Legacy Link Selection
|
|
Best Practice - Starting in R82, use Enhanced Link Selection. |
Overview of Legacy Link Selection
Link Selection is a method to define which interface is used for incoming and outgoing VPN traffic as well as the best possible path for the traffic.
With the Legacy Link Selection, the administrator can choose which IP addresses are used for VPN traffic on each Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources..
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources..
Configuration settings for Remote Access VPN![]() An encrypted tunnel between remote access clients (such as Endpoint Security VPN) and a Security Gateway. clients can be configured together or separately from the Site-to-Site configuration.
An encrypted tunnel between remote access clients (such as Endpoint Security VPN) and a Security Gateway. clients can be configured together or separately from the Site-to-Site configuration.
Configuring Legacy Link Selection
-
From the left navigation panel, click Gateways & Servers.
-
Double-click the Security Gateway / Cluster
 Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. object.
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. object. -
In the left panel, click IPsec VPN > Link Selection.
-
Configure which IP address Remote VPN peers must use to connect to the local Security Gateway.
In the IP Selection by Remote Peer section, select the applicable option:
-
Always use this IP Address:
Select this option and one of the options below to always use a certain IP address when VPN peers are trying to determine the Security Gateway's IP address.
-
Main address
The VPN tunnel is created using the main IP address of the Security Gateway / Cluster object that is configured on the General Properties page on the object.
-
Selected address from topology table
The VPN tunnel is created using the selected IP address (these are the IP addresses that are configured on the Security Gateway / Cluster interfaces as they appear on the Network Management page of the object.
-
Statically NATed IP
The VPN tunnel is created using the IP address you enter in this field.
Use this option if the applicable interface is located behind a static NAT device.
This IP address does not need to appear on the Network Management page of the object.
-
-
Calculate IP based on network topology
The VPN tunnel is created using the IP address that is calculated based on the network topology.
Make sure the settings are correct on the Network Management page of the object > the applicable interfaces > the Topology section.
-
Using DNS resolving:
Select this option if this Security Gateway has a Dynamically Assigned IP Address (DAIP).
A VPN tunnel to a DAIP Security Gateway can only be initiated using DNS resolving because the IP address of the DAIP Security Gateway cannot be known in advance.
If you select this option for a non-DAIP Security Gateway, then you must configure the IP address on the Network Management page of the object. Without DNS resolving, a DAIP Security Gateway can only initiate the first connection between two peers. The second connection can be initiated by the peer gateway as long as the IP address of the DAIP Security Gateway has not changed.
-
Full hostname
Enter the full Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) for this Security Gateway.
The DNS hostname that is used is "
<gateway_name>.<domain_name>".For example, if the Security Gateway object name is "
MyGw", and the domain name is "example.com", then the FQDN will be "MyGw.example.com". -
Gateway's name and domain name (specified in Global Properties)
Uses the combination of these:
-
The Security Gateway object name on the General Properties page.
-
The domain name that must be configured in the Global Properties > VPN > Advanced page > in the section Link Selection settings > in the field Domain name of DNS resolving.
-
-
-
Using probing. Link redundancy mode:
When more than one IP address is available on a Security Gateway / Cluster for VPN, Link Selection may employ the Check Point proprietary RDP probing method to determine which link will be used.
The RDP probing method is implemented using a proprietary protocol that uses UDP port 259. This protocol is proprietary to Check Point and works only between Check Point Security Gateways. This protocol does not comply with RDP as specified in RFC 908 and RFC 1151.
IP addresses you do not want to be examined (meaning, internal IP addresses) may be removed from the list of IP addresses to be examined.
After a Security Gateway maps the links' availability, a Link Selection per connection can be made based on one of the redundancy modes.
-
Select the applicable probing redundancy mode:
-
High Availability
In the High Availability link probing mode, the VPN tunnel uses the first IP address to respond, or the primary IP address if a primary IP address is configured and active. If the chosen IP address stops responding, the connection fails over to another responding IP address. If a primary IP address is configured, the VPN tunnel will stay on the backup IP address until the primary IP address responds again.
-
Load Sharing
In the Load Sharing link probing mode, the encrypted traffic is distributed between all available VPN links. Every new connection ready for encryption uses the next available VPN link in a round robin manner. When a VPN link becomes unavailable, all of its connections are distributed between the other available VPN links. A link's availability is determined using RDP probing.
