Introduction to QoS
Important:
- This guide is only for R77.10 and higher.
- For R77, see the R77 Quality of Service Administration Guide.
Check Point's QoS Solution
QoS is a policy based bandwidth management solution. QoS lets you:
- Prioritize business-critical traffic, such as ERP, database and Web services traffic, over less time-critical traffic.
- Guarantee bandwidth and control latency for streaming applications, such as Voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing.
- Give guaranteed or priority access to specified employees, even if they are remotely accessing network resources.
QoS is deployed with the Security Gateway. QoS is enabled for both encrypted and unencrypted traffic.
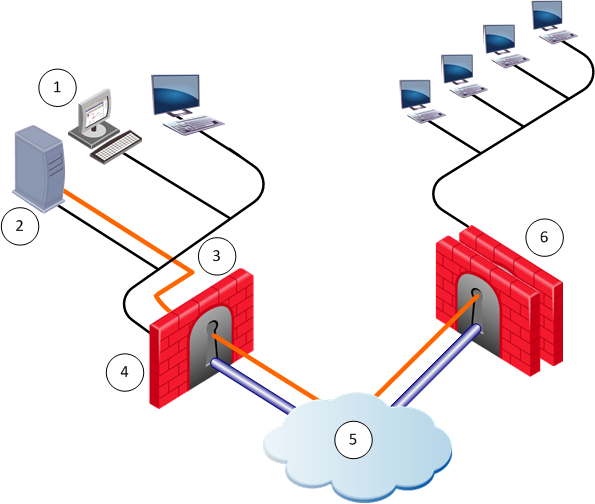
Number
|
Description
|
Number
|
Description
|
1
|
SmartDashboard
|
4
|
QoS gateway
|
2
|
Security Management Server
|
5
|
Internet
|
3
|
QoS Policy
|
6
|
Security Gateway and QoS gateway
|
QoS leverages the industry's most advanced traffic inspection and bandwidth control technologies. Check Point patented Stateful Inspection technology captures and dynamically updates detailed state information on all network traffic. This state information is used to classify traffic by service or application. After traffic has been classified, QoS applies an innovative, hierarchical, Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) algorithm to accurately control bandwidth allocation.
Features and Benefits
QoS gives these features and benefits:
QoS lets you create basic policies that can be modified to include the Advanced QoS features described in this section.
The integration of an organization's security and bandwidth management policies enables easier policy definition and system configuration. This lets you optimize network performance for VPN and unencrypted traffic
Monitor the performance of your system by means of log entries recorded in SmartView Tracker.
Add one or more Diffserv Classes of Service to the QoS Policy Rule Base.
Define special classes of service for "delay sensitive" applications like voice and video to the QoS Policy Rule Base.
Supplies a QoS solution for the Citrix ICA protocol.
QoS and Firewall share a common architecture and many core technology components. User-defined network objects can be used in both solutions.
QoS's monitoring systems let you to be proactive in managing your network and controlling network costs.
QoS offers full support for end-to-end QoS for IP networks by distributing enforcement throughout network hardware and software.
For packet acceleration.
QoS Policy Versus QoS Express Policy
Express mode lets you define a basic policy. Included as a legacy option for backward compatibility, Express mode does not contain most of the features available in the recommended QoS policy option. To use express mode, select the QoS express policy option when creating a new package in .
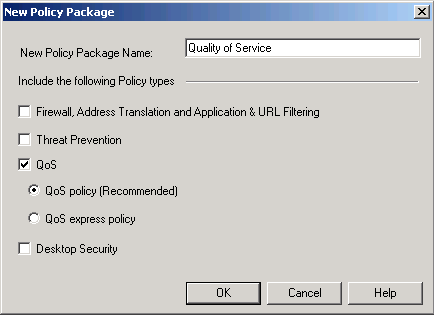
This table compares QoS policy features with QoS Express mode policy features.
* Only supported when SecureXL and CoreXL are disabled.
For more, see the R77.10 Release Notes.
Enabling QoS Acceleration Support
After a clean install or upgrade to R77.10, QoS supports SecureXL and CoreXL acceleration technologies.
Important: After a clean install or upgrade, SecureXL and CoreXL must be manually enabled on the QoS Security Gateway. If the gateway is a member of a cluster, QoS must be manually enabled on all the cluster members.
To enable:
- On the gateway, run:
cpprod_util CPPROD_SetValue FG1 FgWithAcceleration 1 1 1
- Use
cpconfig to turn on SecureXL/CoreXL. - Reboot the gateway.
To disable:
- On the gateway, run:
cpconfig to turn off SecureXL and CoreXL. - Reboot the gateway.
- After reboot, run:
cpprod_util CPPROD_SetValue FG1 FgWithAcceleration 1 0 1
Note: If you have a QoS policy created using R77 and below, note that these features are not supported when acceleration is enabled:
- User Authority Server
- IPSO
- Citrix printing rules
- Security Gateways below R77.10
- SmartView Monitor - QoS views do not correctly show traffic accelerated by SecureXL
For more, see the QoS known limitations in the R77.10 Known Limitations.
