Integrating CloudGuard Network Security NVA with Azure Virtual WAN
Step 1: Deploy Azure Virtual WAN
-
Log in to the Azure Portal, navigate to the Search resources bar, type Virtual WAN in the search box, and select Enter.
-
Select Virtual WANs if needed and select + Create on the Virtual WANs page.
-
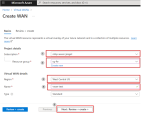
Fill in the necessary fields on the Create WAN page > Basics tab. Keep the Type option as Standard. Click Next : Review + create >.
-
When the validation passes, click Create to create the virtual WAN.
|
|
Important - Terraform and ARM
|
Step 2: Create an Azure Virtual WAN Hub
-
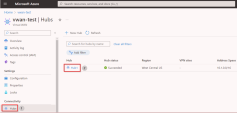
Navigate to the virtual WAN you created. On the virtual WAN left pane, below Connectivity, select Hubs.
-
On the Hubs page, select + New Hub to open the Create virtual hub page. Fill out the applicable fields:
-
Region: Select the region where you want to deploy the virtual hub.
-
Name: The name to assign to the virtual hub.
-
Hub private address space: The hub’s address range in CIDR notation. The minimum address space is /24 to create a hub.
-
Virtual hub capacity: Select from the drop-down. For more information, see Azure Virtual hub settings.
-
Hub routing preference: Leave as default. For more information, see Azure Virtual hub routing preference.
-
-
Once complete, select Review + create.
-
After validation passes, select Create. (Creating a new hub takes approximately 30 minutes).
-
To validate that your Virtual Hub is successfully provisioned, navigate to your Virtual WAN below Connectivity > Hubs, and select the Hub you created.
-
Check the Routing status; if it is still Provisioning, do not proceed.
Once the Routing status states Provisioned, you can proceed to the next step.
Step 3: Add permissions to the user-assigned managed identity
To deploy an CloudGuard Network Security NVA, your subscription requires a user-assigned managed identity with these permissions:
-
Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs/read permission - on the hub where the NVA is created.
-
Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/join/action permission - if a Public IP address is attached for Internet ingress.
|
|
Note - For guidance on creating a user-assigned managed identity, refer to the official Microsoft documentation. |
To assign the Microsoft.Network/virtualHubs/read permission to your user-assigned managed identity in Azure:
-
Go to the Azure portal.
-
Navigate to the Virtual Hub resource where you want to assign the permission.
-
Select Access control (IAM) from the left menu.
-
Click Add role assignment.
-
In the Role drop-down menu, select Reader.
-
In the Assign access to drop-down menu, select Managed identity.
-
Select the user-assigned managed identity you want to assign the role to.
-
Click Save to apply the changes.
To assign the Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/join/action permission to your user-assigned managed identity in Azure:
-
Go to the Azure portal.
-
Navigate to the Public IP Address resource (if it exists), or to the resource group where it will be created.
-
Select Access control (IAM) from the left menu.
-
Click Add role assignment.
-
In the Role drop-down menu, select a custom role that includes the Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/join/action permission.
If you prefer not to create a custom role, you can use the predefined Network Contributor role in Azure.
-
In the Assign access to drop-down menu, select Managed identity.
-
Select the user-assigned managed identity you want to assign the role to.
-
Click Save to apply the changes.
Step 4: Deploy new CloudGuard Network Security NVA in the Virtual WAN Hub
-
Navigate to your Azure Virtual WAN Hub > on the left tree, select Network Virtual Appliance.
-
Click Create Network Virtual Appliance
-
From the Network Virtual Appliance drop down box, select check point and click Create.
-
On the pop-up, select Leave.
-
Click Create on the CloudGuard Network Security for Azure Virtual WAN screen.
-
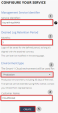
On the Create CloudGuard Network Security for Azure Virtual WAN page, provide this information:
Basics tab
Parameter
Description
Subscription
Azure subscription into which you deploy the NVA object.
Resource group
Azure resource group into which you deploy the NVA object.
Region
Region into which you deploy the NVA object.
Application name
The name of the managed app that is displayed in the Resource Group.
Managed Resource Group
The name of the Azure Managed Resource Group.
Managed Identity tab
Parameter
Description
Subscription
Select the Azure subscription into which you deploy the NVA object.
