Using Traditional Anti-Virus
Managing Traditional Anti-Virus
Traditional Anti-Virus inspection uses these detection modes:
- Proactive mode - a file-based solution where traffic for the selected protocols is trapped in the kernel and forwarded to the security server. The security server forwards the data stream to the Traditional Anti-Virus engine. The data is allowed or blocked based on the response of the Traditional Anti-Virus engine.
- Stream mode - where traffic for the selected protocols is processed in the kernel on the stream of data without storing the entire file. The data is allowed or blocked based on the response of the kernel.
The POP3 and FTP protocols work only in Proactive mode. The SMTP and HTTP protocols can be configured to work in either Proactive or Stream mode. Anti-Virus scanning is applied only to accepted traffic that has been allowed by the security policy.
Use the instructions in this section to configure Traditional Anti-Virus in your system.
Enabling Traditional Anti-Virus
The Anti-Virus blade and Traditional Anti-Virus can be activated on Security Gateways in your system.

|
Note - You cannot activate the Anti-Virus blade and Traditional Anti-Virus on the same Security Gateway.
|
To configure traditional Anti-Virus:
- On the tab, double-click the required Security Gateway network object.
- Select > > .
- Click .
- Define rules in the Rule Base to permit specific services. Anti-Virus scanning is applied only to accepted traffic.
- From tab > , select the services to scan using these options:
- From the page, configure when to perform automatic signature updates or initiate a manual signature update.
- From the > page, configure Anti-Virus scanning options for , , , and services.
- From the > page, configure FTP traffic scanning options.
- From the > page, configure HTTP traffic scanning options.
- From the > page, configure the options to scan, block or pass traffic according to the file type and configure continuous download options.
- From the > page, configure options for file handling and scan failures.
Database Updates
The following kinds of database updates are available:
- Automatic: Updates of the virus signature can be scheduled at a predefined interval.
- Manual: Updates of virus signatures can be initiated at any time.
Download updates from a Check Point server prior to downloading signature updates. First verify that:
- HTTP and HTTPs Internet connectivity with DNS is properly configured.
- You have a valid Check Point User Center user name and password.
The following signature update methods are available (the default update interval is 120 minutes for all methods):
- Download signature updates every x minutes: Enables you to define the update interval.
- Download from Check Point site: Indicates that each Security Gateway is responsible for contacting Check Point's site to obtain Traditional Anti-Virus signatures. Updates are downloaded directly to the CI gateways. This method usually results in faster update times.
- Download from My local Security Management Server: Indicates that updates are only downloaded by the Security Management Server from the default Check Point signature distribution server and then redistributed all CI gateways. This method is useful when Internet access is not available for all gateways or if the download can only occur once for all the gateways.
Understanding Traditional Anti-Virus Scanning Options
Definitions
Scan by File Direction and Scan by IPs are two file scanning methods used by Content Inspection. Traditional Anti-Virus scanning is performed only on traffic that is allowed by the Security Rule Base.
Scan By File Direction
Scan by File Direction scans all files passing in one direction, either to or from the external, internal and/or DMZ networks. Using this method (the default) is fairly intuitive and does not require the specification of hosts or networks. This method also enables you to define exceptions, for example, locations to or from which files are not scanned.
Scan By IP Address
Scan by IPs lets you define the traffic to be scanned. For example, if all incoming traffic from external networks reaches the DMZ using , you can configure Traditional Anti-Virus to scan only traffic to the FTP, SMTP, HTTP and POP3 servers. Conversely, scans all traffic to the DMZ.
When using Scan by IPs, use a Rule Base to specify the source and destination of the data to be scanned. For FTP, for each rule, you can scan either the GET or the PUT methods, or both. For HTTP, for each rule, you can scan either the HTTP Request, the HTTP Response or both.
Comparing Scan by File Direction and by IPs
Scan by File Direction enables you to specify file scanning according to the file's (and not necessarily the connection's) origin and destination.
Scan by IPs enables you to specify file scanning according to the connection they are sent through and the protocol phase/command (where applicable).
