

In This Section: |
This chapter includes information to help you plan your deployment and gives a general overview of the deployment process.
This section includes best practices and other suggestions to help make your Multi-Domain Management deployment work efficiently.
Large enterprises use Multi-Domain Management in a multi-site, High Availability deployment, with many Multi-Domain Servers located at remote sites, often in different countries. Each Multi-Domain Server and Multi-Domain Log Server continuously synchronizes with its remote peers.
The advantages of this type of deployment are:
Small organizations, with moderate traffic volumes can use a single-site deployment, with one Multi-Domain Server that manages a set of Domains.
Best Practice - For this type of deployment, use a backup solution that periodically saves the system databases and settings to another device.
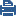
This example shows a single-site Multi-Domain Server deployment with three Domains at remote locations. Each Domain has many Security Gateways to protect the internal networks and resources. This example has only one Multi-Domain Server and does not use High Availability.
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
London Domain and networks |
2 |
New York (Headquarters) Domain and networks |
3 |
Tokyo Domain and networks |
4 |
SmartConsole clients, typically at a network control center. |
5 |
Multi-Domain Server |
6 |
London Domain Management Server |
7 |
New York Domain Management Server |
8 |
Tokyo Domain Management Server |
9 |
Internet |
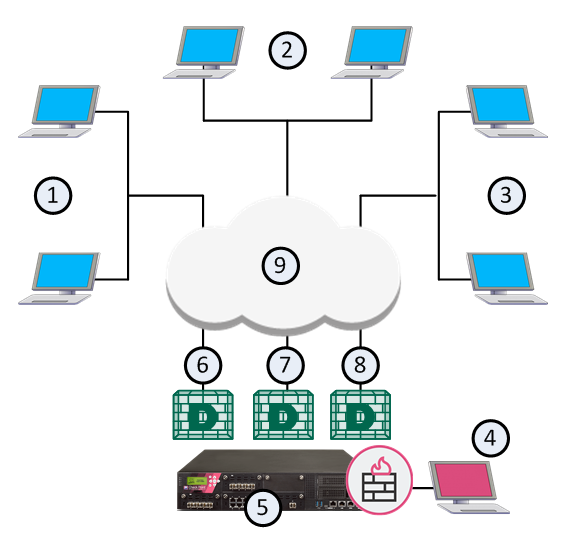
This illustration shows the configuration grid in the SmartConsole Multi Domain view for the example deployment:
Note - The system automatically creates the Global Domain when you install Multi-Domain Management.
Make sure that your Multi-Domain Management system hardware is compliant with the system requirements for this release. If your Multi-Domain Server has more than one interface, make sure that the total traffic load complies with the performance load recommendations for that Multi-Domain Server.
All Multi-Domain Servers must have at least one interface with a routable IP address. You must configure these Multi-Domain Servers to run DNS server queries and to resolve the IP addresses and host names.
Configure your network routing for IP communication between:
Make sure that IP addresses and routing configuration can handle special issues, such as Multi-Domain Servers in different physical locations.
If there is more than one interface on a Multi-Domain Server, you must configure at least one interface to be the leading interface. Multi-Domain Servers (Primary and Secondary) and Multi-Domain Log Servers use the leading interface to communicate with each other for database synchronization.
Make sure that all Multi-Domain Server interfaces are routable. Domain Management Servers must be able to communicate with their Domain Security Gateways. Domain Log Servers must be able to communicate with their Domain Security Gateways.
You define the leading interface during the installation procedure, but you can change it later. If you add a new interface to a Multi-Domain Server after installation, define the Leading Interface manually.
To add a New Leading Interface:
mdsconfig Changing the Leading Interface:
mdsconfig All Multi-Domain Server system clocks must synchronize to approximately one second. Before you create a new Multi-Domain Server or Multi-Domain Log Server, you must synchronize its clock with other system components.
Clock synchronization is important for these reasons:
Use these resources to synchronize component system clocks:
It is a security best practice to deploy a Check Point Security Gateway that protects the Multi-Domain Servers, Multi-Domain Log Server and other components. You can manage this Security Gateway with a Domain Management Server or a Security Management Server that is not part of a Multi-Domain Management environment.
This simple use case shows a small High Availability deployment with a Security Gateway protecting each Multi-Domain Server. One of the Domain Management Servers manages these Security Gateways.
