Security Management behind NAT
Overview
|
|
Note - Security Management Server |
The Security Management Server sometimes uses a private IP address (as listed in RFC 1918), or some other non-routable IP address, because of the lack of public IP addresses.
NAT (Static or Hide) for the Security Management Server IP address can be configured in one click, while still allowing connectivity with managed Security Gateways. All Security Gateways can be controlled from the Security Management Server, and logs can be sent to the Security Management Server. NAT can also be configured for a Management High Availability![]() Deployment and configuration mode of two Check Point Management Servers, in which they automatically synchronize the management databases with each other. In this mode, one Management Server is Active, and the other is Standby. Acronyms: Management HA, MGMT HA. server and a Log Server
Deployment and configuration mode of two Check Point Management Servers, in which they automatically synchronize the management databases with each other. In this mode, one Management Server is Active, and the other is Standby. Acronyms: Management HA, MGMT HA. server and a Log Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to store and process logs..
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to store and process logs..
Example:
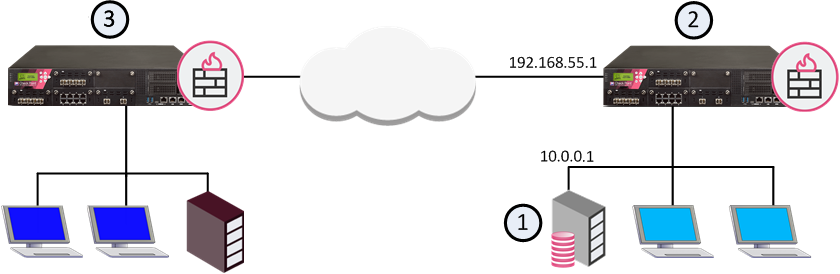
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Primary Security Management Server.
|
|
2 |
Local Security Gateway that is directly connected to the Security Management Server. The Remote Security Gateway connects to the Security Management Server through this Local Security Gateway. |
|
3 |
Remote Security Gateway that must connect to the Security Management Server. |
Configuring NAT for Control Connections on the Security Management Server
-
From the left navigation panel, click Gateways & Servers.
-
Double-click the Security Management Server object.
-
From the left, click NAT.
-
Select Add Automatic Address Translation rules.
-
In the Translation method field, select Static.
-
Configure the applicable IP address.
In our example - 192.168.55.1

Note - In a High Availability environment, you must configure one static IP address for each Security Management Server.
-
Select the Security Gateway that must perform this NAT.
In our example - the local Security Gateway that is directly connected to the Security Management Server.
-
Select Apply for Security Gateway control connections.
-
Click OK.
-
Install the Access Control Policy on the applicable Security Gateways.
Configuring NAT for Control Connections on a Remote Security Gateway
Possible cases when a Security Management Server is located behind NAT:
-
A remote Security Gateway has to connect to the Security Management Server at its real (internal) IP address.
-
A remote Security Gateway has to connect to the Security Management Server at its NATed (external) IP address.
To allow such connections from a remote Security Gateway, configure the required IP address in the applicable configuration file on the remote Security Gateway:
-
Configure NAT for Control Connections on the Security Management Server as described above.
-
Configure the Security Management Server not to override the
$FWDIR/conf/mastersfile on the remote Security Gateway / Cluster Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. Members.
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. Members. Procedure
Procedure
-
Close all SmartConsole
 Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. windows connected to the Security Management Server.
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. windows connected to the Security Management Server. -
Connect with Database Tool (GuiDBEdit Tool) (see sk13009) to the applicable Security Management Server or Domain Management Server.
-
In the top left section, click Table > Network Objects.
-
In the top right section, click network_objects.
-
In the right upper pane, select the object of the remote Security Gateway / Cluster.
-
Press CTRL+F (or go to Search menu > Find) > paste define_logging_servers > click Find Next.
-
In the lower pane, right-click the define_logging_servers > select Edit > select "false" > click OK.
-
Save the changes (click File > Save All).
-
Close the Database Tool (GuiDBEdit Tool).
-
-
Configure the required IP address in the
$FWDIR/conf/mastersfile on the remote Security Gateway / Cluster Members. Procedure
Procedure

Note - In a Cluster, you must configure all the Cluster Members in the same way.
-
Connect to the command line on the Security Gateway / each Cluster Member
 Security Gateway that is part of a cluster..
Security Gateway that is part of a cluster.. -
Log in to the Expert mode.
-
Back up the current file:
cp -v $FWDIR/conf/masters{,_BKP} -
Edit the current file:
vi $FWDIR/conf/masters -
In the [Policy] section and in the [Log Server] section, add a new line above the current line.
In the new line, enter the NATed (external) IP address of the Security Management Server.

Important - If the remote Security Gateway has to connect to the real IP address of the Security Management Server, you must also configure the SIC
 Secure Internal Communication. The Check Point proprietary mechanism with which Check Point computers that run Check Point software authenticate each other over SSL, for secure communication. This authentication is based on the certificates issued by the ICA on a Check Point Management Server. name of the Security Management Server.
Secure Internal Communication. The Check Point proprietary mechanism with which Check Point computers that run Check Point software authenticate each other over SSL, for secure communication. This authentication is based on the certificates issued by the ICA on a Check Point Management Server. name of the Security Management Server.Copy it from the existing line:
CN=cp_mgmt,O=<xxx>.checkpoint.com.<yyy> -
Save the changes in the file and exit the editor.
-
-
 Procedure
Procedure
-
Connect with the SmartConsole to the Security Management Server.
-
Install the Access Control Policy on the remote Security Gateway / Cluster.
-
|
|
Notes:
|