If you want most or all files in a given direction to be Traditional Anti-Virus scanned, select Scan by File Direction.
If you want to specify a connection or part of a connection's source or destination to be scanned, select Scan by IPs.
Comparing Scan by File Direction and by IPs for SMTP Protocol
For the SMTP protocol, Scan by File Direction and Scan by IPs are comparable options. The next figure illustrates that for the SMTP protocol, the files (data) are always sent in the same direction as the connection. The SMTP protocol is used to send mail. Protocols that are used to receive mail (for example, POP3 and IMAP) are not scanned when SMTP is selected.
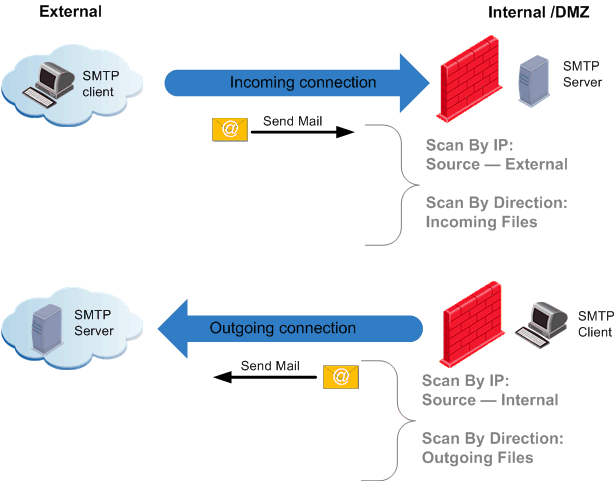
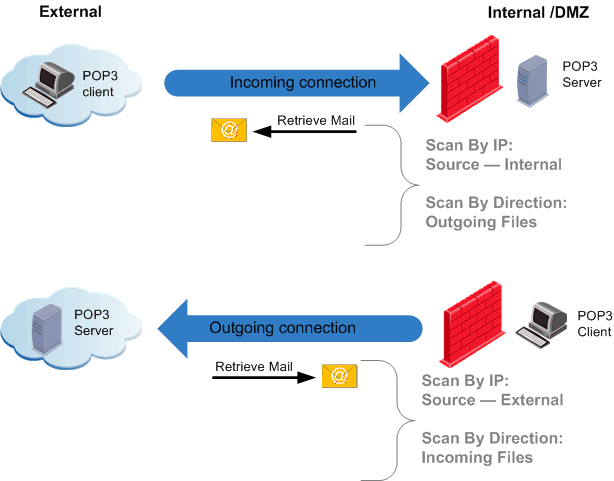
Comparing Scan by File Direction and by IPs for POP3 Protocol
The next figure illustrates that POP3 data files are always sent in the opposite direction of the connection.
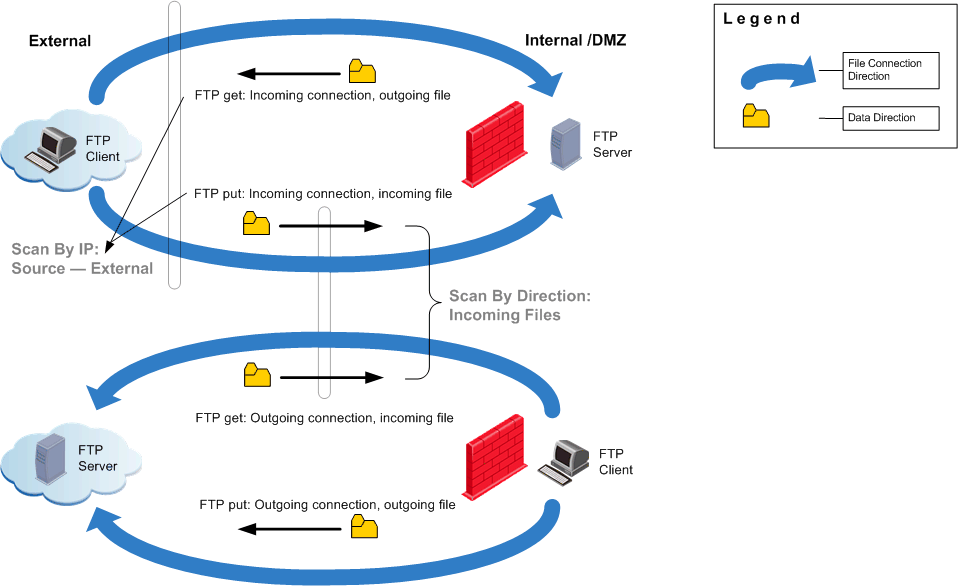
Comparing Scan by File Direction and by IPs for FTP Protocol
For the FTP protocol, the difference between Scan by IPs and Scan by File Direction is illustrated in the next figure. When the FTP GET command is used, files are transferred in the opposite direction to the connection. When the FTP PUT command is used, files are transferred in the same direction as the connection. In this scenario, the Scan by File Direction option enables you to scan files without having to consider the direction of the connection.
