

In This Section: |
ACI supports physical and virtual L4-L7 devices.
For physical devices, use Check Point Appliances. To more information and to verify appliance compatibility, see the R80 vSEC for Cisco ACI Release Notes.
For virtual devices, use Check Point vSEC virtual edition for VMware. For more information, see sk104859.
In the vSEC for ACI model, the L4-L7 devices are mapped to VSX Security Gateways that serve as concrete devices.
When you do the service insertion, the Cisco APIC server supports and provisions virtual systems. See Basic Service Insertion Overview.
To deploy the vSEC Gateway (virtual devices):
These ports are allowed by intermediate devices which inspect the management connections. For more information, see sk52421.
Notes:
To deploy the vSEC Gateway (physical devices):
These ports are allowed by intermediate devices which inspect the management connections. For more information, see sk52421.
$FWDIR/modules/fwkern.conf fwha_enable_arp_resend = 0 Notes:
Install the vSEC Controller Enforcer Hotfix on R77.30 Security Gateways with CPUSE, online or offline.
To install the Hotfix on R77.30 Security Gateways with CPUSE online:
The online installation starts immediately. The gateway reboots when installation is complete.
To install the Hotfix on R77.30 Security Gateways with CPUSE offline:
See Section 3 to find the latest CPUSE build, and Section 4-A to download and import a CPUSE package.
The Import Package window opens.
The offline installation starts immediately. The gateway reboots when installation is complete.
vSEC for ACI solution supports L2 (GoThrough, transparent), and L3 (GoTo, routed) service function modes.
Before you start the deployment, we recommend that you designate the application profiles, network paths, and contracts that require security service, and determine the optimal insertion method. These considerations are specified in the vSEC for ACI TDM document.
ACI deployment topology example:
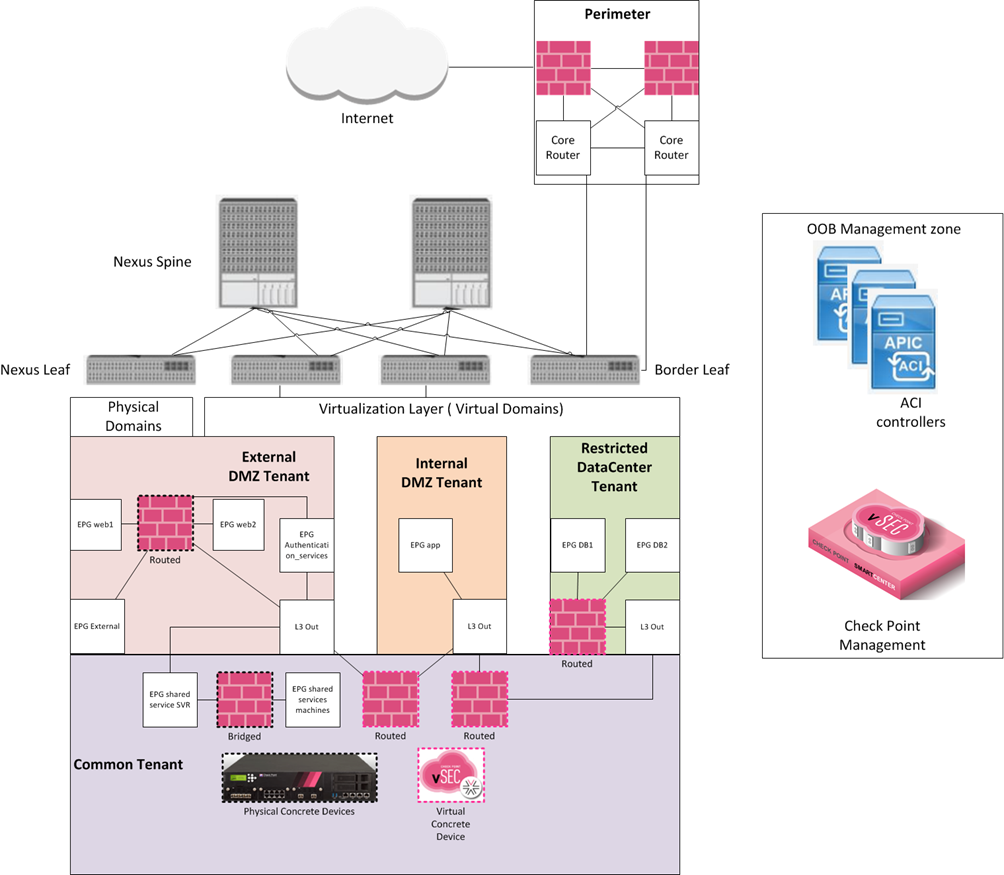
To insert a service installation into the ACI fabric (best practice):
The APIC service insertion process uses the policy package as the Security Policy Name parameter.