Workflow
This workflow shows the basic and advanced steps that System Administrators do for installation, configuration, and operation.
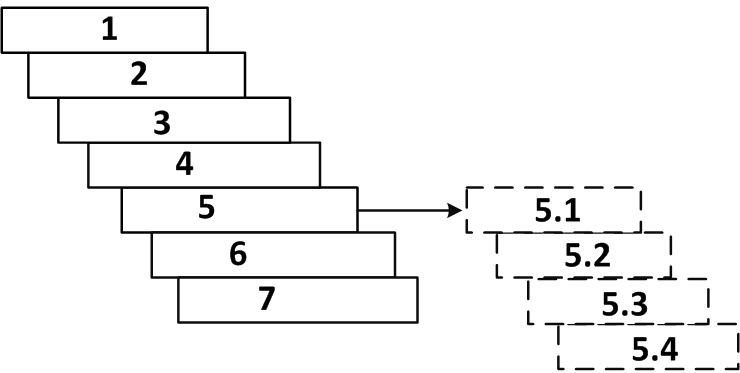
- Open SmartDashboard. See Starting SmartDashboard.
- Define Global Properties. See Defining QoS Global Properties.
- Define the gateway network objects.
- Enable the QoS blade on the QoS gateway.
- Configure the basic rules and sub-rules governing the allocation of QoS flows on the network. See Editing QoS Rule Bases.
After the basic rules have been defined, you can configure these advanced features:
- Implement the Rule Base. See Implementing the Rule Base.
- Enable log collection and monitor the system. See Enabling Log Collection.
Using QoS with SmartProvisioning
For how to activate SmartLSM with QoS, see the R77 SmartProvisioning Administration Guide.
QoS Architecture
Basic Architecture
The architecture and flow control of QoS is similar to firewall.
QoS has three components:
- SmartConsole
- Security Management Server
- Gateway
The components can be installed on one machine or in a distributed configuration on a number of machines.
Bandwidth policy is configured using SmartDashboard. On the Security Management Server, the policy is verified and installed on the QoS gateways. The QoS gateway uses:
- The firewall chaining mechanism to receive, process and send packets.
- A proprietary classifying and rule-matching infrastructure to examine a packet.
Logging information is created using the firewall kernel API.
QoS Gateway
The primary role of the QoS blade is to:
- Implement a QoS policy at network access points
- Control the flow of inbound and outbound traffic.
QoS has two components:
- QoS kernel driver
- QoS daemon
QoS Kernel Driver
The kernel driver is the heart of QoS operations. It is in the kernel driver that IP packets are examined, queued, scheduled and released, enabling QoS traffic control abilities.
QoS Daemon (fgd50)
The QoS daemon is a user mode process that:
- Resolves DNS for the kernel (used for Rule Base matching).
- Resolves Authenticated Data for an IP (using UserAuthority - again for Rule Base matching).
- In a Cluster Load Sharing configuration, updates the kernel of changes in the cluster status. For example, if a cluster member goes down. The daemon recalculates the relative loads of the gateways and updates the kernel.
The primary SmartConsole application is SmartDashboard. Use SmartDashboard to create "bandwidth rules" for the QoS policy.
Other SmartConsole clients are the SmartView Tracker, a log entries browser, and SmartView Monitor. SmartView Monitor shows status information about active QoS gateways and their policies.
QoS in SmartDashboard
SmartDashboard is used to create and change the QoS Policy and define the network objects and services. If both VPN and QoS are licensed, they each have a tab in SmartDashboard.
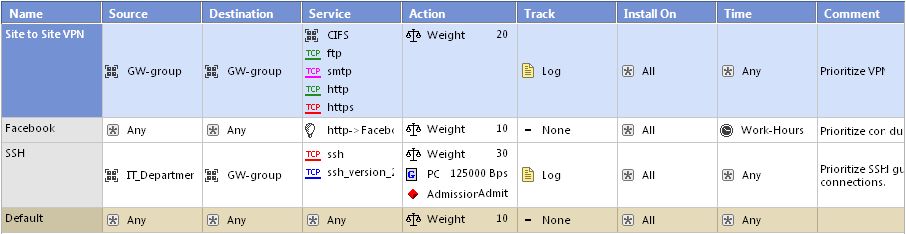
The QoS Policy rules are shown the QoS Rule Base.
QoS Configuration
The Security Management Server and the QoS gateway can be installed on the same machine or on two different machines. When they are installed on different machines, the configuration is known as distributed.