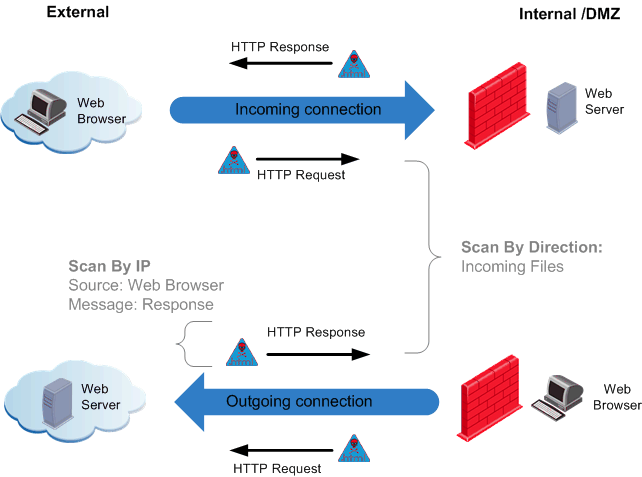
Comparing Scan by File Direction and by IPs for HTTP Protocol
For the HTTP protocol, the difference between Scan by IPs and Scan by File Direction is illustrated in the next figure. Using Scan by IP, the source and destination of the connection are specified and whether the Request, Response or both is scanned.
Scanning by File Direction: Selecting Data to Scan
When using Scan by File Direction, you must select the direction of the data to scan, which depends on whether you want to scan files to or from the internal networks and the DMZ.
What is a DMZ?
The DMZ (demilitarized zone) is an internal network with an intermediate level of security. Its security level lies between trusted internal networks, such as a corporate LAN, and non-trusted external networks, such as the Internet.
Typically, the DMZ contains devices accessible to Internet traffic, for example, Web (HTTP), FTP, SMTP (email), DNS and POP3 servers.
Scan By File Direction enables you to define a level of Traditional Anti-Virus scanning that is specific to the DMZ. For example, you can decide not to scan traffic passing from external networks to the DMZ, but to still scan traffic passing from the DMZ to internal networks and from the external to internal networks.
Scan By File Direction Options
The following Scan By File Direction options are available:
- Incoming files arriving to: Files arriving from external interfaces: the internal networks (1), the DMZ (2) and the DMZ and internal networks (1 and 2).
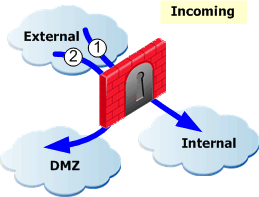
- Outgoing files leaving: Files leaving through external interfaces: the internal networks (1), the DMZ (2) and the DMZ and internal networks (1 and 2).
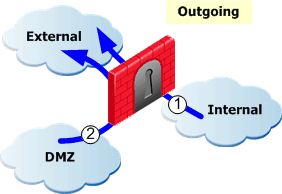
- Internal files: If there is no DMZ, files passing between all internal networks (1). If there is a DMZ, files passing between the DMZ and internal networks and files passing between all internal networks (between internal networks (1), from the DMZ to internal networks (2) and from internal networks to the DMZ (3)).
