Important Information about Creating H.323 Security Rules
|
|
Best Practice - Configure Anti-Spoofing on the interfaces of the Check Point Security Gateway |
-
To allow H.323 traffic, create rules that let H.323 control signals through the Security Gateway.
It is not necessary to Configure a rule
 Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. that specifies which port to open and which endpoint can talk. The Security Gateway automatically gets this information from the signaling. For a given H.323 signaling rule (with RAS and/or H.323 services), the Security Gateway automatically opens ports for the H.245 connections and RTP/RTCP media stream connections.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. that specifies which port to open and which endpoint can talk. The Security Gateway automatically gets this information from the signaling. For a given H.323 signaling rule (with RAS and/or H.323 services), the Security Gateway automatically opens ports for the H.245 connections and RTP/RTCP media stream connections. -
Dynamic ports will only be opened if the port is not used by a different service. This prevents well-known ports from being used illegally.
For example, if the Connect message identifies port 80 as the H.245 port, the port will not be opened.
-
To allow H.323 traffic in the Security Rule Base
 All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase., use regular Network Objects. It is not necessary to configure special Network Objects.
All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase., use regular Network Objects. It is not necessary to configure special Network Objects. -
When you use Hide NAT for H.323, include the hidden IP address in the destination of the H.323 rule. When you include the hidden IP address, this allows the initiation of the TCP handshake from the external network to the hidden IP.
-
Make sure to configure Keep all connections on the Security Gateway. Otherwise, it drops your connection every time you install the policy.
-
Double-click your Security Gateway object.
-
From the left tree, click Other > Connection Persistence.
-
Select Keep all connections.
-
Click OK.
-
Note - The old policy rules are still intact for calls already in-progress and they will not be dropped.
Sample H.323 Rules for an Endpoint-to-Endpoint Topology
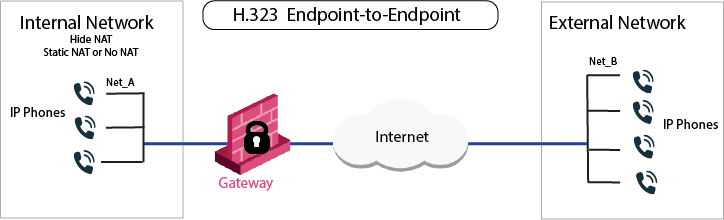
The IP Phones communicate directly, without a Gatekeeper or an H.323 gateway. Static NAT can be configured for the phones on the internal side of the Security Gateway.
An endpoint-to-endpoint topology is shown in the image, with Net_A and Net_B on opposite sides of the Security Gateway.
This procedure explains:
-
How to allow bidirectional calls between the phones in the internal network (Net_A) and phones in an external network (Net_B)
-
How to Configure NAT for the internal phone
No incoming calls can be made when Hide NAT is configured for the internal phones.
VoIP rule for this scenario:
|
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Net_A Net_B |
Net_B Net_A |
H323 |
Accept |
To Configure an H.323 rule for endpoint-to-endpoint topology:
-
Configure an Access Control rule that allows IP phones in Net_A or Net_B to call each other.
-
Select the applicable service.
-
Configure the VoIP rule.
-
Configure Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network.
-
Do this by editing the Network Object
 Logical object that represents different parts of corporate topology - computers, IP addresses, traffic protocols, and so on. Administrators use these objects in Security Policies. for the internal network (Net_A).
Logical object that represents different parts of corporate topology - computers, IP addresses, traffic protocols, and so on. Administrators use these objects in Security Policies. for the internal network (Net_A).See Setting Up Your Network with Network Address Translation (NAT).
-
Install the Security Policy.
Sample H.323 Rules for a Gatekeeper-to-Gatekeeper (or H.323 Gateway) Topology
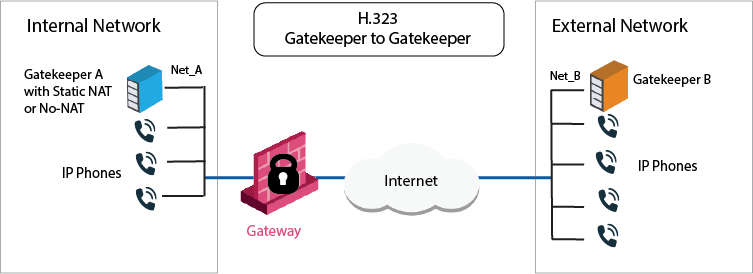
Each Gatekeeper or H.323 gateway controls a separate endpoint domain. Static NAT can be configured for the Internal Gatekeeper. For the internal phones, Hide NAT or Static NAT can be configured.
The illustration shows a Gatekeeper-to-Gatekeeper or Gateway topology, with Net_A and Net_B on opposite sides of the Security Gateway.
This procedure shows you how to:
-
Allow bidirectional calls between phones in the internal network (Net_A), and phones in an external network (Net_B)
-
Define NAT for the internal phones and the internal Security Gateway (GW_A) or Gatekeeper (GK_A).
VoIP Access Control rule for this scenario
|
Source |
Destination |
Service |
Action |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GK_A GK_B GW_A GW_B |
GK_B GK_A GW_B GW_A |
H323 H323_ras |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls |
To define an H.323 rule for Gatekeeper-to-Gatekeeper topology:
-
Define an Access Control rule that allows IP phones in Net_A to call Net_B and the reverse.
