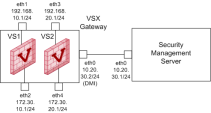
Example 1: VSX Gateway managed by Security Management Server
This example shows:
-
One VSX Gateway
 Physical server that hosts VSX virtual networks, including all Virtual Devices that provide the functionality of physical network devices. It holds at least one Virtual System, which is called VS0. with DMI management connection FIPS
Physical server that hosts VSX virtual networks, including all Virtual Devices that provide the functionality of physical network devices. It holds at least one Virtual System, which is called VS0. with DMI management connection FIPS -
Two Virtual Systems:
-
Each Virtual System
 Virtual Device on a VSX Gateway or VSX Cluster Member that implements the functionality of a Security Gateway. Acronym: VS. connects directly to available physical interfaces on the VSX
Virtual Device on a VSX Gateway or VSX Cluster Member that implements the functionality of a Security Gateway. Acronym: VS. connects directly to available physical interfaces on the VSX Virtual System Extension. Check Point virtual networking solution, hosted on a computer or cluster with virtual abstractions of Check Point Security Gateways and other network devices. These Virtual Devices provide the same functionality as their physical counterparts. Gateway
Virtual System Extension. Check Point virtual networking solution, hosted on a computer or cluster with virtual abstractions of Check Point Security Gateways and other network devices. These Virtual Devices provide the same functionality as their physical counterparts. Gateway -
One Virtual System is configured with the IPsec VPN
 Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides a Site to Site VPN and Remote Access VPN access. Software Blade
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides a Site to Site VPN and Remote Access VPN access. Software Blade Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities.
Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities. -
One Virtual System is configured with the Mobile Access
 Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides a Remote Access VPN access for managed and unmanaged clients. Acronym: MAB. Software Blade
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides a Remote Access VPN access for managed and unmanaged clients. Acronym: MAB. Software Blade
-
-
One Security Management Server
 Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. manages both the VSX Gateway and the two Virtual Systems.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. manages both the VSX Gateway and the two Virtual Systems.
Related documentation:
Topology
Action Plan
-
 Install the Security Management Server
Install the Security Management Server
See the R80.40 Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Step
Instructions
A
Install a Check Point appliance or Open Server
 Physical computer manufactured and distributed by a company, other than Check Point..
Physical computer manufactured and distributed by a company, other than Check Point..B
C
Run the Gaia First Time Configuration Wizard.
These settings are specific to the Security Management Server
 Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server.:
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server.:-
On the Management Connection page, select the applicable interface and configure the applicable IPv4 address.
In our example:
eth0, 10.20.30.1/24 -
On the Installation Type page, select Security Gateway and/or Security Management.
-
On the Products page, select Security Management.
D
Install the applicable licenses.
E
Configure the Security Management Server:
-
Connect with SmartConsole
 Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. to the Security Management Server.
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. to the Security Management Server. -
Configure the applicable Management Software Blades and settings.
-
Publish the SmartConsole session.
-
-
 Install the VSX Gateway
Install the VSX Gateway
See the R80.40 Installation and Upgrade Guide.
Step
Instructions
A
Install a Check Point appliance or Open Server.
B
Install Gaia OS.
C
Run the Gaia First Time Configuration Wizard.
These settings are specific to the VSX Gateway:
-
On the Management Connection page, select the interface for the DMI management connection and configure the applicable IPv4 address.
In our example:
eth0, 10.20.30.2/24 -
On the Internet Connection page, do not configure IP addresses on physical interfaces, to which your Virtual Systems connect directly.
-
On the Installation Type page, select Security Gateway and/or Security Management.
-
On the Products page, select Security Gateway.
-
On the Dynamically Assigned IP page, select No.
D
Make sure to enable the applicable physical interfaces:
To enable a physical interface in Gaia Portal
 Web interface for the Check Point Gaia operating system.
Web interface for the Check Point Gaia operating system.-
Connect to the Gaia Portal in your web browser.
In our example:
https://10.20.30.2 -
Click Network Management > Network Interfaces.