User-assigned managed identity
Select the user-assigned managed identity for this subscription.
CloudGuard NVA Configurations tab
Parameter
Description
Virtual WAN Hub
Select the Virtual WAN Hub to deploy the CGNS NVA into.
NVA name
Name of the new NVA.
Scale unit
The scale unit determines the size and number of resources deployed. The higher the scale unit, the greater the amount of traffic that can be handled.
Version
The CloudGuard Network Security Gateway
 Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. version.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. version.License type
Type of license:
-
Security Enforcement (NGTP) - Check Point Security Gateways (NGTP package).
-
Full Package (NGTX + S1C) - Check Point Security Gateways (NGTX package, i.e. NGTP and Threat Extraction
 Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that removes malicious content from files. Acronym: TEX. and Threat Emulation
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that removes malicious content from files. Acronym: TEX. and Threat Emulation Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that monitors the behavior of files in a sandbox to determine whether or not they are malicious. Acronym: TE.) and Smart-1 Cloud Security Management.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that monitors the behavior of files in a sandbox to determine whether or not they are malicious. Acronym: TE.) and Smart-1 Cloud Security Management. -
Full Package Premium (NGTX + S1C++) - Check Point Security Gateways (NGTX package) and Smart-1 Cloud Security Management, Compliance
 Check Point Software Blade on a Management Server to view and apply the Security Best Practices to the managed Security Gateways. This Software Blade includes a library of Check Point-defined Security Best Practices to use as a baseline for good Security Gateway and Policy configuration., DLP and SmartEvent.
Check Point Software Blade on a Management Server to view and apply the Security Best Practices to the managed Security Gateways. This Software Blade includes a library of Check Point-defined Security Best Practices to use as a baseline for good Security Gateway and Policy configuration., DLP and SmartEvent.
SSH public key source
Select the SSH key source:
-
If you select to generate a new key pair- select an SSH key type and enter a new name for the key pair.
-
If you select to use an existing key stored in Azure - select your key.
-
If you select to use an existing public key - enter the key to the text box
SSH key type
Select the key format. This parameter depends on the selected SSH public key source.
Key pair name
The key pair name. This parameter depends on the selected SSH public key source.
Stored Keys
Select the stored key pair. This parameter depends on the selected SSH public key source.
Confirm SIC key
Enter the same SIC key for verification.
Quick connect to Smart-1 Cloud
If you select yes (and provide tokens), the NVA Gateways deploy with a secured tunnel to the Security Management Server
 Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server..
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server..Smart-1 Cloud Token for instance x
The token you generate in the Smart-1 Cloud portal for Gateway instance number x.
(x between 1 to 5).
CloudGuard Advanced Settings tab
Parameter
Description
Default shell for the admin user
Select the shell for the admin user.
BGP autonomous system number. (BGP ASN 64512 to 65534 excluding 65515, 65520).
Bootstrap script
Custom script that configures the NVA instance after deployment.
You can find custom scripts here.
Use public IP for ingress (public preview)
Select "Yes" to deploy the NVA with the attached public IP address that is used for ingress traffic.
Create new public IP for ingress traffic
Select "Yes" to create the public IP resource with the NVA.
Public IP resource ID
If you selected "No" in the previous section, enter the existing public IP resource ID here.
Tags tab
Parameter
Description
Tags
Azure tags (Name, Value) that you attach to the selected resources.

Notes:
-
Smart-1 Cloud (Check Point's Management Server as a Service) is a recommended option to start using CloudGuard Network Security Gateways.
-
Follow the instructions in sk180501 to create tokens for each member and paste them into the applicable fields.
-
-
On the Review + Create tab, check the radio box to agree to the terms and conditions and click Create.
-
When the NVA creation completes, go to your Virtual WAN, navigate to the hub you selected in the deployment > on the left tree, select Network Virtual Appliance, and make sure you can see your new NVA and its provisioning state is Succeeded (it can take some time).
-
To see the public IP addresses of your CGNS NVA machines click on Click here below Instances info. (Make note of these IP addresses for future use).
|
|
Important - CloudGuard Network Security Gateways deployed in the Virtual WAN hub do not scale in or out in response to demand. If your throughput increases, you must deploy a new Managed Application that supports the required throughput and modify routing intent from old to new. Refer to Upgrading CloudGuard Network Security NVA for Azure Virtual WAN. |
Step 5: Connect to the Security Management Server or Quantum Smart-1 Cloud (Management-as-a-Service)
These steps are required only if you do not have an installed Check Point Security Management Server or Quantum Smart-1 Cloud instance.
