Introduction to QoS
The Check Point QoS Solution
QoS![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides policy-based traffic bandwidth management to prioritize business-critical traffic and guarantee bandwidth and control latency. is a policy based bandwidth management solution that lets you:
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides policy-based traffic bandwidth management to prioritize business-critical traffic and guarantee bandwidth and control latency. is a policy based bandwidth management solution that lets you:
-
Prioritize business-critical traffic, such as ERP, database and Web services traffic, over lower priority traffic.
-
Guarantee bandwidth and control latency for streaming applications, such as Voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing.
-
Give guaranteed or priority access to specified employees, even if they are remotely accessing network resources.
You deploy QoS with the Security Gateway.
QoS is enabled for both encrypted and unencrypted traffic.
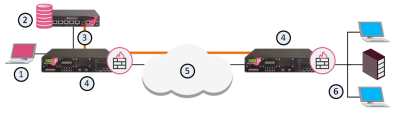
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
QoS Policy |
|
4 |
|
|
5 |
Internet |
|
6 |
Internal network |
QoS leverages the industry's most advanced traffic inspection and bandwidth control technologies. Check Point patented Stateful Inspection technology captures and dynamically updates detailed state information on all network traffic. This state information is used to classify traffic by service or application. After traffic has been classified, QoS applies an innovative, hierarchical, Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ![]() Weighted Fair Queuing. An algorithm to precisely control bandwidth allocation in QoS.) algorithm to accurately control bandwidth allocation.
Weighted Fair Queuing. An algorithm to precisely control bandwidth allocation in QoS.) algorithm to accurately control bandwidth allocation.
|
|
Note - When the QoS Software Blade is disabled, the Security Gateway does not modify DSCP bits in packets that pass through. |
Features and Benefits
QoS gives these features and benefits:
-
Flexible QoS policies with weights, limits and guarantees
QoS lets you create basic policies that can be modified to include the Advanced QoS features described in this section.
-
Integration with the Security Gateway
The integration of an organization's security and bandwidth management policies enables easier policy definition and system configuration. This lets you optimize network performance for VPN and unencrypted traffic.
-
Performance analysis
Monitor system performance with the Logs & Monitor view in SmartConsole.
-
Integrated DiffServ support
Add one or more Diffserv Classes of Service to the QoS Policy Rule Base
 All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase..
All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase.. -
Integrated Low Latency Queuing
Define special classes of service for "delay sensitive" applications like voice and video to the QoS Policy Rule
 Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. Base.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. Base. -
No need to deploy separate VPN, Firewall and QoS devices
QoS and Firewall share a common architecture and many core technology components. User-defined network objects can be used in both solutions.
-
Proactive management of network costs
QoS monitoring systems let you to be proactive in managing your network and controlling network costs.
-
Support for end-to-end QoS for IP networks
QoS offers full support for end-to-end QoS for IP networks by distributing enforcement throughout network hardware and software.
-
CoreXL and SecureXL support
Packet acceleration. IPv6 Support.
-
VSX Support
QoS fully supports VSX.
QoS Policy Types
This release includes two QoS Policy types:
-
Express - Quickly create basic QoS Policies
-
Recommended - Create advanced Policies with the full set of QoS features
This table shows the difference between the Recommended and Express policy types.
|
Features |
Recommended |
Express |
To learn more |
|---|---|---|---|
|
IPv6 Support |
|
|
|
|
Weights |
|
|
|
|
Limits (whole rule) |
|
|
|
|
Logging |
|
|
|
|
Accounting |
|
|
|
|
Support for hardware acceleration |
|
|
|
|
High Availability and Load Sharing |
|
|
|
|
Guarantees |
|
|
|
|
Limits (Per connection) |
|
|
|
|
LLQ |
|
|
|
|
DiffServ |
|
|
|
|
Sub-rules |
|
|
|
|
Matching by URI resources |
|
|
|
|
Matching by DNS string |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SmartLSM clusters |
|
|
|
|
VSX Support |
|
|
|
If you select Paste, then the Paste menu will be opened. You must then select Bottom, Top, Above, or Below to specify where in the Rule Base to paste the rule.
* You must disable SecureXL and CoreXL before you can use this feature.
To select a QoS Policy type:
-
In SmartConsole menu, click Manage policies and layers.
-
In the Manage Policies window, click New or select an existing Policy and then click Edit.
-
Select QoS, and then select Recommended or Express.
Acceleration Support for R77 Policies
After a clean install or upgrade to R81.10, QoS supports SecureXL and CoreXL acceleration technologies.
Important: After a clean install or upgrade, SecureXL and CoreXL are enabled by default. If you have a QoS policy created for R77 and earlier, these features are not supported when acceleration is enabled:
-
IPSO
-
Security Gateways below R77.10
-
SmartView Monitor - QoS views do not correctly show traffic accelerated by SecureXL
To use these features you must disable QoS. See: Disabling QoS Acceleration Support
Workflow
This topic shows a high-level workflow for creating an effective QoS Policy.
|
|
Note: QoS must be enabled on the gateway and at least one interface for the workflow to succeed. If QoS is not enabled on at least one interface, Install Policy will fail. |
Do these steps in SmartConsole:
-
Enable QoS for each applicable Security Gateway.
-
Configure QoS Global Properties.
-
Create or change a QoS Policy.
-
Configure log collection and system monitoring for QoS.
-
Publish the SmartConsole session.
Do these steps in SmartDashboard:
-
Define the gateway networks, services and other related objects.
-
Define QoS rules (basic and advanced).
-
Configure specialized QoS features.
-
Differentiated Services (DiffServ).
-
Low Latency Queuing.
-
Go back to SmartConsole to do these steps:
-
Publish the SmartConsole session.
-
Install Policy.

Note - In the SmartConsole Install Policy window, make sure you select QoS.
Limitations
These limitations apply to Scalable Platforms:
-
QoS is not supported when a Security Group is configured in the Layer 4 distribution mode.
-
QoS policy is applied on each Security Group Member.
-
QoS is not supported on a Security Group in the VSX mode.