Introduction to Quantum Security Management
Check Point offers effective Security Management solutions to help you keep up with constantly growing needs and challenges of your organizational network. This Administration Guide focuses on the basic Security Management Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. deployment.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. deployment.
If you are interested in deployments for organizations with multiple sites, refer to the R82 Multi-Domain Security Management Administration Guide.
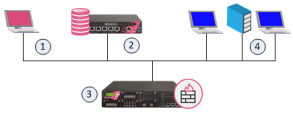
These are the basic components of Check Point security architecture.
Workflow for Configuring Security Management
-
Connect with SmartConsole to the Security Management Server.
See Connecting to the Security Management Server with SmartConsole.
-
Configure the Security Management Server and Security Gateways in your environment.
See Configuring the Security Management Server and Security Gateways.
-
Define the administrators of your environment.
-
Assign permissions to the administrators of your environment.
-
Define users and user groups that your security environment protects.
-
Configure the physical and virtual network components in your environment.
See Managing Objects
-
Configure access rules that govern the protection of your organization's resources.
-
Install the Security Policy.