-
-
Configure the probing settings:
-
Click Configure.
-
Select the applicable option:
For more information, click the Help button.
-
Probe all addresses defined in the topology tab
The Security Gateway sends RDP packets to all IP addresses looking for an available VPN link.
-
Probe the following addresses
Configure a list of interfaces on this Security Gateway to probe.
-
Primary address
Select the IP address of the applicable interface on this Security Gateway that must have priority over the other IP addresses being probed.
-
Using ongoing probing
If a Security Gateway has multiple IP addresses available for VPN traffic, then when a session is initiated, all possible destination IP addresses continuously receive RDP packets until one of them responds. Connections go through the first IP address to respond (or to a primary IP address, if a primary IP address is configured and active), and stay with this IP address until the IP address stops responding. The RDP probing is activated when a connection is opened and continues as a background process.
-
Using one time probing
If a Security Gateway has multiple IP addresses available for VPN traffic, then when a session is initiated, all possible destination IP addresses receive one RDP session to test the route. The first IP address to respond is chosen, and stays chosen until the next time a policy is installed.
-
-
Click OK.
-
The peer Security Gateway that responds to the connection will route the reply traffic through the same route that it was received on, as long as that VPN link is available.
-
-
-
Configure the outgoing route selection:
For outbound traffic, there are different methods that can be used to determine which path to use when connecting with a remote VPN peer.
-
In the Outgoing Route Selection section, select how to determine the outgoing interface:
-
Operating system routing table
With this method, the Security Gateway examines its routing table to find the VPN link with the lowest metric (the highest route priority) to send traffic.
-
Route based probing
With this method, the Security Gateway examines its routing table to find the VPN link with the lowest metric (the highest route priority) to send traffic. However, before choosing a VPN link to send traffic, all routing possibilities are examined to check that the selected VPN link is active. The Security Gateway then selects the best match (highest prefix length) active route with the lowest metric, and hence the highest priority. This method is recommended when there is more than one external interface.
If in the section IP Selection by Remote Peer you selected Using probing. Link redundancy mode with Load Sharing, it also affects Route based probing link selection. In this case, Route based probing distributes the outgoing encrypted traffic between all available VPN links. All possible VPN links to the peer Security Gateway are derived from the routing table and the VPN link's availability is tested with the Check Point RDP probing. Every new connection ready for encryption uses the next available VPN link in a round robin manner.
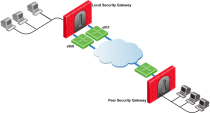
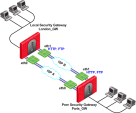
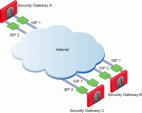
 Example for Route Based Probing
Example for Route Based Probing
The local Security Gateway, with RDP probing, considers all possible routes between itself and the remote peer Security Gateway.
The Security Gateway then decides on the most effective route between the two Security Gateways:
In this scenario:
Security Gateway "A" has two external interfaces, 192.168.10.10 and 192.168.20.10.
Peer Security Gateway "B" also has two external interfaces: 192.168.30.10 and 192.168.40.10.
For Security Gateway "A", the routing table reads:
Destination
Netmask
Next hop
Metric
192.168.40.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.10.20
1
192.168.40.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.20.20
2
192.168.30.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.10.20
3
192.168.30.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.20.20
4
For Security Gateway "B", the routing table reads:
Destination
Netmask
Next hop
Metric
192.168.20.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.40.20
1
192.168.20.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.30.20
2
192.168.10.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.40.20
3
192.168.10.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.30.20
4
If all routes for outgoing traffic from Security Gateway "A" are available, the route from 192.168.10.10 to 192.168.40.10 has the lowest metric (highest priority) and is therefore the preferred route.

Notes:
-
For IKE and RDP sessions, route based probing uses the same IP address and interface for responding traffic.
-
Route based probing enables the use of On Demand Links (ODL), which are triggered upon failure of all primary links.
You can run a script to activate an On Demand Link when all other links with higher priorities become unavailable.
For more information, see On Demand Links (ODL).
-
Some network protocols (for example, TCP) might timeout in the time between link failure and the next attempt to resolve. Administrators can decrease these default values.