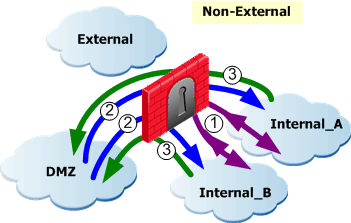
Understanding Proactive and Stream Mode Detection
Traditional Anti-Virus scanning can be enabled in either the proactive or stream detection mode.
- Proactive detection mode - a comprehensive, file-based Traditional Anti-Virus solution where traffic for the selected protocols is trapped in the kernel of the Security Gateway and forwarded to the security server for scanning. It detects not only known viruses, but also zero-day attacks, by using advanced proactive techniques.
This mode uses sandboxes and heuristics to detect malicious code throughout the traffic as opposed to passive signature based detection. Scanned data is either allowed or blocked based on the response of the state-of-the-art Traditional Anti-Virus engine.
Proactive detection provides a high level of protection but has an impact on performance. The FTP and POP3 protocols only work in Proactive mode.
This mode is not available for Virtual System gateways.
- Stream detection mode - where traffic is scanned for viruses as it passes through the network on streams of data, without storing entire files and without causing an impact on performance. The SMTP and HTTP protocols can be set to work in either mode.
This mode is based on state-of-the-art virus signatures that are frequently updated in order to detect recent Malware outbreaks.
In newly installed systems, stream mode is activated by default.
In upgraded systems, the detection mode that is activated by default is dependent upon whether the Traditional Anti-Virus feature was previously activated or not.
- In upgraded systems that previously used the Traditional Anti-Virus scanning feature, proactive detection is activated by default.
- In upgraded systems that previously did not use the Traditional Anti-Virus scanning feature, stream mode detection is activated by default.
You can configure which detection mode to use from SmartDashboard for the SMTP and HTTP protocols.
Continuous Download
The Traditional Anti-Virus engine acts as a proxy which caches the scanned file before delivering it to the client for files that need to be scanned.
When scanning large files, if the whole file is scanned before being made available, the user may experience a long delay before the file is delivered. A similar problem may arise when using client applications with short timeout periods (for example, certain FTP clients) to download large files. If the whole file is cached and scanned before being delivered, the client applications may time out while waiting.
To address this problem, Continuous Download starts sending information to the client while Traditional Anti-Virus scanning is still taking place. If a virus is found during the scan, file delivery to the client is terminated.

|
Note - Continuous Download is only relevant if you have selected to use the Activate proactive detection option.
|
You can specify the file types for which you do not want Continuous Download to occur. Some file types (for example, Adobe Acrobat PDF and Microsoft Power Point files) can open on a client computer before the whole file has been downloaded. If Continuous Download is allowed for those file types, and a virus is present in the opened part of the file, it could infect the client computer.

|
Note - The SMTP and POP3 protocols support Continuous Download for the entire email message.
|
File Type Recognition
IPS has a built-in File Type recognition engine, which identifies the types of files passed as part of the connection and enables you to define a per-type policy for handling files of a given type.
You can specify safe file types that are allowed to pass through IPS without being scanned for viruses. It is also possible to configure file types to be scanned or blocked.
The following file types can be configured:
- Scan: Performs Traditional Anti-Virus file scanning according to the settings in the different services pages. By default, all unrecognized file types are scanned.
- Block: Does not allow passage of file types that are preset for blocking according to IPS advisories.
- Pass: Allows files to pass though the Security Gateway without being scanned for viruses. Files specified as this type are considered to be safe.
File types are considered to be safe if they are not known to contain viruses, for example, some picture and video files are considered safe. Other formats are considered to be safe because they are relatively hard to tamper with. What is considered to be safe changes according to published threats and depends on how the administrator balances security versus performance considerations.