You must install the vSEC device package on Cisco APICs to enable the insertion of managed L4-L7 Check Point devices. The vSEC device package is compatible with APIC from version 1.2.
You can manually upload the vSEC device package into the Cisco APIC. See the Cisco Administration Guide, Installing Device Packages. You can do this automatically with the vsec_config
To configure a device package username and password:
vsec_config vsec_configTo automatically upload a device package:
Note - To upload the device package directly from the Check Point Security Management Server, verify that the credentials used to integrate vSEC controller with Cisco APIC allow device package upload.
To learn more, see the vSEC Controller R80 Administration Guide.
vsec_configIf more than one Cisco APIC data center object exists, select the Data Center Server which represents the specified Cisco APIC server.
In Multi Domain deployment, use the domain context to upload the package.
Notes:
vsec_configWhen you configure a new device, it must be part of a domain that assigns dynamic VLANs.
Note - When you change the password for a device, the password for the concrete device under the main device does not change automatically.
To add an L4-L7 device:
General |
|
Managed |
Make sure this option is selected. |
Name |
Use the exact VSX object name which you created in SmartConsole. |
Service Type |
Select Firewall. |
Device Type |
Select PHYSICAL for a Check Point appliance or VIRTUAL for vSEC virtual edition. |
Domain |
Select the physical or VMM domain where the VSX gateway is deployed. |
Mode |
Select Single node for single VSX gateway. Select HA cluster for VSX cluster based solution. |
Device Package |
Select gateway Device Package from the drop down list. |
Model |
Select the relevant model for all Check Point appliances:
|
Function Type |
Select GoTo for routed (L3) mode use case. Select GoThrough for transparent (L2) mode use case. |
Connectivity |
|
APIC to Device Management Connectivity |
Configure according to environment design. Check Point recommends you use Out Of Band connectivity for management connections. |
Credentials |
|
Username |
Enter the username provided in |
Password |
Enter the password provided in |
Device 1 (and Device 2 when High Availability cluster is selected) |
|
Management IP address |
Enter the IP address of the Check Point Security Management Server. For management HA, use the primary server IP address. |
Management Port |
Select https. |
VM (relevant to 'VIRTUAL ' device type only) |
Select the vSEC Virtual Edition VM used to inspect the traffic. |
Chassis |
(leave blank) |
Device Interfaces |
Physical domain:
Virtual domain:
|
Cluster |
|
Management IP address |
Enter the Check Point Security Management Server IP address. For Management High Availability, use the primary server IP address. |
Management Port |
Select https. |
Device Manager |
For Management High Availability, select the device manager configured. For more information, see Configuring Management HA Integration. For others, leave blank. |
Cluster Interfaces |
Physical device:
Virtual device:
|
To create an L4-L7 Service Graph template:
Property |
Action |
|---|---|
Graph Name |
Enter the graph name. |
Graph Type |
Select the graph creation options:
When Clone An Existing One is selected, enter the graph template if you select clone. |
Type |
Select the graph type based on the design considerations:
|
Profile |
Select the default profile provided. |
When you apply a service graph describing a Check Point L4-L7 device insertion, a Virtual System is created automatically or an existing Virtual System is added with interfaces and routes based on the configured parameters.
For a directly connected (General) insertion, any new interface configured for the device (that connects it to the bridge domain that contains the EPG) is automatically added to the Virtual System.
Note - Directly connected (L2 adjacency) insertion requires enabling ARP Flooding on the Bridge Domains connected to the L4-L7 Device.