Note that high resolution frequency can overload the Security Gateway.
This configuration also changes the default resolution timeouts for the MEP mechanism.
-
For Layer 2 links, there must be routes to the peer's encryption domains through the local Layer 2 interface device.
-
The Link Selection route based probing is resolved using a "resolver" mechanism.
To determine if a selected route failed, this mechanism uses the sum of the values of these parameters:
-
resolver_session_intervalDefines for how many seconds the remote peer status (up or down) stays valid.
Default value: 30 seconds
-
resolver_ttlDefines how many seconds the Security Gateway waits before it decides that a remote peer is down.
Default value: 10
To change the default values:
-
In the top left corner of SmartConsole
 Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on., click Menu > click Global properties.
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on., click Menu > click Global properties. -
In the left panel, click the Advanced page > click Configure.
-
In the left panel, expand FireWall-1 and click Resolver.
-
Configure the required values.
-
Click OK to close the Advanced Configuration window.
-
Click OK to close the Global Properties window.
-
Install the Access Control policy.
-
-
-
-
In the Outgoing Route Selection section, select how to determine the outgoing interface when responding to a remotely initiated VPN tunnel.

Note - These settings apply only to IKE and Check Point RDP connections.
Click Setup and select the applicable option:
-
Use outgoing traffic configuration
Select this option to choose an interface with the same method selected in the Outgoing Route Selection section of the Link Selection page.
-
Reply from the same interface
Select this option to send the returning traffic through the same interface and next hop IP address, through which it arrived.
When you select the Route Based Probing option, the default option becomes Reply from the same interface.
-
-
In the Outgoing Route Selection section, select which source IP address to use for outgoing packets initiated by the Security Gateway.
Click Source IP address settings and select the applicable option:
-
Automatic (derived from the method of IP selection by remote peer)
Uses the source IP address based on the method selected in the IP Selection by Remote Peer section:
-
If you selected the Main address or Selected address from topology table method, then the source IP address for initiating a VPN tunnel is the IP address that you configured in that method.
-
If you selected the Calculate IP based on network topology, Statically NATed IP, Use DNS resolving, or Use probing method, then the source IP address for initiating a VPN tunnel is the IP address of the chosen outgoing interface.
-
-
Manual
-
Main IP address
Uses the main IP address of the Security Gateway object configured on the General Properties page.
-
Selected address from topology table
Uses the selected IP addresses.
-
IP address of chosen interface
Uses the IP address of the interface, through which the traffic is being routed.
-
-
-
-
Configure how the Security Gateway needs to notify you about every new resolving decision performed with one of its remote VPN peers.
In the Tracking section, in the Outgoing Link Tracking field, select the applicable option:
-
None
The Security Gateway does not any notification - neither log, nor alert.
-
Log
The Security Gateway generates a log.
-
Popup Alert
The Security Gateway generates a predefined alert that appears in SmartView Monitor GUI (when it is open) in a popup window.
-
SNMP Trap Alert
The Security Gateway sends a predefined SNMP Trap that appears in SmartView Monitor GUI (when it is open).
-
User Defined Alert
The Security Gateway generates a user-defined alert that appears in SmartView Monitor GUI (when it is open) in a popup window.

Notes:
-
When you select any option other than None, the Security Gateway sends a log for every new resolving decision performed with one of its remote VPN peers.
-
If you selected Using probing. Link redundancy mode or selected Route based probing, then the Security Gateway sends a log for all resolving changes.
For example, if the used VPN link becomes unavailable and a new available VPN link is chosen.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control policy.
|
|
Note - When a local Security Gateway performs a successful IKE negotiation with a VPN peer Security Gateway, that VPN peer uses the local Security Gateway's IP address as the destination IP address for the next IPsec traffic and IKE negotiations that it initiates. This does not apply if you selected "Using probing. Link redundancy mode". |
Legacy Link Selection Examples
Link Selection can be used in many environments.
This section describes various scenarios and how the Legacy Link Selection should be configured in each scenario.
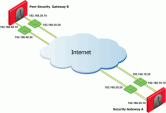
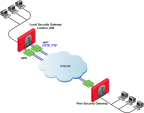
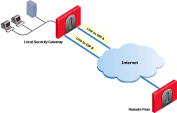
This is the simplest scenario, where the local Security Gateway has a single external interface for VPN traffic.
