

In This Section: |
Check Point Log Exporter is a method to export Check Point logs over syslog in R80.20 management. For information on deployment in R77.30 and R80.10 servers, see sk122323.
Log Exporter supports:
Log Exporter is a multi-threaded daemon service which runs on a log server. Each log that is written on the log server is read by the Log Exporter daemon. It is then transformed into the desired format and mapping and sent to the end target.
On Multi-Domain Server / Multi-Domain Log Server, if Log Exporter is deployed on several domains, each domain server has its own Log Exporter daemon service. If you export the logs to several targets, each target has its own Log Exporter daemon.
Common method for creating \ modifying log exporters \ targets.
To configure a new target for the logs:
cp_log_export add name <name> [domain-server <domain-server>] target-server <target-server> target-port <target-port> protocol <(udp|tcp)> format <(syslog)|(cef)> [optional arguments]
$EXPORTERDIR/targets/<deployment_name>. Note - This deployment exports the logs in clear text.
Unless apply-now is used within the command, the new Log Exporter does not start automatically and requires a manual start command.
For information on how to send the logs over an encrypted connection, see TLS Configuration.
Advanced parameters for creating \ modifying Log Exporter\targets
Usage
cp_log_export <command-name> [command-arguments]
To understand a specific command usage:
Run: cp_log_export <command-name> help
Commands
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
add |
Deploy a new Check Point Log Exporter |
set |
Update an existing exporter's configuration |
delete |
Remove an exporter |
show |
Print an exporter's current configuration |
status |
Show an exporter's overview status |
start |
Start an exporter process |
stop |
Stop an exporter process |
restart |
Restart an exporter process |
reexport |
Reset the current position and reexport all logs per the configuration |
Parameters
Name |
Description |
add |
set |
delete |
show/status/ |
reexport |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
name |
Unique name of the exporter configuration |
Mandatory |
Mandatory |
Mandatory |
Optional - Default all |
Mandatory |
domain-server |
The relevant domain-server name or IP |
Mandatory |
Mandatory |
Mandatory |
Optional - Default all |
Mandatory |
target-server |
Export the logs to this IP address |
Mandatory |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
target-port |
The port on the target |
Mandatory |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
protocol |
Transport protocol to use |
Mandatory |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
format |
The format in which the logs are exported |
Optional |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
enabled |
Allow log_exporter to start on cpstart/mdsstart |
Optional |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
encrypted |
Use TSL (SSL) encryption to export the logs |
Optional |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
ca-cert |
Full path to the CA pem certificate file Relevant only when encrypted is true |
Optional |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
client-cert |
Full path to the client p12 certificate Relevant only when encrypted is true |
Optional |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
client-secret |
The challenge phrase used to create the client p12 certificate Relevant only when encrypted is true |
Optional |
Optional |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
apply-now |
Applying any change that was done immediately. |
Optional |
Optional |
Mandatory |
N/A |
Mandatory |
How to get a secured connection between the Log Exporter and the syslog server.
The only allowed authentication method via TLS is mutual authentication. For mutual authentication, Log Exporter needs these certificates:
If you do not already have the required certificates, this procedure is an example of how to create the required certificates. There are also alternative procedures.
All commands need to run on the CA server.
Note - The CA server needs to be routable from the Log Exporter device.
To create a self signed CA:
Run this if you do not already have a trusted CA pem:
openssl genrsa -out RootCA.key 2048
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key RootCA.key -days 2048 -out RootCA.pem
An example of the prompt to provide information:
---
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:US
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:New York
Locality Name (eg, city) []:MyCity
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:MyCompany
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:MyDepartment
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:www.company.com
Email Address []:
To create a client (log_exporter) .p12 certificate file:
openssl genrsa -out log_exporter.key 2048
openssl req -new -key log_exporter.key -out log_exporter.csr
openssl x509 -req -in log_exporter.csr -CA RootCA.pem -CAkey RootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out log_exporter.crt -days 2048 -sha256
openssl pkcs12 -inkey log_exporter.key -in log_exporter.crt -export -out log_exporter.p12
Note - The challenge phrase used in this conversion is required in the log_exporter TLS configuration.
After you create the required certificates, update the security parameters on the Check Point exporting server:
To update the security parameters:
mdsenv <domain server name or ip>
cd $EXPORTERDIR/targets/<deployment name>
mkdir certs
RootCA.pem and log_exporter.p12 to the certs directoryRootCA.pem and log_exporter.p12 execution privilegeschmod +r RootCA.pem
chmod +r log_exporter.p12
targetConfiguration.xml file with the full path to the certificates and the challenge phrase used to create the .p12 certificateTo create a server (target) certificate:
openssl genrsa -out syslogServer.key 2048
openssl req -new -key syslogServer.key -out syslogServer.csr
openssl x509 -req -in syslogServer.csr -CA RootCA.pem -CAkey RootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out syslogServer.crt -days 2048 -sha256
Configuring Log Exporter without using the deployment script.