-
Define the Network Objects for the Security Gateway objects (GW_A and GW_B)
OR
-
Define the Network Object for the Gatekeeper objects (GK_A and GK_B).
-
Define the VoIP rule.
-
Configure Static NAT for the Internal Gatekeeper.
-
Define Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network.
Do this by editing the Network Object for the internal network (Net_A).
See Setting Up Your Network with Network Address Translation (NAT).
-
Install the Security Policy.
Sample H.323 Rules for a Gatekeeper (or H.323 Gateway) in an External Network
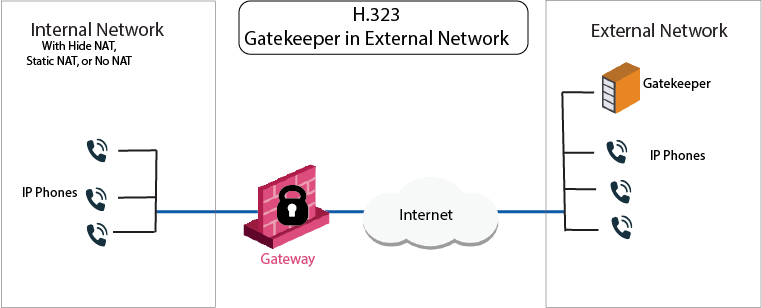
The IP phones use the services of a Gatekeeper or H.323 gateway on the external side of the Security Gateway. This topology enables the use of the services of a Gatekeeper or an H.323 gateway that is maintained by another organization. It is possible to configure Hide NAT or Static NAT (or No-NAT) for the phones on the internal side of the Security Gateway.
The image shows a topology with an H.323 Gateway, with Net_A and Net_B on opposite sides of the Security Gateway.
This procedure shows you how to:
-
Allow bidirectional calls between the phones in the internal network (Net_A) and phones in an external network (Net_B)
-
Configure NAT for the internal phones
VoIP Access Control rule for this scenario:
|
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Action |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Net_A Net_B GK_B |
GK_B Net_A |
H323_ras |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls. |
To configure an H.323 rule for a Gatekeeper in the external network:
-
Configure the Network Objects. In the image, these are Net_A and Net_B.
-
Configure the Network Object for the Gatekeeper (GK_B) or Security Gateway (GW_B).
-
Configure the VoIP rule.
-
Configure Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network.
Do this by editing the Network Object for the internal network (Net_A).
See Setting Up Your Network with Network Address Translation (NAT).
-
Install the Security Policy.
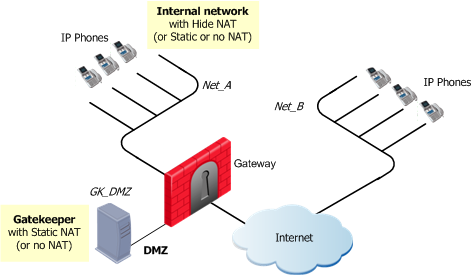
Defining H.323 Rules for a Gatekeeper in DMZ Topology
The image shows an H.323-based VoIP topology where a Gatekeeper is installed in the DMZ. This procedure explains how to:
-
Allow bidirectional calls between the phones in the internal network (Net_A) and phones in an external network (Net_B)
-
Define NAT for the internal phones and the Gatekeeper in the DMZ (GK_DMZ)
VoIP rule for this scenario:
|
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Action |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GK_DMZ Net_A Net_B |
Net_A Net_B GK_DMZ |
H323 H323_ras |
Accept |
Bidirectional calls. |
Static NAT rules for the Gatekeeper in the DMZ:
|
Original |
Translated |
Comments
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
Source |
Destination |
Services & Applications |
|
|
GK_DMZ |
Net_B |
*Any |
GK_DMZ: |
= |
= |
Outgoing calls |
|
Net_B |
GK_DMZ_NATed |
*Any |
= |
GK_DMZ: |
= |
Incoming calls |
To define an H.323 rule for a Gatekeeper in the DMZ:
-
Define the network objects (nodes or networks) for the phones that:
-
Use the Gatekeeper for registration
-
Are allowed to make calls, and their calls tracked by the Security Gateway
In the image, these are Net_A and Net_B.
-
-
Define the network object for the Gatekeeper (GK_DMZ).
-
Configure the VoIP rule.
To define Hide NAT or Static NAT for the phones in the internal network, edit the network object for Net_A.
-
Select NAT > Advanced.
-
Check the box Add automatic address translation rules to hide this Gateway behind another Gateway.
-
Select the Translation method, Hide, or Static.
If you select Hide NAT:
-
Create a node object with the Hide NAT IP address
-
Select the Security Policies tab.
-
Add the service to the Services & Applications column.
-
Add the node object to the Destination of the rule.
-
-
-
Define Static NAT for the Gatekeeper in the DMZ:
-
Create a Node object for the Static address of the Gatekeeper (for example: GK_DMZ_NATed).
-
Define the manual Static NAT rules.
-
Configure proxy-ARPs.
You must associate the translated IP address with the MAC address of the Security Gateway interface that is on the same network as the translated addresses.
See sk30197.
-
-
Make the time-out of the
H323_rasservice greater or equal to the Gatekeeper registration time-out.-
In the Manage & Settings tab, go to Blades > General, select Inspection Settings.
The Inspection Settings window opens.
-
From the General tab, in the search window, enter H.323.
-
The H.323 - General Settings window shows. Double-click the service. A window opens.
-
Configure the Timeouts
-
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Security Policy.