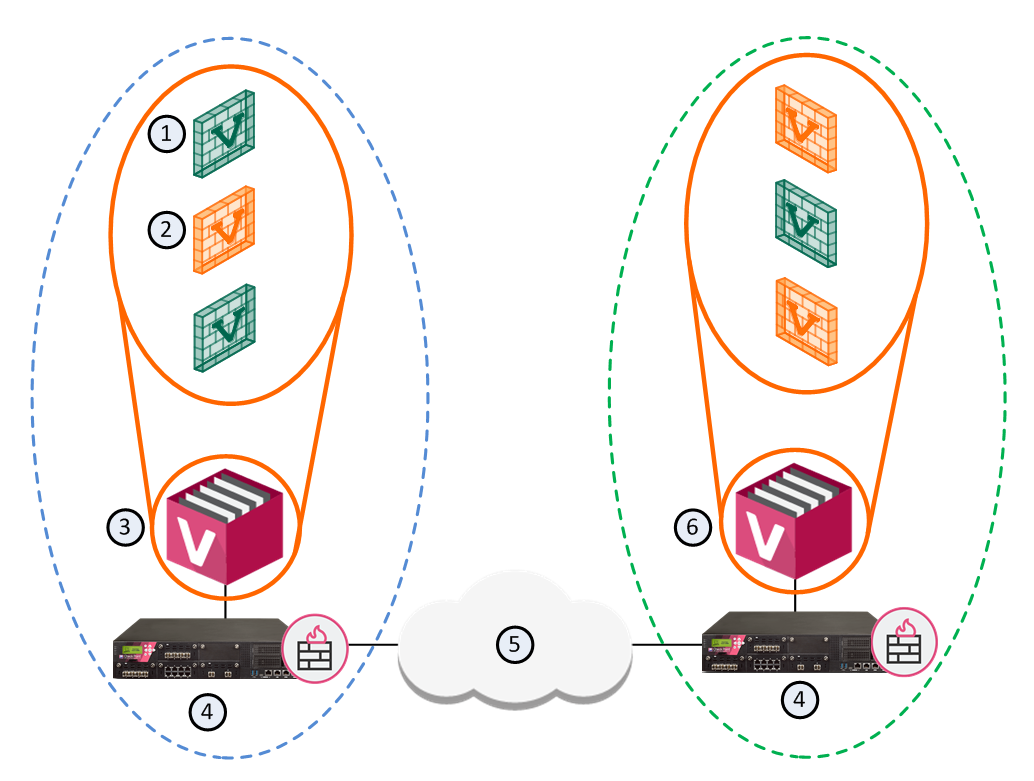
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Active Domain Management Servers |
2 |
Standby Domain Management Servers |
3 |
Primary Multi-Domain Server with Active and Standby Domain Management Servers |
4 |
Security Gateways |
5 |
Internet |
6 |
Secondary Multi-Domain Server with Active and Standby Domain Management Servers |
You can create a Domain and Domain Management Server to manage the Policies for Security Gateways that protect Multi-Domain Servers in your environment.
Workflow for this scenario:
You must create rules in your Security Policies to allow communication between the different Multi-Domain Management components. You can define these rules in global configurations or in local Domain Policies.
Use this table as a guideline to allow connections between specified components:
Activity |
Source |
Destination |
|---|---|---|
Allow connections between SmartConsole and the Multi-Domain Server |
SmartConsole |
Multi-Domain Server |
Allow connections between Multi-Domain Servers |
Multi-Domain Servers |
Multi-Domain Servers |
Allow connections between Domain Management Servers and Security Gateways |
Domain Management Server |
Security Gateway |
Allow Domain Management Server status data and certificate exchange between Domain Management Server High Availability peers Allow Domain Management Server synchronization between peers |
Domain Management Server peer |
Domain Management Server peer |
See the R80.20 Security Management Administration Guide to learn how to create a Security Policy.
Multi-Domain Management supports these external authentication solutions:
When an administrator logs in, an authentication requests goes to the external authentication server, which sends a reply to the Multi-Domain Server. TACACS and RADIUS use the Multi-Domain Server as a proxy between the Domain Management Server and the external authentication server. To make this work correctly, you must configure each Multi-Domain Server on the authentication server.
Note - If the Multi-Domain Server is DOWN, the Domain Management Server cannot authenticate administrators.
To configure External Authentication:
sdconf.rec on the ACE/Server, and configure the user to use Tokencode only.sdconf.rec to /var/ace/ on each Multi-Domain Server./etc/services in a text editor and add the following lines:securid 5500/udp
securidprop 5510/tcp
Note - The <authentication_server> parameter is required for TACACS and RADIUS.