To apply the service graph to a contract:
EPGs and Contract Information
Property |
Action |
|
|---|---|---|
EPGs Information |
||
Consumer EPG/External Network |
Select the consumer EPG name or the external network name. |
|
Provider EPG/External Network |
Select the provider EPG name or external network name. |
|
Contract Information |
||
Contract |
Select one of these options:
|
|
Contract Name (new contract only) |
Enter the contract name. |
|
No Filter (new contract only) |
If No Filter is selected, the contract applies to all traffic types and security is enforced only based on the Check Point security policy installed on the device. If No Filter is unchecked, the Filter Entries table opens and shows the ACI filters you can add before Check Point inspection. |
|
Existing Contracts with Subject |
The contract subject name. |
|
Consumer, Provider, and Route Configurations
Property |
Action |
|---|---|
Graph Template |
Verify the graph template name. |
Consumer Connector |
General – Used to configure a directly connected (L2 adjacency) service insertion. In this mode, the routed or transparent service interface is connected directly to BD that contains the protected EPG. In General mode, configure the Broadcast domain that is connected to the device on the consumer interface, and select Cluster Interface consumer. Virtual Deployment - Select the corresponding interface name. Route Peering – Used to configure route peering (L3 out) service insertion. In this mode, the device learns networks through static or dynamic routing, and traffic is steered to the device through the external L3 network. In Route Peering mode, you configure the L3 external network connected to the device on the consumer interface, and select Cluster Interface consumer. |
Provider Connector |
General – Used to configure a directly connected (L2 adjacency) service insertion. In this mode, the routed or transparent service interface is connected directly to BD that contains the protected EPG. In General mode, configure the BD connected to the device on the provider interface and select Cluster Interface provider. Virtual Deployment - Select the corresponding interface name. Route Peering – Used to configure route peering (L3 out) service insertion. In this mode, the device learns networks through static or dynamic routing and traffic is steered to the device through the external L3 network. In Route Peering mode, configure the L3 external network connected to the device on the provider interface and select Cluster Interface provider. |
Routing Config (Route Peering only) |
Select:
|
Device Parameters
Parameter |
Function |
|---|---|
Consumer Facing Address |
Configures the network interfaces IP address and prefix for the consumer and provider interfaces. Use this format: X.X.X.X/mask-length, for example: 192.168.1.1/24 |
Provider Facing Address |
|
Instance Name |
Used for instantiation of a new VS on the VSX gateway. For an instance that runs the required policy already exists on the device, the existing instance is modified, and a new instance is not created. If you specify a different name, it forces a new VS instance (the default is empty – meaning according to APIC logic). |
Security Domain |
Required for Multi Domain Management deployment (the default is no MDM). Specifies the domain server name that contains the device. |
Security Policy Name |
Determines the policy package that is installed on the security instance. The policy package must exist on the Security Management Server. |
Route Entry |
Static routes are added to the VS routing table. Multiple routing entries may be added. Static route entries include:
|
To configure Management High Availability integration, you must create a Device Manager.
To configure Management High Availability integration:
vsec_configNote - Only Management High Availability with two devices is supported.
Note - The Management IP address defined in Adding an L4-L7 Device is treated as the primary management.
The Cisco ACI solution is VSX based.
You can select the domain that holds and manages the VS.
You must configure the domain in the Service Parameters to integrate the solution with Check Point Multi-Domain Server.
To configure the domain in the Service Parameters:
Note - The domain name is part of the VS object name that is provisioned by the APIC.
Before you remove a tenant, we recommend that you remove all service graphs from the contracts. APIC removes tenants by best effort, which can leave configuration and constructs in the tenant (such as service graphs), that you would have removed.
When you remove a service graph used to insert a Check Point device, interfaces and routes configured by APIC on the inserted Virtual System are also removed. When you remove all service graphs attachments that render a specific Virtual System, that Virtual System is also removed entirely, including from the Security Management Server.
To remove Service Insertion:
To remove L4-L7 managed devices:
Note - Make sure that there are no entries that are related to the L4-L7 device you want to remove in the Deployed Devices section and in the Deployed Graph Instances sections.
You can view reported faults from Check Point vSEC for ACI solution on the APIC Server Web UI.
The faults show on:
To view these faults, select the designated tenant > L4-L7 Services > L4-L7 Devices, and select the L4-L7 device.
To view these faults, select the designated tenant > L4-L7 Services > Deployed Devices, and select the L4-L7 device instance.
To make sure the L4-L7 vSEC service insertion provisioning works properly, there must always be communication between the APIC and the Management and between the Management and the Gateways.
Before you start the troubleshooting process:
These are the main faults that can occur when you do the L4-L7 vSEC service insertion:
Message |
Fault meaning |
Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
|
You try to send an empty user or password in the L4-L7 Device (often, this is an error with an APIC API). |
Make sure the username and password fields are not empty. |
|
One of these happened:
|
Make sure the APIC CLI can ping the device. |
|
There was a problem when you try to retrieve the device information from Check Point Security Management Server. |
Make sure the Security Management Server is up and running. |
|
The device name (VSX object name) is not defined on Check Point Security Management Server. |
Use SmartConsole to verify the VSX device configuration. Make sure the device name on the APIC matches the name of the VSX on SmartConsole. |
|
The username and password do not match. Access to Check Point Security Management Server denied. |
Verify user name and password are set correctly on the APIC L4-L7 device configuration and in For Management HA – Verify user name and password are set correctly on the APIC Device Manager. |
|
APIC failed to communicate with Check Point Security Management Server. |
Make sure Management is up and running and |
|