Because there is only one interface available for VPN, configure one of these settings in the IP Selection by Remote Peer section and install the Access Control policy:
-
Select Main address.
-
Select Selected address from topology table and select the required IP address.
-
If the IP address of the local Security Gateway is located behind a Static NAT device, select Statically NATed IP and enter the NATed IP address.
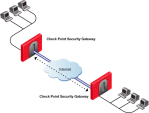
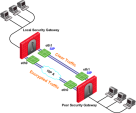
In this scenario:
-
The local Security Gateway has a point-to-point connection from two different interfaces.
-
Each interface is used by a different VPN peer.
The local Security Gateway has two IP addresses used for VPN:
-
One interface is used for VPN with the peer Security Gateway "A".
-
One interface is used for VPN with the peer Security Gateway "B".
Configure these settings in the IP Selection by Remote Peer section:
-
Select Using probing. Link redundancy mode.
-
Select High Availability.
-
Click Configure.
-
Select Probe all addresses defined in the topology tab.
-
Select Using one time probing.
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control policy.
Because only one IP address is available for each VPN peer, probing only has to take place one time.
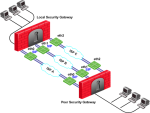
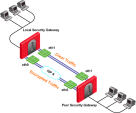
In this scenario:
-
The local Security Gateway has two external interfaces available for VPN traffic -
eth0andeth1. -
The IP address of the interface
eth0is translated using a static NAT device:
Configure these settings in the IP Selection by Remote Peer section:
-
Select Using probing. Link redundancy mode.
-
Select High Availability.
-
Click Configure.
-
Select Probe all addresses defined in the topology tab.
To probe the Static NATed IP address, select Probe the following addresses > click Add > enter the NATed IP address > click OK.
-
Select Using ongoing probing.
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control policy.
Distributing VPN Traffic Between VPN Peers
Depending on your configuration, there are many ways to distribute VPN traffic between the local Security Gateway and its VPN peers, between available VPN links on the local Security Gateway.
In the following scenario, the local Security Gateway and the VPN peer Security Gateway each have two external interfaces available for VPN traffic - eth0 and eth1.
Configure these settings in the IP Selection by Remote Peer section in each Security Gateway (local and each VPN peer):
-
Select Using probing. Link redundancy mode.
-
Select Load Sharing.
-
Click Configure.
-
Select Probe all addresses defined in the topology tab.
To probe only specific external interfaces, select Probe the following addresses > click Add > enter the IP addresses of the applicable interfaces > click OK.
-
Select Using ongoing probing.
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control policy.
If one VPN link goes down (for example, eth0), traffic is automatically routed through the other VPN link (for example, eth1).
To support this configuration, make sure that the routing tables allow packets to flow back and forth:
-
Between the
eth0interfaces of the local Security Gateway and of the VPN peer Security Gateway -
Between the
eth1interfaces of the local Security Gateway and of the VPN peer Security Gateway
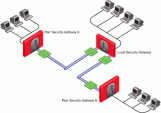
In the following scenario:
-
The local Security Gateway has two external interfaces available for VPN traffic -
eth0andeth1. -
The VPN peer Security Gateway has one external interface for VPN traffic.
Configure these settings on the local Security Gateway:
-
In the IP Selection by Remote Peer section:
-
Select Using probing. Link redundancy mode.
-
Select Load Sharing.
As a result, the peer Security Gateway will distribute its outgoing VPN traffic between the interfaces
eth0andeth1of the local Security Gateway. -
-
In the Outgoing Route Selection section:
Select the applicable option:
-
If you select Operating system routing table, then:
-
The local Security Gateway only uses one of its local interfaces for outgoing VPN traffic.
-
The local Security Gateway only uses the route with the lowest metric and best match to reach the single IP address of the peer Security Gateway, based on the routing table.
-
-
If you select Route based probing, then:
The local Security Gateway distributes the outgoing VPN traffic between both outbound VPN links.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control policy.
Service-Based Legacy Link Selection
For configuration steps, refer to sk56384 to configure the required settings in the Security Gateway object, and on the Management Server![]() Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. in the
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. in the $FWDIR/conf/vpn_service_based_routing.conf file.