If you already have a Check Point Security Management Server installed or Quantum Smart-1 Cloud instance configured, skip to Step 5.
|
|
Notes:
|
Deploying a Security Management Server in Azure
|
Item |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
From the Azure Marketplace, deploy this solution to create a Check Point Security Management Server: |
||
|
2 |
Select the Check Point Security Management software plan.
Use these parameters:
|
||
|
3 |
This template deploys the Security Management Server in the selected subnet. When the management instance starts, it automatically executes the Gaia First Time Configuration Wizard. This can take up to 30 minutes. |
Deploying a Security Management Server On-premises
Follow the instructions in the Check Point Installation and Upgrade Guide for your Security Management Server version.
Configuring the Security Management Server
-
Download, install, and configure the latest CME (Cloud Management Extension).
To download and install the CME on the Security Management Server or Multi-Domain Security Management Server, see sk157492.
To configure the CME, see the Cloud Management Extension Administration Guide.
-
Configure the Security Policy
 Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. in SmartConsole.
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. in SmartConsole.
|
|
Note - By default, you can access each Check Point Security Gateway and Security Management Server's Gaia Portal |
Configuring a Quantum Smart-1 Cloud Instance
If this is your first Check Point deployment, note that the Quantum Smart-1 Cloud service is included with CloudGuard Network Security for Azure Virtual WAN when purchased with these bundles:
-
Full Package
-
Full Package Premium
Primary benefits of using Quantum Smart-1 Cloud:
-
Always the latest security management
The newest features are automatically updated in a unified management platform.
-
Zero Maintenance
No installation, no upgrade.
-
On-demand Expansion
Seamlessly expand capacity by supporting additional Gateways and storage.
|
|
Note - You can set up Smart-1 Cloud before configuring the CloudGuard NVA Security Gateways in Azure. |
-
Navigate to https://portal.checkpoint.com and click Don’t have an account? Register here.
-
Fill in the Create Your Infinity Account form (required fields have an *) and click Next.
After that, an Account Created Successfully message is displayed and an email is sent to the email address you provided to complete the registration.
-
Log in to the Infinity Portal.
-
Click the menu button in the top left corner and then Smart-1 Cloud below the Quantum column.
-
Select the checkbox to accept the terms of service and click Try Now.
-
Click Get Started.
-
Configure the service and click Create.
You are now ready to connect your CloudGuard Network NVA Security Gateways.
Step 6: Configure NVA Security Gateways on the Security Management Server or Quantum Smart-1 Cloud
There are three options to configure the NVA Security Gateways: with the CME API (recommended), cme_menu, and manually.
For detailed information about Azure vWAN NVA Security Gateways provisioning and configuration, refer to the Cloud Management Extension Administration Guide > Azure Virtual WAN > Configure the NVA with CME API.
API Documentation:
-
SwaggerHub: Azure Virtual WAN
-
Postman Collection: CME API Postman collection
To provision NVA Security Gateways with the CME API:
Send a POST request:
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.1/azure/virtualWANs/accounts/<account_id>/resourceGroups/<nva_resource_group>/provision/<nva_name>
Required parameters:
-
account_id: Your Azure account name from the CME configuration file.
-
nva_resource_group: The resource group containing your NVA.
-
nva_name: Your NVA's name.
Request body parameters:
-
base64_sic_key: Base64-encoded Secure Internal Communication (SIC) key to use with the Security Management Server.
-
policy: A Security Policy to install on Security Gateways (for example, "Standard").
-
autonomous_threat_prevention: Enable/disable the Autonomous Threat Prevention blade.
-
identity_awareness: Enable/disable the Identity Awareness
 Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that enforces network access and audits data based on network location, the identity of the user, and the identity of the computer. Acronym: IDA. blade.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that enforces network access and audits data based on network location, the identity of the user, and the identity of the computer. Acronym: IDA. blade.
This asynchronous operation returns a request_id to monitor the provisioning status.
You check the status with a GET request:
GET https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/cme-api/status/<request_id>
Procedure:
-
Connect to the command line on the Security Management Server.
-
Log in to the Expert mode.
