Introduction to SIP
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is transported over UDP and TCP. It is an Application Layer control protocol that creates, modifies, and terminates sessions with one or more participants. SIP is a peer-to-peer protocol.
SIP uses design elements similar to the HTTP request/response transaction model. SIP clients usually use TCP or UDP on port numbers 5060 or 5061 to connect to SIP servers and other SIP endpoints. Port 5060 is commonly used for non-encrypted signaling traffic, whereas port 5061 is typically used for traffic encrypted with Transport Layer Security (TLS).
To configure your environment with SIP in SmartConsole![]() Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on.:
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on.:
-
For NAT rules, see Setting Up Your Network with Network Address Translation (NAT).
-
For examples of Rule Base
 All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase. configuration, see Important Information About Creating SIP Security Rules.
All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase. configuration, see Important Information About Creating SIP Security Rules.
For important information about SIP, refer to the other topics in this chapter and to sk95369.
Basic SIP Configuration
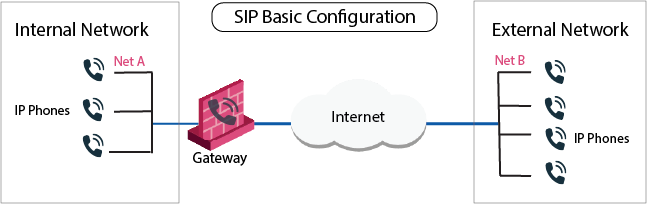
In a basic SIP configuration, a Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. sits between an Internal Network
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. sits between an Internal Network![]() Computers and resources protected by the Firewall and accessed by authenticated users. and an External Network, with or without a proxy.
Computers and resources protected by the Firewall and accessed by authenticated users. and an External Network, with or without a proxy.