After deploying a new instance of Log Exporter, all related files to that deployment can be found under $EXPORTERDIR/targets/<deployment name>.
On an Multi-Domain Server / Multi-Domain Log Server server, the EXPORTERDIR environment variable is per domain. The value is changed automatically when you switch between domain server contexts with the mdsenv command.
Target Configuration XML
The target configuration file, located under each deployment folder: $EXPORTERDIR/targets//targetConfiguration.xml
Note - You must restart the Log Exporter process for the new setting to take effect.
These are some of the configuration options:
Parameter |
Description |
Possible/Default Values |
|---|---|---|
<version></version> |
Current Log Exporter version - used for upgrades |
|
<is_enabled></is_enabled> |
Determines if the process is monitored by the watch dog |
true/false |
Destination Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
Possible/Default Values |
|---|---|---|
type |
Reserved for future use |
|
<ip></ip> |
The IP address of the target that receives the logs |
Any IPv4 address |
<port></port> |
The port on the target |
Any valid port number |
<protocol></protocol> |
The protocol used in the connection |
UDP/TCP |
Security Parameters
These are discussed in more detail in TLS Configuration.
Parameter |
Description |
Possible/Default Values |
|---|---|---|
<security></security> |
Determines if the connection is sent in clear text or encrypted |
clear [default] / tls |
<pem_ca_file></pem_ca_file> |
The location of the root CA pem file |
|
<p12_certificate_file></p12_certificate_file> |
The location of the client key pair in p12 format |
|
<client_certificate_challenge_phrase></client_certificate_challenge_phrase> |
The challenge phrase used to create the p12 certificate. It is hashed when the Log Exporter is started or restarted. |
|
Source Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
Possible/Default Values |
|---|---|---|
<folder></folder> |
The path where the log files are located |
Default location is |
<log_files></log_files> |
Determines which log files are exported |
on-line| read logs from [number - default=1] days back (recommended) | specific file name |
<log_types></log_types> |
Determines which log file types (by extension) are exported |
|
Resolver Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
Possible/Default Values |
|---|---|---|
<mappingConfiguration></mappingConfiguration> |
The XML file that contains the log field mapping scheme. Uses the default settings if left empty. |
Default values are based on the format |
<exportAllFields>true</exportAllFields> |
When this field is set to When set to |
true/false |
Format Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
Possible/Default Values |
|---|---|---|
<formatHeaderFile></formatHeaderFile> |
The XML file that contains the log header format scheme. Uses the default settings if left empty. |
Default values are based on the format |
Filters Parameters
The Log Exporter solution supports a basic filtering ability that allows you to not export firewall connections logs. All other logs are exported.
Parameter |
Description |
Possible/Default Values |
|---|---|---|
<filter filter_out_by_connection="false"> |
Determines if the Access logs should be filtered out. When set to Note - These are the only blade filters currently supported. |
true/false |
Format Configuration XML
Body
Parameter |
Description |
Syslog |
CEF |
LEEF |
Generic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<start_message_body></start_message_body> |
The character that precedes the log data payload |
[ |
|
|
|
<end_message_body></end_message_body> |
The character that follows the log data payload |
] |
|
|
|
<message_separator></message_separator> |
The delimeter that separates logs |
( =='\n') |
('\n') |
('\n') |
('\n') |
<fields_separatator></fields_separatator> |
The delimeter that separates log fields |
'; ' (semi colon, space) |
' ' (space) |
	 (<TAB>) |
' ' (space) |
<field_value_separatator></field_value_separatator> |
The assignment operator |
: |
= |
= |
= |
<value_encapsulation_start>"</value_encapsulation_start> |
The value encapsulation operator (start) |
" |
|
" |
" |
<value_encapsulation_start>"</value_encapsulation_start> |
The value encapsulation operator (end) |
" |
|
" |
" |
<escape_chars> <char> <orig></orig> <escaped></escaped> </char> </escape_chars> |
To escape unwanted characters The escape functionality replaces the string that is encapsulated by the |
\ --> \\ " --> \" --> ' ' ] --> \] |
\ --> \\ = --> \= --> ' ' | --> \| |
= --> \=
--> ' ' |
\ --> \\
" --> '
--> ' ' |
Header
Parameter |
Description |
Default values for syslog |
Default values for CEF |
|---|---|---|---|
<header_format></header_format> |
The delimeter between the header values and the number of values. Every {} is replaced with one value. |
' ' (space) |
| |
Field Mapping Configuration XML
Parameter |
Description |
Possible/ Default Values |
|---|---|---|
<table> |
Some fields appear in the tables based on the log format. This information can be found in the |
|
<exported></exported> |
Optional - You can use the exported true/false tag in the mapping configuration file to filter out specific fields. Alternatively, if the 'exportAllFields' tag in the 'targetConfiguration.xml' file is set to |
true/false |
<origName></origName> |
The name of the field that is mapped to <dstName> |
|
<dstName></dstName> |
The new mapping scheme name for the desired field. |
|
<required></required> |
Optional - When set to |
true/false |
How to configure SIEM applications to optimally receive logs.