-
In the upper left corner, click the lock icon to obtain the configuration lock.
-
Select the applicable physical interface > click Edit.
-
Select Enable.
-
Click OK.
To enable a physical interface in Gaia Clish
 The name of the default command line shell in Check Point Gaia operating system. This is a restricted shell (role-based administration controls the number of commands available in the shell)., run:
The name of the default command line shell in Check Point Gaia operating system. This is a restricted shell (role-based administration controls the number of commands available in the shell)., run:-
set interface <Name of Physical Interface> state on -
save config
E
Install the applicable licenses.
-
-
 Create the VSX Gateway object in SmartConsole
Create the VSX Gateway object in SmartConsole
Step
Instructions
A
At the top, click Objects > More object types > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > VSX > New Gateway.
B
On the VSX Gateway General Properties (Specify the object's basic settings) page:
-
In the Enter the VSX Gateway Name field, enter the applicable name for this object.
In our example:
MyVsxGw -
In the Enter the VSX Gateway IPv4 field, enter the same IPv4 address you configured during the First Time Configuration Wizard of the VSX Gateway on the Management Connection page.
In our example:
10.20.30.1/24 -
In the Enter the VSX Gateway IPv6 field, enter the same IPv6 address you configured during the First Time Configuration Wizard of the VSX Gateway on the Management Connection page.
-
In the Select the VSX Gateway Version field, select the Check Point version.
In our example:
R80.40 -
Click Next.
C
On the VSX Gateway General Properties (Secure Internal Communication) page:
-
In the Activation Key field, enter the same Activation Key you entered during the First Time Configuration Wizard of the VSX Gateway.
-
In the Confirm Activation Key field, enter the same Activation Key again.
-
Click Initialize.
-
Click Next.
If the Trust State field does not show Trust established, perform these steps:
-
Connect to the command line on the VSX Gateway.
-
Make sure there is a physical connectivity between the VSX Gateway and the Management Server (for example, pings can pass).
-
Run:
cpconfig -
Enter the number of this option:
Secure Internal Communication -
Follow the instructions on the screen to change the Activation Key.
-
On the VSX Gateway General Properties page, click Reset.
-
Enter the same Activation Key you entered in the
cpconfigmenu. -
Click Initialize.
D
On the VSX Gateway Interfaces (Physical Interfaces Usage) page:
-
Examine the list of the interfaces - it must show all the physical interfaces on the VSX Gateway.
-
If you plan to connect more than one Virtual System directly to same physical interface, you must select VLAN Trunk for that physical interface.
-
Click Next.
E
On the Virtual Network Device Configuration (Specify the object's basic settings) page:
-
You can select Create a Virtual Network Device and configure the first applicable Virtual Network Device at this time (we recommend to do this later) - Virtual Switch
 Virtual Device on a VSX Gateway or VSX Cluster Member that functions as a physical switch. Acronym: VSW. or Virtual Router
Virtual Device on a VSX Gateway or VSX Cluster Member that functions as a physical switch. Acronym: VSW. or Virtual Router Virtual Device on a VSX Gateway or VSX Cluster Member that functions as a physical router. Acronym: VR..
Virtual Device on a VSX Gateway or VSX Cluster Member that functions as a physical router. Acronym: VR.. -
Click Next.
F
On the VSX Gateway Management (Specify the management access rules) page:
-
Examine the default access rules.
-
Select the applicable default access rules.
-
Configure the applicable source objects, if needed.
-
Click Next.
Important - These access rules apply only to the VSX Gateway (context of VS0), which is not intended to pass any "production" traffic.
G
On the VSX Gateway Creation Finalization page:
-
Click Finish and wait for the operation to finish.
-
Click View Report for more information.
-
Click Close.
H
Examine the VSX configuration:
-
Connect to the command line on the VSX Gateway.
-
Log in to Gaia Clish, or Expert mode.
-
Run:
vsx stat -v
-
-
 Configure the VSX Gateway object in SmartConsole
Configure the VSX Gateway object in SmartConsole
See Working with VSX Gateways.