-
Run the command:
cme_menu -
On the menu, select Azure (1) > vWAN (2) > Configure NVA gateways on management server (1).
-
Enter the requested parameters.
The logs are stored in the /var/log/CPcme/cme_menu.log file.
For details regarding the automatic configuration, refer to the instructions in the Cloud Management Extension Administration Guide > Azure Virtual WAN guide.
|
|
Note - Make sure the NVA Security Gateway objects in SmartConsole have {tags=vwan} in the Comment field (this enables For example: |
To configure NVA Security Gateways on the Security Management Server:
-
Open SmartConsole and create a new Security Gateway object for each NVA instance.
-
Give each Security Gateway the IP address of a Network Virtual Appliance in Step 4: Deploy new CloudGuard Network Security NVA in the Virtual WAN Hub, point 3.
-
Disable anti-spoofing on external (eth0) and internal (eth1) interfaces on each Security Gateway.
-
If VPN is enabled, enter the Security Gateway's external IP address in Statically NATed IP.

-
Install the policy.

Note - Make sure not to block Management or SSH access to the Security Gateway from the Internet because it is not possible to connect to the deployed Security Gateway instances with a serial console.
To configure NVA Security Gateways in Smart-1 Cloud
-
Navigate to the Infinity Portal's Welcome page and click Open Streamed SmartConsole.

Note - Make sure pop-up blockers are disabled.
-
A new tab opens. Click Gateways & Servers.
-
Click +Add new Gateway below the Connect Gateways section.
-
Click the large + sign. Repeat this step for each NVA Security Gateway.
-
On the Register Security Gateway screen, give the first NVA Security Gateway a name and click Register (the name cannot include spaces or special characters). Repeat this step for each NVA Security Gateway.
After you add your NVA Security Gateway objects, you see the state: Waiting for Connection.
-
Click Connect Gateway. Repeat this step for each NVA Security Gateway.
-
On the Instructions to Connect Gateway screen, click the Copy icon and then click Close.
-
Log in to the related NVA Security Gateways Gaia CLI and paste the command.
-
The output must show successful connectivity to Smart-1 Cloud, for example:
-
On the Smart-1 Cloud portal, the Security Gateways are in a Pending Trust (SIC) Establishment status.
You are ready to securely connect your NVA Security Gateways to Smart-1 Cloud, install Security Policy on the Security Gateways, and collect logs and other telemetry information
-
Go to Gateways & Servers and double-click the first NVA Security Gateway to open its properties.
-
Click Communication.
-
In the One-time password field, enter the SIC key you provided during the initial NVA Security Gateway creation.
-
Click Initialize. If successful, the Certificate state shows Trust established. Click OK.
-
The Topology Results show. Click Close.
-
Click Network Management, then double-click on eth0 (repeat for eth1). Then click Modify and clear the checkbox next to Perform Anti-Spoofing based on interface topology. Click OK on the applicable dialog boxes.
-
Click OK on the main properties screen when you complete the two interfaces (eth0 and eth1).
-
Repeat steps 2 to 8 for all remaining NVA Security Gateways.
-
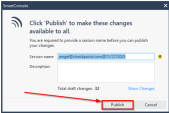
Click Publish to commit the changes to Smart-1 Cloud.
-
In the SmartConsole window, enter a Session name and Description and click Publish again.
You can now create and install a security policy for your NVA Security Gateways. Refer to the Security Management Administration Guide for full guidance on creating a policy that fits your organization's needs.
After you configure your policy, you can install it. On the first policy installation, only the Access Control policy is installed. On the next installations, you can also include the Threat Prevention policy.
After you set Routing Intent in your Hub, the Security Gateways start inspecting traffic.
Step 7: Set Routing Intent and Routing Policies
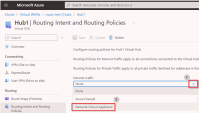
Select your Virtual WAN > Select the applicable virtual hub > on the left tree, select Routing Intent and Routing Policies.
-
For Internet bound Traffic:
In the Internet Traffic drop-down select Network Virtual Appliance, in the Next Hop Resource select the NVA you created and click Save. -
For private traffic:
In the Private Traffic drop-down select Network Virtual Appliance, in the Next Hop Resource select the NVA you created and click Save.
|
|
Note - To add prefixes for routing intent click on Additional prefixes. |
Step 8: Configure NAT
For outbound traffic, the packets should be NATTed behind the Security Gateway's IP address.
