Introduction to Azure Virtual WAN
Microsoft Azure Virtual WAN is a service that lets customers easily establish optimized large-scale branch connectivity with Azure and the Microsoft global network.
Microsoft Azure Virtual WAN is a networking service that provides optimized and automated branch-to-branch connectivity through Azure.
This guide describes the integration of CloudGuard Network Security NVA![]() Network Virtual Appliance - A resource deployed in Azure's Virtual Hub that includes Security Gateways and other networking infrastructure. (Gateways) into the Azure Virtual WAN Hub and provides step-by-step instructions to configure and use the CloudGuard Network Security NVA in Microsoft Azure Virtual WAN Hub.
Network Virtual Appliance - A resource deployed in Azure's Virtual Hub that includes Security Gateways and other networking infrastructure. (Gateways) into the Azure Virtual WAN Hub and provides step-by-step instructions to configure and use the CloudGuard Network Security NVA in Microsoft Azure Virtual WAN Hub.
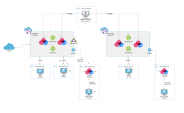
Reference architecture:
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
Microsoft Azure Virtual Hub (for example: East US) |
|
3 |
First CloudGuard Network Security NVA instance |
|
4 |
Second CloudGuard Network Security NVA instance |
|
5 |
Internal Load Balancer |
|
6 |
Express route on Azure virtual Hub |
|
7 |
Azure VPN Gateway |
|
8 |
IPsec Site to Site VPN tunnel from the first on-premises Security Gateway (10) to the Microsoft Azure Virtual Hub (2) |
|
9 |
First Branch |
|
10 |
On-premises Security Gateway (for example: USA, Ohio) |
|
11 |
On-premises host |
|
12 |
Connection between the Microsoft Azure Virtual Hub (2) and the first VNet (13) |
|
13 |
First VNet |
|
14 |
Host in Azure VNet |
|
15 |
External Load Balancer |
For more information, see the Azure Virtual WAN Documentation.
Prerequisites
Check Point:
|
Check Point |
Software Version |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Security Management Server, Multi-Domain Management Server or Quantum Smart-1 Cloud. |
R81.10 and higher or R81 with JHF take 42 and higher. |
Security Management Server must have Internet connectivity (inbound and outbound). |
Azure:
-
A user-assigned managed identity with these permissions:
-
Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs/read on the hub where the NVA is created.
-
Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/join/action only if a Public IP is attached for Internet ingress.
-
-
A deployed Virtual WAN with Virtual Hub.
For more information refer to:
Workflow
The workflow for integrating CloudGuard Network Security NVA with Azure Virtual WAN:
-
Deploy Azure Virtual WAN (if already completed, skip to step #3).
-
Create an Azure Virtual WAN Hub with your Azure Virtual WAN deployment (if already completed, skip to step #3)
-
Add permissions to the user-assigned managed identity for your Azure subscription.
See Step 3: Add permissions to the user-assigned managed identity.
-
Create a CloudGuard Network Security NVA in the Virtual WAN hub in the Azure portal.
See Step 4: Deploy new CloudGuard Network Security NVA in the Virtual WAN Hub.
-
Connect the CloudGuard Network Security NVA to the Check Point Security Management Server or to Check Point Smart-1 Cloud SaaS Security Management service.
See Step 5: Connect to the Security Management Server or Quantum Smart-1 Cloud (Management-as-a-Service).
-
Configure the CloudGuard Network Security NVA in the Security Management Server
 Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server..
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server..See Step 6: Configure NVA Security Gateways on the Security Management Server or Quantum Smart-1 Cloud
-
Set the Azure Virtual WAN hub's routing intent policies in the Azure portal to route Internet-bound and Private Traffic through the CloudGuard Network Security NVA.
-
Connect Azure VNets, branch sites, Express Routes, and VPN connections to your Azure Virtual WAN.
See Connecting Spokes in CloudGuard Network Security NVA for Azure Virtual WAN.
Follow the steps and considerations outlined in the instructions to make sure the integration is successful.