This fault is sent when new settings are deployed on Check Point Security Management Server. Fault should be cleared automatically by APIC (or manually by re-query) |
If this fault persists, try to Re-Query for Device Validation. If the fault is not cleared contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent when Virtual System creation failed. |
Make sure Management server is up and running, management IP and port are correct and database is not locked. Make sure VSX is up and running and has a valid policy. |
|
This fault is sent when there was a failure when you try to read the VSX information from the database. |
Make sure there is connectivity between Check Point Security Management Server and the gateway. |
|
This fault is sent when policy installation on the Virtual System failed. |
Verify software blades are activated correctly and license is valid. |
|
This fault is sent when enable of the IDA blade on the Virtual System failed. |
Activate IDA API manually by issuing |
|
This fault is sent when an attempt to remove the Virtual System failed. |
Check the Virtual System settings. Make sure the Virtual System configuration is aligned with the device parameter configuration on the APIC. |
|
This fault is sent when the database is locked. |
Close all VSX and VS objects in SmartConsole and publish your changes. |
|
This fault is sent when management is not active. |
Make sure Management is active. Management HA - Make sure there is an access to the active Management. |
|
General error sent from Check Point Security Management Server. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent if the wrong input is sent to Check Point Security Management Server. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent if the wrong input is sent to Check Point Security Management Server. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent if there was a problem when you try to add a new interface to the Virtual System. |
Check the Virtual System settings and verify that there is no conflict with another interface IP address. Make sure there is connectivity between Check Point Security Management Server and the gateway. |
|
This fault is sent if there was a problem when you try to add a new interface to the VSBM (GoThrough). |
Check the configuration on the APIC. Make sure there is no conflict in the interface configuration you want to create on the Virtual System, on the device parameter settings. |
|
This fault is sent if there was a problem when you try to remove an interface. |
Check the Virtual System settings. Make sure the Virtual System configuration is aligned with the device parameter configuration on the APIC. |
|
This fault is sent if there was a problem when you try to set a Virtual System main IP. |
Check the Virtual System settings. Make sure the Virtual System configuration is aligned with the device parameter configuration on the APIC. |
|
This fault is sent if there was a problem when you set the Domain Server context. |
Check the Virtual System settings. Check the device parameters on the APIC and verify that the Domain Server is correctly defined. |
|
This fault is sent when there was a failure when you try to establish Management API session. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent when there was a failure when you try to establish VSX provisioning session. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent when Check Point Security Management Server receives a Virtual System name that is not in a valid format. |
Make sure Virtual System name was not edited manually for managed VSX device. Remove the Virtual System and retry. |
|
This fault is sent when there was a failure while trying to switch to the Domain Server context. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent when there was a failure when you try to connect to Check Point Security Management Server. |
Verify the management address and port are correct. If the issue persists, contact Check Point. |
|
L4-L7 Device name is not in a valid format. |
The Device name must contain only these characters: "-.0-9A-Z_a-z" and must not contain the "--" combination. |
|
This fault is sent when the number of interfaces defined for the L4-L7 Device cluster is not two (For "Device Type: PHYSICAL" only). |
Check the interface configuration on the L4-L7 Device Cluster. |
|
This fault is sent when the interface information is not sent in the expected format. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent when the interface name is not in a valid format. |
The interface name can contain only these characters: "-.0-9A-Z_a-z" and must not contain the "--" combination. |
|
This fault is sent when the Next Hop Gateway address, set on the device parameter configuration, is not one of the device interface addresses. |
Check the interfaces and route settings on the device parameter configuration on the APIC. The Next Hop Gateway address must be one of the network interface addresses. |
|
This fault is sent when the route Destination Address is missing. |
Check the route settings on the device parameters configuration on the APIC. |
|
This fault is sent when the interface address is missing. |
Check the interface settings on the device parameter configuration on the APIC. |
|
This fault is sent when the wrong type of provisioning command arrives at the Security Management Server. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent when the content of the provisioning command that arrives at the Security Management Server is not what is expected. |
Contact Check Point Support. |
|
This fault is sent if the Virtual System name exceeded the maximum allowed name length. |
As we set the name automatically, these name combinations should not exceed 100 characters: |
|
This fault is sent if there is a problem in the IP address and netmask set on the device parameter configuration. |
Check the interface settings on the device parameter configuration. |
|
This fault is sent if two different Virtual Systems try to use the same interface. |
All EPGs are part of the same BD and are assigned the same interface by the fabric. A single sub-interface is created on the VSX. The sub-interface cannot be shared between Virtual Systems.
|
|
This fault is sent if the provisioning assigned the same IP addresses to two different interfaces on a Virtual System. |
Check the interface settings on the device parameter configuration. |
Note - For faults related to vSEC L4-L7 service insertion not listed in this table, contact Check Point Support.
Check Point vSEC for ACI supports multi-tenancy. It uses Check Point VSX on the gateway side, and multi-domain management on the Security Management Server side.
With the VSX Security Gateway infrastructure, Virtual Systems are created automatically by APIC instruction and configured to process the designated traffic.
Virtual Systems are completely separated instances that can run their own security policy and networking configuration.
Virtual Systems contained by the same L4-L7 device can be deployed on separate tenants.