2013 CHECK POINT ANNUAL SECURITY REPORT
02
_ THREATS TO YOUR ORGANIZATION
012
There are multiple entry points to breach an organization’s
network defenses: browser-based vulnerabilities, mobile
phones, malicious attachments and removable media, to
name a few. In addition, the rapid proliferation of Web
2.0 applications and social networks used as business tools
present hackers with vast new opportunities to lure victims
to click on malicious links or “malvertisements“ (i.e.
malicious advertisements running on legitimate websites).
Although botnets are considered to be one of the most
prominent network security threats today, organizations
are also facing additional security threats from damaging
malware such as viruses, worms, spyware, adware, trojans,
etc. Our research shows that in 75% of the organizations we
scanned, a host accessed a malicious website.
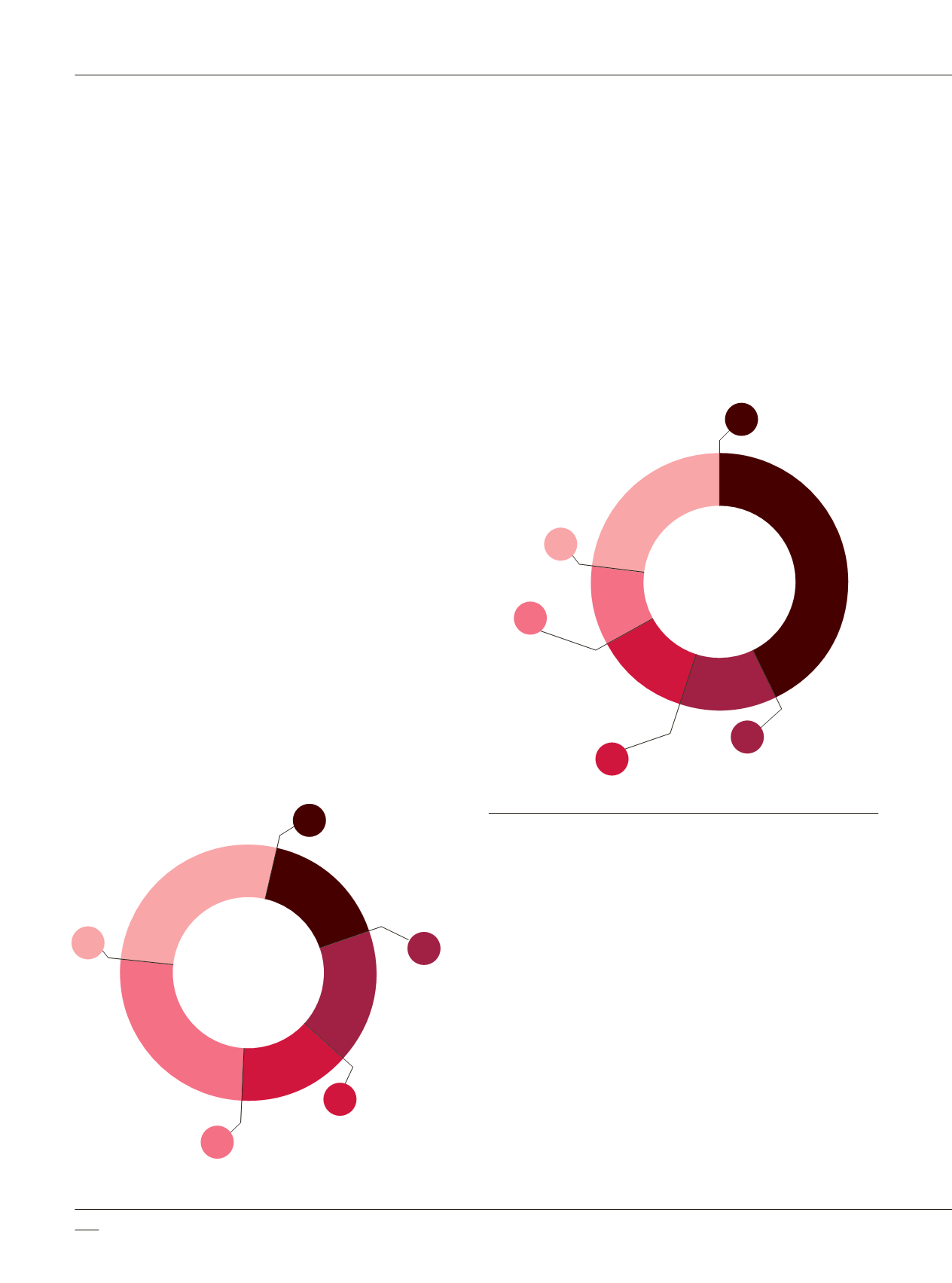
Chart 2-D presents the number of hosts that accessed
a malicious website by the percentage of organizations.
In over 50% of the test organizations, at least five hosts
accessed a malicious website.
A malware can be downloaded by a user or by a bot located
in an infected host. We found that in 53% of the researched
18
%
3-4 hosts
31
%
1-2 hosts
16
%
9-16 hosts
15
%
More than 16 hosts
20
%
5-8 hosts
Access to Malicious Sites by Number of Hosts
(% of Organizations)
organizations, a malware was downloaded from the
corporate network. Of these organizations, over 50% had
more than four hosts which have downloaded malware.
Chart 2-E below presents the average frequency of malware
downloads in the organizations we researched.
Chart 2-G presents the number of hosts that downloaded
a malware. In more than 50% of the scanned organizations,
Malware Download Frequency
(% of Organizations)
43
%
More than a day
14
%
Up to 2 hours
19
%
2-6 hours
12
%
6-12 hours
12
%
12-24 hours
EVERY 23 MINUTES
A HOST ACCESSES A
MALICIOUS WEBSITE
at least five hosts downloaded a malware.
Our findings reveal that the majority of malware was found
in the USA, followed by Canada and the United Kingdom
as shown in Chart 2-F.
Anti-virus protection is one method to effectively protect
against malware infections. However, our research shows
that 23% of hosts in organizations did not update their
anti-virus software on a daily basis. Hosts not running the
latest anti-virus software are susceptible to attacks by the
newest viruses. We also found that 14% of hosts in test
organizations did not even have anti-virus software installed
on their computers. These host computers are in extreme
high risk of being infected with a malware.
Chart 2-D
Chart 2-E
Source: Check Point Software Technologies
Source: Check Point Software Technologies