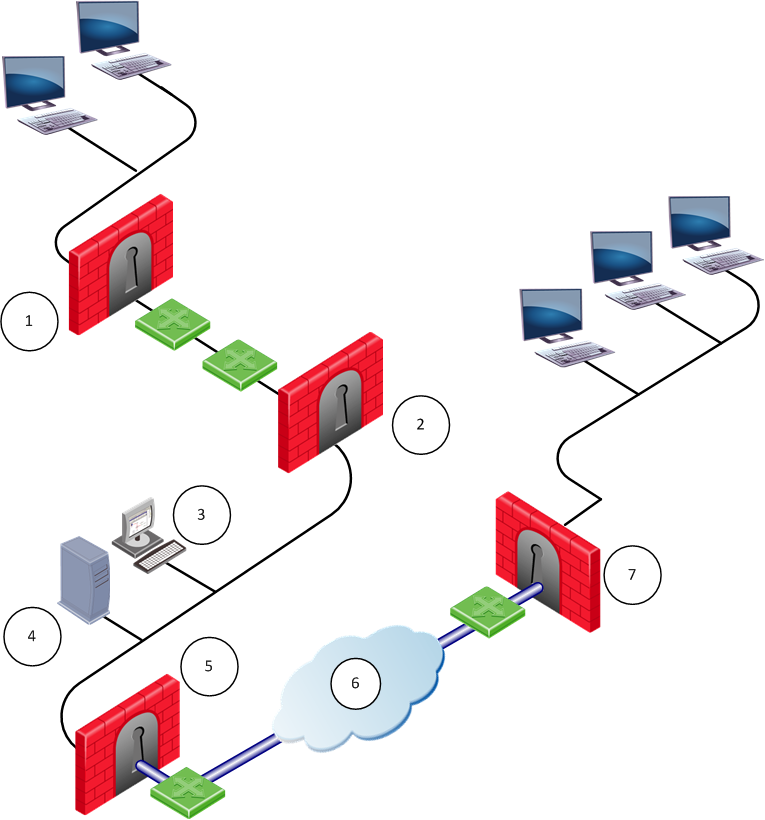
Number
|
Description
|
Number
|
Description
|
1
|
QoS gateway
|
5
|
QoS gateway
|
2
|
QoS gateway
|
6
|
Internet
|
3
|
SmartConsole
|
7
|
QoS gateway
|
4
|
Security Management Server
|
|
|
The example shows a distributed configuration, in which one Security Management Server (consisting of a Security Management Server and a SmartConsole controls four QoS gateways. The four QoS gateways manage bandwidth allocation on three QoS enabled lines.
One Security Management Server can control and monitor multiple QoS gateways. The QoS gateway operates independently of the Security Management Server. QoS gateways can operate on more Internet gateways and interdepartmental gateways.
Client-Server Interaction
SmartConsole and the Security Management Server can be installed on the same machine or on two different machines. When they are installed on two different machines, QoS implements the Client/Server model, in which a SmartConsole controls a Security Management Server.
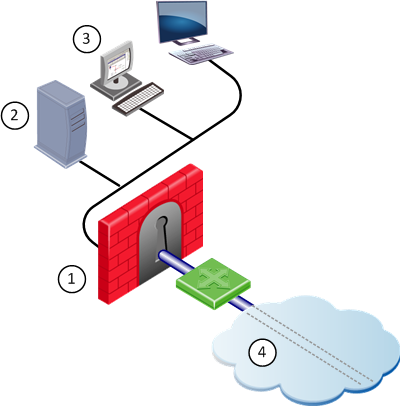
Number
|
Description
|
Number
|
Description
|
1
|
London QoS gateway
|
3
|
Bridge SmartConsole
|
2
|
Tower Security Management Server
|
4
|
Internet
|
In the configuration depicted in the above figure, the functionality of the Security Management Server is divided between two workstations (Tower and Bridge). The Security Management Server with the database is on Tower. The SmartConsole is on Bridge.
The user, working on Bridge, maintains the QoS Policy and database, which reside on Tower. The QoS gateway on London enforces the QoS Policy on the QoS enabled line.
The Security Management Server is started with the cpstart command, and must be running if you wish to use the SmartConsole on one of the client machines.
A SmartConsole can manage the Server only if both the administrator logged into SmartConsole and the computer on which the SmartConsole is running have been authorized to access the Security Management Server. Use cpconfig to:
- Add SmartConsole as gui client authorized to access the Security Management Server
- Define administrators for the Security Management Server.
Concurrent Sessions
To prevent more than one administrator from modifying a QoS Policy at the same time, QoS implements a locking mechanism. All but one open policy is 'Read Only'.
Interaction with VPN
Interoperability
QoS and firewall share many core technology components. The same user-defined network objects can be used in both solutions. The integration of an organization's security and bandwidth management policies gives easy policy definition and system configuration. For efficient traffic inspection and enhanced performance, the blades share state table information. The QoS blade and firewall blade let users define bandwidth allocation rules for encrypted and NATed traffic.
Security Management Server
QoS uses the Security Management Server and shares the objects database (network objects, services and resources) with the firewall. Some objects have properties that are product specific. For example, the Firewall has encryption properties which are not related to QoS. A QoS network interface has speed properties that are not related to the firewall.
|