IPS reliably identifies binary file types by examining the file type signatures (magic numbers). IPS does not rely on the file extension (such as *.GIF), which can be spoofed. It also does not use the MIME headers (such as image/gif) in HTTP and mail protocols, which can also be spoofed.
Configuring Traditional Anti-Virus
For detailed explanations regarding the options described in the procedures in this section, see Understanding Traditional Anti-Virus Scanning Options.
Configuring Mail Traditional Anti-Virus
The Mail Traditional Anti-Virus policy prevents email from being used as a virus delivery mechanism.
- In the Traditional Anti-Virus tab, click Traditional Anti-Virus > Security Gateway > Mail Protocols > Mail Traditional Anti-Virus.
- Set the slider to Block.
- Select tracking options for either all POP3 and SMTP mail, or just blocked mail. Tracking options include:
- None (no logging)
- Log
- Popup alert
- Mail alert
- SNMP trap alert
- Three custom user-defined scripts
Configuring Zero Hour Malware
By proactively scanning the Internet, the Data Center identifies massive virus outbreaks as soon as they occur. This Zero-Hour solution provides protection during the critical time it takes to discover a new virus outbreak and assign it a signature.
- In the Traditional Anti-Virus tab, click Traditional Anti-Virus > Security Gateway > Mail Protocols > Zero Hour Malware Protection.
- Using the slider, select a Zero hour malware protection level:
- Select tracking options for blocked, SMTP and POP3 mail. Tracking options include:
- None (no logging)
- Log
- Popup alert
- Mail alert
- SNMP trap alert
- Three custom user-defined scripts
Configuring SMTP, POP3, FTP and HTTP
SMTP and POP3 traffic can be scanned according to direction or by IPs.
- In the Traditional Anti-Virus tab, click Traditional Anti-Virus > Security Gateway > Mail Protocols > SMTP, POP3, FTP or HTTP.
- Using the slider, select a protection level:
- Off
- Monitor Only - SMTP and HTTP are the only protocols that support this protection level
- Block
- When scanning by File Direction, select a scanning direction for:
- Incoming files
- Outgoing files
- Internal files through the gateway
- When scanning by IPs, create rules for the Rule Base to specify the source and destination of the data to be scanned.
- For SMTP and HTTP, select the Activate Proactive Detection (impacts performance) checkbox to enable file-based Traditional Anti-Virus detection. Clear the checkbox to enable stream mode detection. See Understanding Proactive and Stream Mode Detection for further information. FTP and POP3 are set to Proactive Detection mode automatically.
- If Proactive Detection has been configured, select the Activate Continuous Download checkbox to avoid client time-outs when large files are scanned.
See Continuous Download for further information.
Configuring File Types
You can set an action to take place when a file of a certain type passes through the gateway. Certain file types can pass through the gateway without being scanned for viruses. For example, picture and video files are normally considered safe. Other formats can be considered safe because they are relatively hard to tamper with. Update the list as necessary.
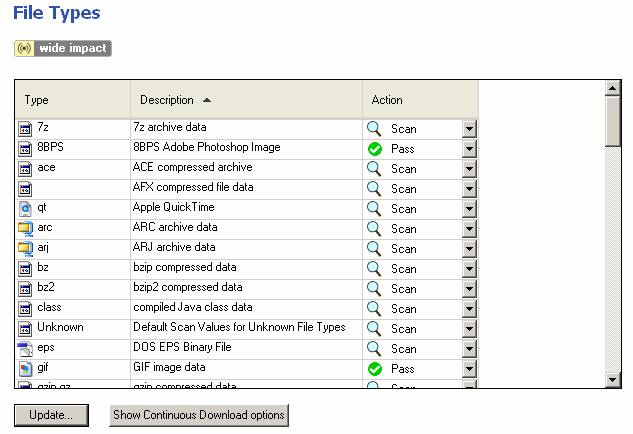
- In the Anti-Spam tab, click Traditional Anti-Virus > Security Gateway > File Types page and set the actions. See File Type Recognition for more information.