With the Service-Based Legacy Link Selection, administrators can control outgoing VPN traffic and bandwidth use by assigning a service or a group of services to a specific interface for outgoing VPN routing decisions.
The encrypted traffic of an outgoing connection is routed through the configured interface according to the traffic's service.
The VPN links to the peer Security Gateway are derived from the routing table and the VPN link's availability is tested with RDP probing.
If all VPN links through the interface assigned to a specific service stop responding to RDP probing, a VPN link failover occurs, as in any other probing mode.
When a VPN link through the assigned interface is restored, new outgoing encrypted connections are assigned to it, while existing encrypted connections are maintained over the backup VPN link until they are completed.
It is possible to configure the traffic of a specific service not to fail over. In this case, traffic of the configured service is routed only through interfaces assigned to this service, even if these interfaces stop responding to RDP probing.
If the same service is assigned to more than one interface, this service's traffic is distributed between the configured interfaces. Every new outgoing encrypted connection uses the next available link in a round robin manner.
All traffic from services that are not assigned to a specific interface is distributed between the remaining interfaces.
If all VPN links through these interfaces are down, the encrypted traffic is distributed between the interfaces that are configured for specific services.
Service-Based Legacy Link Selection is supported on Security Gateways R71 and higher.
In the scenario below, the local and peer Security Gateways each have two external interfaces for VPN traffic - eth0 and eth1.
In this example, the interface eth1 of both Security Gateways is dedicated to HTTP and FTP traffic. All other traffic is routed to the interface eth0.
If the available link through the interface eth1 stops responding to RDP probing, HTTP and FTP traffic will fail over to the interface eth0.
It is possible to specify that HTTP and FTP traffic should only be routed through the interface eth1 even if the link through the interface eth1 stops responding. Specify this by including the string "dont_failover" when editing the $FWDIR/conf/vpn_service_based_routing.conf file.
All other traffic that is not HTTP or FTP will be routed through the interface eth0. If the link through the interface eth0 stops responding to RDP probing, all traffic will be routed through the interface eth1.
The Service-Based Link Selection configuration file for this environment should look like this:
|
Security Gateway |
Interface |
Service |
[dont_failover] |
|---|---|---|---|
|
London_GW |
eth1 |
http |
|
|
London_GW |
eth1 |
ftp |
|
|
Paris_GW |
eth1 |
http |
|
|
Paris_GW |
eth1 |
ftp |
|
Alternatively, in SmartConsole, you can create a Services Group that includes HTTP and FTP services.
In the example below, this group is called http_ftp_grp. With this Services Group, the Service-Based Link Selection configuration file for this environment should look like this:
|
Security Gateway |
Interface |
Service |
[dont_failover] |
|---|---|---|---|
|
London_GW |
eth1 |
http_ftp_grp |
|
|
Paris_GW |
eth1 |
http_ftp_grp |
|
In the following scenario, the local and peer Security Gateways each have three external interfaces available for VPN - eth0, eth1, and eth2.
To use all three external interfaces and distribute the VPN traffic between the available VPN links, configure these settings on each Security Gateway:
-
In the IP Selection by Remote Peer section:
-
Select Using probing. Link redundancy mode.
-
Select Load Sharing.
-
-
In the Outgoing Route Selection section:
Select Route based probing.
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control policy.
To control your bandwidth use, dedicate one or more links to a specific service or services using Service-Based Legacy Link Selection.
In this scenario, the interfaces eth0 and eth1 of both Security Gateways are dedicated to SIP traffic.
SIP traffic is distributed between the interfaces eth0 and eth1. All other traffic is routed through the interface eth2.
If either the link through the interface eth0 or the link through the interface eth1 stops responding to RDP probing, SIP traffic will fail over to the other SIP interface (eth1 or eth0, respectively).
If the link through the interface eth2 stops responding to RDP probing, all traffic will be routed though the interface eth0 or the interface eth1.
In the following scenario:
-
The local Security Gateway has two external interfaces available for VPN traffic -
eth0andeth1. -
The peer Security Gateway has a single external interface for VPN traffic.