Creating Dynamic Objects 'LocalGatewayExternal' and 'LocalGatewayInternal'
For the manual NAT rules, you must create these Dynamic Objects in SmartConsole:
-
LocalGatewayExternal
-
LocalGatewayInternal
Procedure:
-
Click Objects menu > More object types > Network Object > Dynamic Object > New Dynamic Object.
-
Enter this exact name (case-sensitive, no spaces):
LocalGatewayExternal
-
Click OK.
-
Click Objects menu > More object types > Network Object > Dynamic Object > New Dynamic Object.
-
Enter this exact name (case-sensitive, no spaces):
LocalGatewayInternal
-
Click OK.
-
Publish the SmartConsole session.
|
|
Note - The NVA instances IP addresses are automatically associated with the LocalGatewayInternal and LocalGatewayExternal objects. |
Creating Manual NAT Rules
Add these two manual NAT rules to the Access Policy:
-
No NAT for internal communication:
Source
Destination
Port
Xlate Source
Xlate Destination
Xlate Port
Internal Networks Group
Internal Networks Group
Any
Original
Original
Original
-
For Internet access, Hide NAT to external interface:
Source
Destination
Port
Xlate Source
Xlate Destination
Xlate Port
Internal Networks Group
All Internet
Any
LocalGatewayExternal
Original
Original
-
Publish the SmartConsole session.
Step 9: Configure Ingress traffic
Prerequisites:
-
Generate a public IP address with the standard SKU (in the same region as the NVA in the Azure portal).
-
A deployed NVA with attached public IP.
-
NVA instances are configured (See Step 5).
-
See the CME API requirements in the Cloud Management Extension Administration Guide > Azure Virtual WAN.
-
The Security Gateway image version must be at minimum 8120.900631.1522 for R81.20 and 8110.900335.1522 for R81.10.
Configuring rules for ingress traffic
We recommend using CME API to configure ingress rules. For detailed information about configuring ingress rules in Azure vWAN NVA, refer to the Cloud Management Extension Administration Guide > Azure Virtual WAN > Configure Ingress Rules for NVA with CME API.
API Documentation:
-
SwaggerHub: Azure Virtual WAN
-
Postman Collection: CME API Postman collection
To configure ingress rules with the CME API:
Send a POST request:
POST https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/v1.8/cme-api/v1.2.1/azure/virtualWANs/accounts/<account_id>/resourceGroups/<nva_resource_group>/inboundRules/<nva_name>
Required parameters:
-
account_id: Your Azure account name from the CME configuration file.
-
nva_resource_group: The resource group containing your NVA.
-
nva_name: Your NVA's name.
Rule parameters:
-
name: Unique rule
 Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. identifier.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. identifier. -
original_source: Where traffic comes from (IP address).
-
lb_public_ips: Load Balancer public IP addresses attached to the NVA.
-
original_ports: Ports to accept traffic on.
-
protocol: TCP or UDP.
|
|
Notes - This API:
|
This asynchronous operation returns a request_id to track progress.
You check progress using a separate GET request:
GET https://<Management_IP_address>/web_api/cme-api/status/<request_id>
To enable ingress traffic, in addition to the rules on the Azure side created with CME API, you also need to add manually the corresponding access and NAT rules on the Security Management Server.
Attach or detach additional existing public IP addresses to the Network Virtual Appliance (NVA) SLB:
-
Log in to Azure Portal.
-
Enter your virtual WAN and navigate to your Hub.
-
On the left tree, click Network Virtual Appliance.
-
Select the applicable NVA and, below NVA Configuration, click Manage Configuration.
-
On the left tree, click Internet Inbound.
-
Click the Add or Delete button on the top left.
-
For adding IP address only:
-
Select the resource group where you created the public IP address and the public IP address name and click Save.
-
After the process is complete, make sure that the NVA provisioning state is Succeeded.
-
To configure ingress rules with cme_menu:
-
Connect to the command line on the Security Management Server.
-
Log in to the Expert mode.
-
Run the command:
cme_menu. -
Enter the requested parameters.
-
Use the Ingress Menu to add, edit, and delete rules.
For details regarding the cme_menu, refer to the Cloud Management Extension Administration Guide > Azure Virtual WAN.