
Original Source
-
Original Destination
-
|
|
Notes:
|
Default-features
Default-features is a section in the CME configuration. It contains Configuration Template attributes, which are enabled automatically for each new Configuration Template.
Default-features section:
-
Initializing CME with autoprov_cfg init creates/copies the Default-features section based on:
-
If there is no CME configuration on this server, the Default-features section is being created with the latest available Default features.
-
If there is a CME configuration on the server, the Default-features section is copied (if it exists) from the former configuration.
-
-
To see the existing Default-features, look for the Default-features value in the CME configuration:
autoprov_cfg show all
New template creation:
When you create a new Configuration Template, if the Default-features section exists, its attributes are automatically added to the template (without specifying its attributes in the command).
|
|
Note - If an attribute has version limitations, it is added automatically only if the template's versions is applicable for the attribute. |
To see the existing configuration template, run:
|
|
Enabling and Disabling Software Blades
See Supported Configuration Template parameters for parameter information.
|
Step |
Instructions |
|---|---|
|
1 |
From the left navigation panel, click Gateways & Servers. |
|
2 |
Double-click the Security Gateway object. |
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
Click OK. |
|
5 |
Install the applicable policy on the Security Gateway. |
|
Step |
Instructions |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Connect to the command line on the Security Management Server. |
||||
|
2 |
Log in to the Expert mode. |
||||
|
3 |
Enable the Software Blades: To enable one Software Blade at a time, run:
Example:
To enable multiple Software Blades at a time, run:
Example:
|
|
Step |
Instructions |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Connect to the command line on the Security Management Server. |
||||
|
2 |
Log in to the Expert mode. |
||||
|
3 |
Enable the Software Blades: To enable one Software Blade at a time, run:
Example:
To enable multiple Software Blades at a time, run:
Example:
|
Autonomous Threat Prevention
Autonomous Threat Prevention is an innovative Threat Prevention management model. For more details, refer to the Threat Prevention Administration Guide for your version.
Auto Scaling instances do not support Threat Extraction and Zero Phishing software blades. Therefore, when enabling Autonomous Threat Prevention in CME, Zero-Phishing and Threat Extraction blades are inactivated in the Threat Prevention Global Exception rules.
Configuring the tgw_menu
The Transit Gateway menu is a command-line based menu to configure the AWS Transit Gateway solution.
For more information, see the CloudGuard Network for AWS Auto Scale Group with Transit Gateway Deployment Guide
Implied Rules and Restrictive Policy
A restrictive access policy package has only a drop-all cleanup rule. During Security Gateway provisioning cycle (scale out), CME can first install a restrictive policy package to prevent Security Gateway from answering load balancer's health probes.
-
CME Take 250 and higher:
Azure:
Gateway version
Load Balancer
Gateway Load Balancer
Application Gateway
All versions
SKIP
SKIP
INSTALL
AWS:
Gateway version
Network Load Balancer
Gateway Load Balancer
Application Load Balancer
R81.10 and higher
SKIP
SKIP
INSTALL
R81 and lower
INSTALL
SKIP
INSTALL
GCP
Gateway version
All Load Balancer types
R81.10 and higher
SKIP
R81 and lower
INSTALL
Private Cloud Vendors (NSX-T, Nutanix): CME installs restrictive policy on all solutions.
-
CME Take 250 and lower:
CME always installs restrictive policy.
For CME Takes lower than 250, if the Implied Rules are disabled, it is required to configure a custom restrictive policy package and to set it in the Configuration Template.
For more details, see:
If it is necessary to use the Multi-Domain Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to host virtual Security Management Servers called Domain Management Servers. Synonym: Multi-Domain Security Management Server. Acronym: MDS. Global Policy together with automatic provisioning, see Global Policy on a Multi-Domain Server.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to host virtual Security Management Servers called Domain Management Servers. Synonym: Multi-Domain Security Management Server. Acronym: MDS. Global Policy together with automatic provisioning, see Global Policy on a Multi-Domain Server.