To use all external interfaces and distribute the VPN traffic between the available VPN links, configure these settings on the local Security Gateway "London_GW":
-
In the IP Selection by Remote Peer section:
-
Select Using probing. Link redundancy mode.
-
Select Load Sharing.
-
-
In the Outgoing Route Selection section:
Select Route based probing.
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control policy.
To control your bandwidth use, dedicate the interface eth1 of the local Security Gateway to HTTP and FTP traffic.
The local Security Gateway will route outgoing HTTP and FTP connections through the interface eth1.
All other traffic, not HTTP or FTP, will be routed through the interface eth0.
In this scenario, HTTP and FTP traffic should not fail over. HTTP and FTP traffic should only be routed through the interface eth1, even if the link through the interface eth1 stops responding to RDP probing. This is configured by specifying the string "dont_failover" when editing the $FWDIR/conf/vpn_service_based_routing.conf file.
The Service-Based Legacy Link Selection configuration file for this environment should look like this:
|
Security Gateway |
Interface |
Service |
[dont_failover] |
|---|---|---|---|
|
London_GW |
eth1 |
http |
dont_failover |
|
London_GW |
eth1 |
ftp |
dont_failover |
Because the Service-Based Legacy Link Selection configuration applies only to outgoing VPN traffic of the local Security Gateway, the VPN peer Security Gateway can send HTTP and FTP traffic to either interface of the local Security Gateway.
The outgoing VPN traffic of the peer Security Gateway is distributed between the interfaces eth0 and eth1 of the local Security Gateway.
Trusted Links
The Trusted Links feature allows you to configure an interface as "trusted" for VPN traffic, so that traffic sent on that link is not encrypted.
|
|
Warning - Configure a trusted link if you are confident that the link is already encrypted and secure and you do not need a second encryption. |
If you configure an interface as trusted, traffic routed through that interface will be sent in clear-text, while traffic sent through other interfaces will still be encrypted.
Trusted interfaces should be configured symmetrically on the local Security Gateway and the VPN peer Security Gateway.
If only one side of the link is configured as trusted for VPN traffic, clear traffic received by a non-trusted interface will be dropped by the VPN peer Security Gateway.
If you have configured a specific link as trusted for VPN traffic and you use probing, the probing method considers all links, including the trusted link, when choosing a link for a connection.
The probing method chooses the link based on these criteria:
-
The configured redundancy mode.
In the IP Selection by Remote Peer section, select Using probing. Link redundancy mode and then select High Availability or Load Sharing.
-
If Service-Based Legacy Link Selection is configured in the
$FWDIR/conf/vpn_service_based_routing.conffile.
If the trusted link is chosen for a connection, the traffic is not encrypted.
If another, non-trusted, link is chosen, the traffic is encrypted.
In an MEP configuration (see Multiple Entry Point (MEP) VPNs), trusted links are only supported for connections initiated by a peer Security Gateway to a MEP Security Gateway. Unencrypted VPN connections routed through a trusted interface and initiated by a MEP Security Gateway may be dropped by the peer Security Gateway.
Trusted links are not supported in the Traditional VPN mode, in which trusted link settings are ignored and VPN traffic is always encrypted.
Trusted links are supported on Security Gateways R71 and higher.
Use the Database Tool (GuiDBEdit Tool) to configure Trusted Links:
-
Close all SmartConsole windows connected to the Management Server.
-
Connect with Database Tool (GuiDBEdit Tool) to the Management Server.
-
In the top left pane, go to Network objects > network_objects.
-
In the top right pane, click the Security Gateway / Cluster object that you want to edit.
-
In the bottom pane, search for the interface that you want to configure as trusted from within the interfaces set.
The interface name appears in the "
officialname" attribute. -
Within the trusted interface set, change the value of the "
vpn_trusted" attribute to "true" (default value: "false"). -
Configure trusted interfaces symmetrically on the peer Security Gateways.
If only one side of the link is configured as trusted for VPN traffic, clear traffic received by a non-trusted interface will be dropped by the peer Security Gateway.
-
Save changes (File menu > Save All).
-
Connect with SmartConsole to the Management Server.
-
In SmartConsole, install the Access Control Policy on the Security Gateway / Cluster object.
