SCCP-Based VoIP
Introduction to SCCP Security and Connectivity
SCCP (Skinny Client Control Protocol) controls telephony gateways from external call control devices called Call Agents (also known as Media Gateway Controllers).
Connectivity and network level security for SCCP-based VoIP communication is supported. All SCCP traffic is inspected and legitimate traffic is allowed. Attacks are blocked. Other firewall gateway capabilities are supported, such as anti- spoofing and protection against denial of service attacks.
The validity of SCCP message states is verified for all SCCP messages. For a number of key messages, the existence and validity of the message parameters is also verified.
Encrypted Protocol Support
The gateway enables secure connectivity for mixed secure and non-secure SCCP (Skinny) environments. In these environments, phones communicate using encrypted or clear text signaling protocols.
Encrypted protocols prevent traditional firewalls from identifying the secure phones or understanding the encrypted signaling stream. Ports must be kept permanently open for all phones. The gateway guarantees secure connectivity by:
- Dynamically identifying the secure phones
- Opening ports only for required phones
- Closing ports when the call completes
Non-secure SCCP uses TCP port 2000. Secure SCCP uses TCP port 2443. For more on encrypted protocol support, see the section on securing encrypted SCCP.
SCCP Supported Deployments
These SCCP deployments supported:
- Call Manager in internal network
- Call Manager in the DMZ
- Call Manager in external network

|
Important - NAT on SCCP devices is not supported.
|
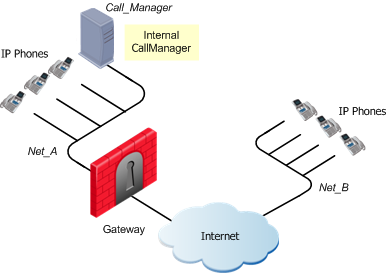
Call Manager in the Internal Network
|
The IP Phones use the services of a Call Manager in an internal network
|
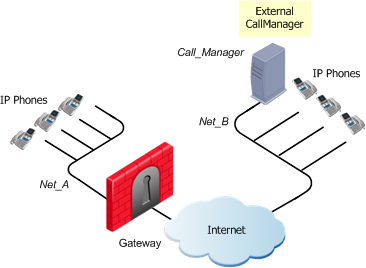
Call Manager in an External Network
|
The IP Phones use the services of a Call Manager on the external side of the gateway. This topology enables using the services of a Call Manager that is maintained by another organization.
|
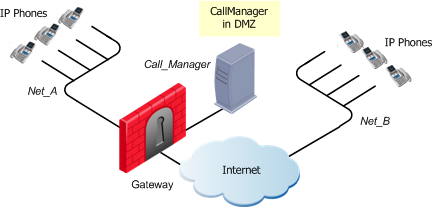
Call Manager in the DMZ
|
The same Call Manager controls both endpoint domains. This topology makes it possible to provide Call Manager services to other organizations.
|
Configuring SCCP Connectivity and Security
This section explains how to configure security rules that allow SCCP calls through the gateway. After the Rule Base is configured, all SCCP communication is fully secured by IPS.
General Guidelines for SCCP Security Rule Configuration
SCCP has a centralized call-control architecture. The CallManager manages SCCP clients (VoIP endpoints), which can be IP Phones or Cisco ATA analog phone adapters. The CallManager controls all the features of the endpoints. The CallManager requests data (such as station capabilities) and sends data (such as the button template and the date/time) to the VoIP endpoints.
The CallManagers are defined in SmartDashboard, usually as Host objects. The networks containing directly-managed IP Phones are also defined in SmartDashboard. Usually it is not necessary to define network objects for individual phones. Cisco ATA devices that are managed by a CallManager must be defined in SmartDashboard, but the connected analog phones are not defined.
When configuring a security rule, if you want calls that are in progress not to be dropped during Install Policy, make sure to select in the Service Properties dialog box.

|
Note - even if the new policy does not allow calls like those in progress, they will not be dropped during Install Policy.
|
SCCP-Specific Services
These predefined SCCP services are available:
Service
|
Purpose
|
TCP:SCCP
|
Used for SCCP over TCP
|
Other:high_udp_for_secure_SCCP
|
Used for media from Secure SCCP phones
|
Securing Encrypted SCCP
To secure encrypted SCCP, use these services in the Security Rule Base:
When an SCCP phone is turned on and identified as Secure SCCP, the phone's IP address is added to the database of secure SCCP phones.
When RTP traffic arrives at the gateway, it is allowed only if the source or destination is in the database of secure SCCP phones.
Configuring the Rule Base for SCCP
To allow VoIP calls, you must create rules that let VoIP control signals pass through the gateway. It is not necessary to define a media rule that specifies which ports to open and which endpoints can talk. The gateway derives this information from the signaling. For a given VoIP signaling rule, the gateway automatically opens ports for the endpoint-to-endpoint RTP/RTCP media stream.

|
Important - Before configuring security rules for SCCP, makes sure that anti-spoofing is configured on the gateway interfaces.
|
VoIP rule for this scenario:
Source
|
Destination
|
Service
|
Action
|
Comment
|
Net_A
Net_B
Call_Manager
|
Net_A
Net_B
Call_Manager
|
SCCP
|
Accept
|
Incoming and Outgoing calls
|
To configure the Rule Base for secure SCCP-based VoIP:
- Define Network objects (Nodes or Networks) for SCCP endpoints (Cisco ATA devices or IP Phones) controlled by the CallManagers.
- Define a host object for the CallManager.
- Define the SCCP VoIP rules.
- Define other rules for SCCP and the other VoIP protocols. (SCCP interoperates with other VoIP protocols.)
This rule let all phones in Net_A and Net_B make calls to each other:
- To secure encrypted SCCP over TCP connections:
- Create an identical rule
- In the cell, add only:
TCP:Secure_SCCP Other:high_udp_for_secure_SCCP.
- Install the policy.
|