ArcSight
ArcSight recommends that you name the certificate syslog-ng.
To name the certificate:
Convert the key to p12 format:
openssl pkcs12 -inkey syslogServer.key -in syslogServer.crt -export -out syslog-ng.p12 -name "syslogng-alias" -password pass:changeit
To make sure the environment variable ARCSIGHT_HOME is the connector install directory:
ARCSIGHT_HOME/current/bin/arcsight agent keytoolgui$ARCSIGHT_HOME/current/jre/lib/security/cacerts (password "changeit").Ca.pem and save it.To edit the agent.properties file to enable mutual authentication:
Use vi $ARCSIGHT_HOME//current/user/agent/agent.properties:
syslogng.mutual.auth.enabled=false -> true
syslogng.tls.keystore.file=user/agent/syslog-ng.p12
syslogng.tls.keystore.alias=syslogng-alias
/etc/init.d/arc_connector_name restartSplunk
cat syslogServer.crt syslogServer.key RootCA.pem > splunk.pem
inputs.conf file on the Splunk server:vi /opt/splunk/etc/apps/search/local/inputs.conf
[SSL]
serverCert = /etc/ssl/my-certs/splunk.pem
sslPassword = <challenge password>
requireClientCert = true
[tcp-ssl://<port>]
index = <index>
server.conf file on the Splunk servervi /opt/splunk/etc/system/local/server.conf
[sslConfig]
sslRootCAPath = /etc/ssl/my-certs/RootCA.pem
/opt/splunk/bin/splunk restart
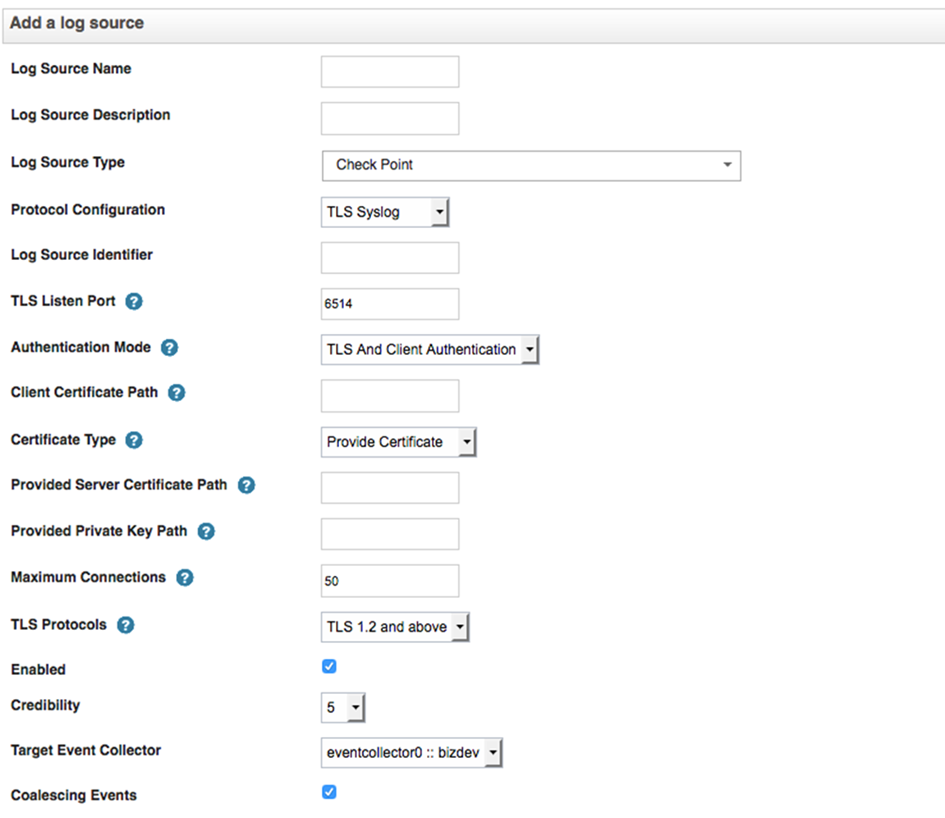
QRadar
When you use Client Authentication, you must provide the absolute path to the client certificate.