Step
Instructions
A
From the left navigation toolbar, click Gateways & Servers.
B
Open the VSX Gateway object.
In our example:
MyVsxGwC
Enable the applicable Software Blades.
Refer to:
-
sk106496 - Software Blades updates on VSX R75.40VS and above - FAQ
-
Applicable Administration Guides on the R80.40 Home Page.
D
Configure other applicable settings.
E
Click OK to push the updated VSX Configuration.
Click View Report for more information.
F
Install policy on the VSX Gateway object:
-
Click Install Policy.
The Install Policy window opens.
-
In the Policy field, select the default policy for this VSX Gateway object.
This policy is called:
<Name of VSX Gateway object>_VSX.In our example:
MyVsxGw_VSX -
Click Install.
G
Examine the VSX configuration:
-
Connect to the command line on the VSX Gateway.
-
Log in to Gaia Clish, or Expert mode.
-
Run:
vsx stat -v
-
 Create the first Virtual System object in SmartConsole
Create the first Virtual System object in SmartConsole
See Working with Virtual Systems.
Step
Instructions
A
At the top, click Objects > More object types > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > VSX > New Virtual System.
B
On the VSX System General Properties (Define the object name and the hosting VSX) page:
-
In the Name field, enter the applicable name for this object.
In our example:
MyVs1 -
In the VSX Gateway / Cluster field, select the applicable VSX Gateway object.
In our example:
MyVsxGw -
Click Next.
C
On the Virtual System Network Configuration (Define Virtual System Interfaces and Routes) page:
In our example, this Virtual System connects directly to two physical interfaces on the VSX Gateway.
In the Interfaces section, add the "external" interface:
-
Click Add > Regular.
-
In the Interface field, select the applicable physical interface.
In our example:
eth1 -
In the IPv4 Configuration section, enter the applicable IP Address and Net Mask.
In our example:
192.168.10.1/24You can select Propagate route to adjacent Virtual Devices (IPv4) to "advertise" this Virtual System to neighboring Virtual Devices. This enables IPv4 connectivity between neighboring Virtual Devices.
-
In the IPv6 Configuration section, enter the applicable IPv6 Address and Prefix.
You can select Propagate route to adjacent Virtual Devices (IPv6) to "advertise" this Virtual System to neighboring Virtual Devices. This enables IPv6 connectivity between the neighboring Virtual Devices.
-
Click OK.
In the Interfaces section, add the "internal" interface:
-
Click Add > Regular.
-
In the Interface field, select the applicable physical interface - this is the "internal" interface.
In our example:
eth2 -
In the IPv4 Configuration section, enter the applicable IP Address and Net Mask.
In our example:
172.30.10.1/24You can select Propagate route to adjacent Virtual Devices (IPv4) to "advertise" this Virtual System to neighboring Virtual Devices. This enables IPv4 connectivity between the neighboring Virtual Devices.
-
In the IPv6 Configuration section, enter the applicable IPv6 Address and Prefix.
You can select Propagate route to adjacent Virtual Devices (IPv6) to "advertise" this Virtual System to neighboring Virtual Devices. This enables IPv6 connectivity between the neighboring Virtual Devices.
-
Click OK.
In the Routes section, click Add to configure the applicable static routes and the Default Route.
Click Next.
D
On the VSX System Creation Finalization page:
-
Click Finish and wait for the operation to finish.
-
Click View Report for more information.
-
Click Close.
E
Examine the VSX configuration:
-
Connect to the command line on the VSX Gateway.
-
Log in to Gaia Clish, or Expert mode.
-
Run:
vsx stat -v
-
-
 Configure the first Virtual System object in SmartConsole
Configure the first Virtual System object in SmartConsole
See Working with Virtual Systems.
Step
Instructions
A
From the left navigation toolbar, click Gateways & Servers.
B
Open the first Virtual System object.
In our example:
MyVs1C
Enable the applicable Software Blades.