In the following scenario:
-
Both the local Security Gateway and the VPN peer Security Gateway have two external interfaces available for VPN traffic -
eth0andeth1. -
The interface
eth1on both Security Gateways has been configured as a trusted interface.
Therefore, traffic sent from the interface eth1 of the local Security Gateway is sent unencrypted and is accepted by the interface eth1 of the peer Security Gateway, and the other way around.
If in the IP Selection by Remote Peer section, you selected Using probing. Link redundancy mode, selected High Availability, then clicked Configure, selected Primary IP address, and selected the IP address of the trusted link, then the trusted link will be used for VPN traffic. If the trusted link stops responding to RDP probing, the link through Interface eth0 will be used for VPN traffic and traffic will be encrypted.
If in the IP Selection by Remote Peer section, you selected Using probing. Link redundancy mode and selected Load Sharing, then the VPN traffic will be distributed between the available VPN links. Connections routed through the interface eth0 will be encrypted, while connections routed through the trusted link will not be encrypted.
In the following scenario:
-
The local and peer Security Gateways have two external interfaces available for VPN traffic -
eth0andeth1. -
The interface
eth1on both Security Gateways is configured as a trusted interface for VPN traffic because encryption is not needed on that link. -
In addition, the interface
eth1of both Security Gateways is dedicated to SIP traffic using the Service-Based Legacy Link Selection.
SIP traffic is routed through the trusted link between the two interfaces eth1 and will not be encrypted. If the trusted link stops responding to RDP probing, SIP traffic will be routed through the interfaces eth0 and will be encrypted.
All other traffic that is not SIP is encrypted and routed through the interface eth0 link. However, if the interface eth0 stops responding to RDP probing, all the traffic will be routed through the trusted link and will not be encrypted.
On Demand Links (ODL)
Route based probing enables the use of an On Demand Link (ODL), which is triggered upon failure of all primary links.
When a failure is detected, a custom script is used to activate the ODL and change the applicable routing information.
The ODL's metric must be set to be larger than a configured minimum for it to be considered an ODL.
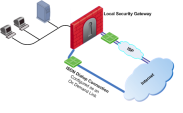
The Security Gateway has two external links for Internet connectivity: one to an ISP, the other to an ISDN dial-up. The ISDN dial-up connection is configured as an On Demand Link.
On the Security Gateway, the Route based probing mechanism probes all of the non-On Demand Links and selects the active link with the lowest metric.
In this case, it probed the ISP link. A script is run to activate the On Demand Link when all other links with higher priorities become unavailable. When the link becomes available again, a shutdown script is run automatically and the connection continues through the link with the ISP.
Note - On Demand Links are probed only one time with a single RDP session. Failover between On Demand Links is not supported.
You can enable On Demand Links only if in the section Outgoing Route Selection you selected Route based probing.
Configure On Demand Links commands with Database Tool (GuiDBEdit Tool).
|
Attribute in Security Gateway Object |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enables on-demand links. The default is |
|
|
Defines the minimum metric level for an on-demand link. This value must be equal to or higher than the configured minimum metric. |
|
|
The name of the on-demand script, which runs when all not-on-demand routes stop responding. Put the script in the |
|
|
This script is run when the failed links become available. Put the script in the |
If you do not want to use Database Tool (GuiDBEdit Tool), you can configure the "use_on_demand_links" and "on_demand_metric_min" settings in SmartConsole:
-
Click > Global properties.
-
In the left panel, click Advanced page and click the Configure button.
-
Expand VPN Advanced Properties and click Link Selection.
-
Select use_on_demand_links to enable On Demand Links.
-
In the on_demand_metric_min field, configure the minimum metric level for an On Demand Link.
-
Click OK to close the Advanced Configuration window.
-
Click OK to close the Global Properties window.
-
Install the Access Control Policy.
Legacy Link Selection and ISP Redundancy
ISP Redundancy enables reliable Internet connectivity by allowing a single or clustered Security Gateway to connect to the Internet via redundant ISP connections.
ISP Redundancy offers two modes of operation:
-
Load Sharing mode
-
Primary/Backup mode
Configure Link Selection and ISP Redundancy in the Other > ISP Redundancy page of the Security Gateway object:
-
Load Sharing mode connects to both ISPs while sharing the load of outgoing connections between the ISPs according to a designated weight assignment. New connections are randomly assigned to a link. If a link fails, all new outgoing connections are directed to the active link. This configuration effectively increases the WAN bandwidth while providing connectivity protection. The assigned ISP Links weight is only supported for Security Gateway traffic.