In this window, you can also configure Continuous Download options. Continuous Download options are only relevant if scanning is set to Proactive Detection. See Continuous Download for more information.
Configuring Security Gateway Settings
In Traditional Anti-Virus tab, click Traditional Anti-Virus > Security Gateway > Mail Protocols > Settings you can configure scan failure settings and Proactive scan settings (file handling and archive file handling).
Scan Failure
The following scan failure options are available:
- When Traditional Anti-Virus engine is overloaded or scan fails: Determines whether to scan or block the file.
- When Traditional Anti-Virus engine fails to initialize: Determines whether to scan or block the file.
File Handling
The following file handling options are available:
- Maximum file size to scan: Limits the file size that is allowed to pass through the gateway. If the file is a compressed archive, the limit applies to the file after decompression (the Traditional Anti-Virus engine decompresses archives before scanning them). Before performing Traditional Anti-Virus scanning, the gateway reassembles the entire file and then scans it. The limit protects the gateway resources and the destination client.
An archive is a file that contains one or more files in a compressed format. Archives (and all other file types) are recognized by their binary signature. By default, any file type that is not identified as non-archive is assumed to be an archive and the Traditional Anti-Virus engine tries to expand it. - When file exceeds limit: Determines whether to scan or block the file.

|
Note - An email is treated as an archive and as a result it is not affected when the file exceeds the limit.
|
Archive File Handling
The following file handling archiving options are available:
- Maximum archive nesting level: Limits the number of nested archives (one within another). This limit protects the gateway and destination client from attacks that employ deep nesting levels.
- Maximum compression ratio: Prevents attacks that employ a small size archive that decompresses into a very large file on target.
- When archive file exceeds limit or extraction fails: Determines whether to scan or block the file.
Logging and Monitoring
Logging information on the Traditional Anti-Virus scan is sent to the Security Management Server and can be viewed using SmartView Tracker. Scan results information is shown in the logs. In addition, there are logs for signature updates, new update checks, and download results.
The Traditional Anti-Virus status is monitored using SmartView Monitor. The Traditional Anti-Virus status appears under the Firewall product. The status contains information on the currently installed signature file and the Traditional Anti-Virus engine version. The Traditional Anti-Virus status also includes statistics about scanned files and found viruses.
UTM-1 Edge Traditional Anti-Virus
You can now enable Traditional Anti-Virus protection within UTM-1 Edge. Selecting the Enable Traditional Anti-Virus option indicates that Traditional Anti-Virus protection is installed and that updates are sent to the specified gateway.
Using UTM-1 Edge Traditional Anti-Virus, you can define the maximum archive file sizes for UTM-1 Edge machines that are scanned, and configure procedures for when these limits are exceeded and/or the scan fails.
The UTM-1 Edge Traditional Anti-Virus feature enables you to automatically or manually update virus signatures for UTM-1 Edge machines and provides you with the tools to configure how UTM-1 Edge traffic is scanned.

|
Note - It is important to configure a valid DNS server address on your management and gateway in order for the signature update to work.
|
The UTM-1 Edge Traditional Anti-Virus scanning policy enables you to select the service(s) to and from which a source and/or destination is scanned. Files set for scanning is determined using a classic Rule Base, which defines the source and destination of the connection to be scanned. It is recommended to use this method if you want to define exactly which traffic to scan, for example, if all incoming traffic from external networks reaches the DMZ, you can specify that only traffic to the Traditional Anti-Virus servers is scanned.
To enable and configure Traditional Anti-Virus protection:
- From the General Properties tab of the UTM-1 Edge gateway, select the > > .
- In the Edge Traditional Anti-Virus section of the Traditional Anti-Virus tab, configure Traditional Anti-Virus to work on UTM-1 Edge gateways. All of the Traditional Anti-Virus settings in the Traditional Anti-Virus tab do not work for UTM-1 Edge machines. The Edge Traditional Anti-Virus settings in the Traditional Anti-Virus tab only work for UTM-1 Edge machines.
|