In our example:
IPsec VPNbladeRefer to:
-
sk106496 - Software Blades updates on VSX R75.40VS and above - FAQ
-
Applicable Administration Guides on the R80.40 Home Page.
D
Configure other applicable settings.
E
Click OK to push the updated VSX Configuration.
F
Configure and install the applicable policy on the first Virtual System object.
G
Examine the VSX configuration:
-
Connect to the command line on the VSX Gateway.
-
Log in to Gaia Clish, or Expert mode.
-
Run:
vsx stat -v
-
 Create the second Virtual System object in SmartConsole
Create the second Virtual System object in SmartConsole
See Working with Virtual Systems.
Step
Instructions
A
At the top, click Objects > More object types > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > VSX > New Virtual System.
B
On the VSX System General Properties (Define the object name and the hosting VSX) page:
-
In the Name field, enter the applicable name for this object.
In our example:
MyVs2 -
In the VSX Gateway / Cluster field, select the applicable VSX Gateway object.
In our example:
MyVsxGw -
Click Next.
C
On the Virtual System Network Configuration (Define Virtual System Interfaces and Routes) page:
In our example, this Virtual System connects directly to two physical interfaces on the VSX Gateway.
In the Interfaces section, add the "external" interface:
-
Click Add > Regular.
-
In the Interface field, select the applicable physical interface.
In our example:
eth1 -
In the IPv4 Configuration section, enter the applicable IP Address and Net Mask.
In our example:
192.168.20.1/24You can select Propagate route to adjacent Virtual Devices (IPv4) to "advertise" this Virtual System to neighboring Virtual Devices. This enables IPv4 connectivity between Virtual Devices.
-
In the IPv6 Configuration section, enter the applicable IPv6 Address and Prefix.
You can select Propagate route to adjacent Virtual Devices (IPv6) to "advertise" this Virtual System to neighboring Virtual Devices. This enables IPv6 connectivity between Virtual Devices.
-
Click OK.
In the Interfaces section, add the "internal" interface:
-
Click Add > Regular.
-
In the Interface field, select the applicable physical interface - this is the "internal" interface.
In our example:
eth2 -
In the IPv4 Configuration section, enter the applicable IP Address and Net Mask.
In our example:
172.30.20.1/24You can select Propagate route to adjacent Virtual Devices (IPv4) to "advertise" this Virtual System to neighboring Virtual Devices. This enables IPv4 connectivity between the neighboring Virtual Devices.
-
In the IPv6 Configuration section, enter the applicable IPv6 Address and Prefix.
You can select Propagate route to adjacent Virtual Devices (IPv6) to "advertise" this Virtual System to neighboring Virtual Devices. This enables IPv6 connectivity between the neighboring Virtual Devices.
-
Click OK.
In the Routes section, click Add to configure the applicable static routes and the Default Route.
Click Next.
D
On the VSX System Creation Finalization page:
-
Click Finish and wait for the operation to finish.
-
Click View Report for more information.
-
Click Close.
E
Examine the VSX configuration:
-
Connect to the command line on the VSX Gateway.
-
Log in to Gaia Clish, or Expert mode.
-
Run:
vsx stat -v
-
-
 Configure the second Virtual System object in SmartConsole
Configure the second Virtual System object in SmartConsole
See Working with Virtual Systems.
Step
Instructions
A
From the left navigation toolbar, click Gateways & Servers.
B
Open the second Virtual System object.
In our example:
MyVs2C
Enable the applicable Software Blades.
In our example:
Mobile AccessbladeRefer to:
-
sk106496 - Software Blades updates on VSX R75.40VS and above - FAQ
-
Applicable Administration Guide on the R80.40 Home Page.
D
Configure other applicable settings.
E
Click OK to push the updated VSX Configuration.
F
Configure and install the applicable policy on the second Virtual System object.
G
Examine the VSX configuration:
-
Connect to the command line on the VSX Gateway.
-
Log in to Gaia Clish, or Expert mode.
-
Run:
vsx stat -v