-
Primary/Backup mode connects to an ISP through the primary link, and switches to a backup ISP if the primary ISP link fails. When the primary link is restored, new outgoing connections are assigned to it, while existing connections are maintained over the backup link until they are complete.
The settings configured in the ISP Redundancy window are by default, applied to the Link Selection page and will overwrite any pre-existing configuration.
The following settings carry over:
-
When ISP Redundancy is configured, the default setting in the Link Selection page is Use ongoing probing. However, Link Selection only probes the ISPs configured in the ISP Redundancy window. This enables connection failover of the VPN tunnel if connectivity to one of the Security Gateway interfaces fails.
-
If the ISP Redundancy mode is Load Sharing, the Probing redundancy mode in the Link Selection page is also Load Sharing.
-
If the ISP Redundancy mode is Primary/Backup, the Probing redundancy mode in the Link Selection page is High Availability.
-
The Primary ISP link of the ISP redundancy is set as the Primary Address of the Link Selection probing. The Primary Address is set under: IP Selection by Remote Peer > Use Probing > Configure (or View, if the settings are derived from the ISP Redundancy settings).
-
If you do not want the ISP Redundancy settings to affect the Link Selection settings, on the ISP Redundancy page, clear the check box that says Apply settings to VPN traffic and configure the required VPN settings on the Link Selection page. This may apply when you want to route VPN traffic differently than the clear traffic. For example, if you want to use Load Sharing for clear traffic and High Availability for VPN traffic, or if you want to use different primary ISPs for clear and VPN traffic.
In the following scenario, the local Security Gateway maintains links to ISP "A" and ISP "B", both of which provide connectivity to the Internet with ISP Redundancy.
In the Topology > ISP Redundancy window, configure the ISP Redundancy settings, such as ISP Links and Redundancy mode. The ISP Redundancy settings are applied by default to VPN traffic. The derived Link Selection settings are visible in the IPsec VPN > Link Selection window.
In the following scenario, the Apply settings to VPN traffic on the ISP Redundancy page was cleared, and there are different setting configured for Link Selection and ISP Redundancy.
In this scenario:
-
Security Gateways "A", "B", and "C" each have two interfaces configured as ISP links.
-
ISP Redundancy is configured on Security Gateway "A".
-
Security Gateway "A" should use ISP 1 to connect to Security Gateway "B" and ISP 2 to connect to Security Gateway "C". If one of the ISP links becomes unavailable, the other ISP should be used.
In this scenario, the administrator of Security Gateway "A" needs to:
-
Clear the box Apply settings to VPN traffic in the ISP Redundancy window.
-
Reconfigure the Outgoing Route Selection to Route based probing in the Link Selection window.
-
Configure the routing table so that ISP 1 is the highest priority for peer Security Gateway "B" and ISP 2 has the highest priority for peer Security Gateway "C".
Legacy Link Selection with non-Check Point Devices
RDP probing, the probing method used for certain Link Selection features, is proprietary to Check Point and only works between Check Point entities. It is not supported with non-Check Point devices.
Since RDP probing is not active on non-Check Point Security Gateways, the following results apply if a Check Point Security Gateway sends VPN traffic to a non-Check Point Gateway:
-
In the IP Selection by Remote Peer section, the option Use probing. Link redundancy mode cannot be used by locally managed Check Point Security Gateways to determine the IP address of non-Check Point devices. Use another method in this section.
-
This combination of settings does not work with non-Check Point Gateways:
-
If in the Outgoing Route Selection section you selected Route based probing and Load Sharing.
-
You configured Service-Based Legacy Link Selection.
If either Load Sharing or Service-Based Legacy Link Selection is enabled on the local Security Gateway, but the VPN peer is a non-Check Point device, the local Security Gateway will only use one link to the non-Check Point device - the best match (highest prefix length) link with the lowest metric.
-
-
If in the Outgoing Route Selection section you selected Route based probing for VPN traffic to a non-Check Point device, the local Security Gateway always uses the best match (highest prefix length) link with the lowest metric.