To move from the existing LEA connector to the new Log Exporter:
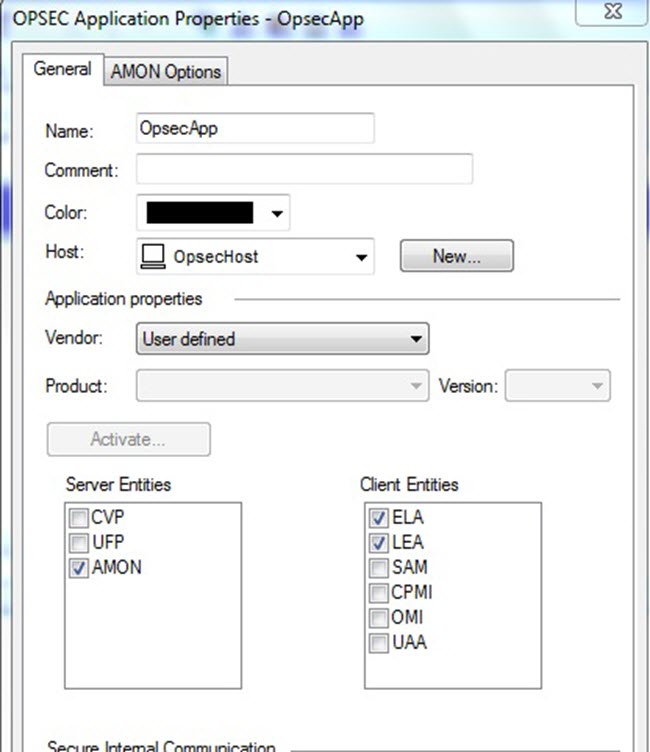
Comment out these lines:
From |
To |
|---|---|
# |
# |
lea_server auth_port 18184 |
# lea_server auth_port 18184 |
lea_server port 0 |
# lea_server port 0 |
# |
# |
To move from the existing CPLogToSyslog to the new Log Exporter:
Special log fields
loguid - Some Check Point logs are updated over time. Updated logs have the same loguid value. Check Point SmartLog client correlates those updates into a single unified log. When the update logs are sent to 3rd party servers, they arrive as distinct logs. Administrators can use the loguid field to correlate updated logs and get the full event chain.
An example of updated logs includes the total amount of bytes sent and received over time or the severity field which is updated over time as more information becomes available.
hll_key (High Level Log key) - This concept was introduced in R80.10. Multiple connection logs can comprise one session with one shared hll_key. For example, when you browse to a webpage, you may have multiple connection logs which are related to the same session. Connection logs which are part of the same session share the same hll_key value.
Syslog-NG Listener configuration
We recommend you use the syslog-protocol flag when you configure a source on a Syslog NG server.
For example: source s_network { network(transport("tcp") port(514) flags(syslog-protocol) ); };
Splunk Listener configuration
We recommend that you add these time settings to your sourcetype:
TIME_FORMAT = %sTIME_PREFIX = time=MAX_TIMESTAMP_LOOKAHEAD = 15ArcSight Listener configuration
The Log Exporter solution does not work with the OPSEC LEA connector. Instead, you must install the ArcSight Syslog-NG connector.
ArcSight Common Event Format (CEF) Mapping
CEF is an extensible, text-based format that supports multiple device types by offering the most relevant information. Message syntaxes are reduced to work with ESM normalization. Specifically, CEF defines a syntax for log records comprised of a standard header and a variable extension, formatted as key-value pairs. The CEF format can be used with on-premises devices by implementing the ArcSight Syslog SmartConnector. CEF can also be used by cloud-based service providers by implementing the SmartConnector for ArcSight Common Event Format REST.
CEF Header format
|
Version |
Device Vendor |
Device Product |
Device Version |
Device Event Class ID |
Name |
Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Default |
CEF:0 |
Check Point |
Log Update |
Check Point |
Log |
Log |
0 |
Values |
- |
- |
Product Name (Blade) |
- |
|
|
|
QRadar Log Event Extended Format (LEEF) Mapping
The LEEF is a customized event format for IBM Security QRadar.
LEEF Header Format
|
LEEF: Version |
Vendor |
Product |
Version |
EventID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Default |
LEEF:2.0 |
Check Point |
Log Update |
1.0 |
Check Point Log |
Values |
- |
- |
Product Name (Blade) |
- |
|
Note - The time format is not compliant with the official LEEF format.
As there is currently no epoch time format, Log Exporter with LEEF format is only partially supported.