

Description
Displays the status and statistics information of Check Point applications.
Syntax
cpstat [-d] [-h <Host>] [-p <Port>] [-s <SICname>] [-f <Flavor>] [-o <Polling Interval> [-c <Count>] [-e <Period>]] <Application Flag> |
Note - You can write the parameters in the syntax in any desired order.
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Optional. Runs the command in debug mode. Use only if you troubleshoot the command itself. The output shows the SNMP queries and SNMP responses for the applicable SNMP OIDs. |
|
Optional. When you run this command on a Management Server, this parameter specifies the managed Security Gateway.
The default is |
|
Optional. Port number of the Application Monitoring (AMON) server. The default port is 18192. |
|
Optional. Secure Internal Communication (SIC) name of the Application Monitoring (AMON) server. |
|
Optional. Specifies the type of the information to collect. If you do not specify a flavor explicitly, the command uses the first flavor in the |
|
Optional. Specifies the desired polling interval (in seconds) - how frequently the command collects and shows the information.
Use this parameter together with the " Example: |
|
Optional. Specifies how many times the command runs and shows the results before it stops. You must use this parameter together with the "
Example: |
|
Optional. Specifies the time (in seconds), over which the command calculates the statistics. You must use this parameter together with the " You can use this parameter together with the " Example: |
|
Mandatory. One of these:
|
These flavors are available for the application flags
-------------------------------------------------------------- |Flag |Flavours | -------------------------------------------------------------- |os |default, ifconfig, routing, routing6, | | |memory, old_memory, cpu, disk, perf, | | |multi_cpu, multi_disk, raidInfo, sensors, | | |power_supply, hw_info, all, average_cpu, | | |average_memory, statistics, updates, | | |licensing, connectivity, vsx | -------------------------------------------------------------- |persistency |product, TableConfig, SourceConfig | -------------------------------------------------------------- |thresholds |default, active_thresholds, destinations, | | |error | -------------------------------------------------------------- |ci |default | -------------------------------------------------------------- |https_inspection |default, hsm_status, all | -------------------------------------------------------------- |cvpn |cvpnd, sysinfo, products, overall | -------------------------------------------------------------- |fw |default, interfaces, policy, perf, hmem, | | |kmem, inspect, cookies, chains, | | |fragments, totals, totals64, ufp, http, | | |ftp, telnet, rlogin, smtp, pop3, sync, | | |log_connection, all | -------------------------------------------------------------- |vsx |default, stat, traffic, conns, cpu, all, | | |memory, cpu_usage_per_core | -------------------------------------------------------------- |vpn |default, product, IKE, ipsec, traffic, | | |compression, accelerator, nic, | | |statistics, watermarks, all | -------------------------------------------------------------- |blades |fw, ips, av, urlf, vpn, cvpn, aspm, dlp, | | |appi, anti_bot, default, | | |content_awareness, threat-emulation, | | |default | -------------------------------------------------------------- |identityServer |default, authentication, logins, ldap, | | |components, adquery | -------------------------------------------------------------- |appi |default, subscription_status, | | |update_status, RAD_status, top_last_hour, | | |top_last_day, top_last_week, | | |top_last_month | -------------------------------------------------------------- |urlf |default, subscription_status, | | |update_status, RAD_status, top_last_hour, | | |top_last_day, top_last_week, | | |top_last_month | -------------------------------------------------------------- |dlp |default, dlp, exchange_agents, fingerprint| -------------------------------------------------------------- |ctnt |default | -------------------------------------------------------------- |antimalware |default, scanned_hosts, scanned_mails, | | |subscription_status, update_status, | | |ab_prm_contracts, av_prm_contracts, | | |ab_prm_contracts, av_prm_contracts | -------------------------------------------------------------- |threat-emulation |default, general_statuses, update_status, | | |scanned_files, malware_detected, | | |scanned_on_cloud, malware_on_cloud, | | |average_process_time, emulated_file_size, | | |queue_size, peak_size, | | |file_type_stat_file_scanned, | | |file_type_stat_malware_detected, | | |file_type_stat_cloud_scanned, | | |file_type_stat_cloud_malware_scanned, | | |file_type_stat_filter_by_analysis, | | |file_type_stat_cache_hit_rate, | | |file_type_stat_error_count, | | |file_type_stat_no_resource_count, | | |contract, downloads_information_current, | | |downloading_file_information, | | |queue_table, history_te_incidents, | | |history_te_comp_hosts | -------------------------------------------------------------- |scrub |default, subscription_status, | | |threat_extraction_statistics | -------------------------------------------------------------- |gx |default, contxt_create_info, | | |contxt_delete_info, contxt_update_info, | | |contxt_path_mng_info, GXSA_GPDU_info, | | |contxt_initiate_info, gtpv2_create_info, | | |gtpv2_delete_info, gtpv2_update_info, | | |gtpv2_path_mng_info, gtpv2_cmd_info, all | -------------------------------------------------------------- |fg |all | -------------------------------------------------------------- |ha |default, -------------------------------------------------------------- |polsrv |default, all | -------------------------------------------------------------- |ca |default, -------------------------------------------------------------- |mg |default | -------------------------------------------------------------- |cpsemd |default | -------------------------------------------------------------- |cpsead |default | -------------------------------------------------------------- |ls |default | -------------------------------------------------------------- |PA |default | -------------------------------------------------------------- |
Example 1
[Expert@MyGW:0]# cpstat -f interfaces fw
Network interfaces -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |Name|IP |Netmask |Flags|Peer name|Remote IP|Topology|Proxy name|Slaves|Ports|IPv6 Address|IPv6 Len| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |eth0|192.168.30.40|255.255.255.0| 0| | 0.0.0.0| 4| | | | ::| 0| |eth1| 172.30.60.80|255.255.255.0| 0| | 0.0.0.0| 4| | | | ::| 0| |eth2| 0.0.0.0| 0.0.0.0| 0| | 0.0.0.0| 4| | | | ::| 0| |eth3| 0.0.0.0| 0.0.0.0| 0| | 0.0.0.0| 4| | | | ::| 0| |eth4| 0.0.0.0| 0.0.0.0| 0| | 0.0.0.0| 4| | | | ::| 0| |eth5| 0.0.0.0| 0.0.0.0| 0| | 0.0.0.0| 4| | | | ::| 0| |eth6| 0.0.0.0| 0.0.0.0| 0| | 0.0.0.0| 4| | | | ::| 0| |eth7| 0.0.0.0| 0.0.0.0| 0| | 0.0.0.0| 4| | | | ::| 0| --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[Expert@MyGW:0]# |
Example 2
[Expert@MyGW:0]# cpstat -f default fw
Policy name: MyGW_Policy Install time: Wed May 23 18:14:32 2018
Interface table --------------------------------------- |Name|Dir|Total |Accept|Deny |Log| --------------------------------------- |eth0|in | 2393126| 32589| 2360537| 52| |eth0|out| 33016| 33016| 0| 0| |eth1|in | 2360350| 0| 2360350| 0| |eth1|out| 0| 0| 0| 0| |eth2|in | 2360350| 0| 2360350| 0| |eth2|out| 0| 0| 0| 0| |eth3|in | 2348704| 0| 2348704| 1| |eth3|out| 0| 0| 0| 0| |eth4|in | 2360350| 0| 2360350| 0| |eth4|out| 0| 0| 0| 0| --------------------------------------- | | |11855896| 65605|11790291| 53| ---------------------------------------
... ... [truncated for brevity] ... ...
[Expert@MyGW:0]# |
Example 3
[Expert@MyGW:0]# cpstat os -f perf -o 2 -c 2 -e 60
Total Virtual Memory (Bytes): 12417720320 Active Virtual Memory (Bytes): 3741331456 Total Real Memory (Bytes): 8231063552 Active Real Memory (Bytes): 3741331456 Free Real Memory (Bytes): 4489732096 Memory Swaps/Sec: - Memory To Disk Transfers/Sec: - CPU User Time (%): 0 CPU System Time (%): 0 CPU Idle Time (%): 100 CPU Usage (%): 0 CPU Queue Length: - CPU Interrupts/Sec: 135 CPUs Number: 8 Disk Servicing Read\Write Requests Time: - Disk Requests Queue: - Disk Free Space (%): 61 Disk Total Free Space (Bytes): 12659716096 Disk Available Free Space (Bytes): 11606188032 Disk Total Space (Bytes): 20477751296
Total Virtual Memory (Bytes): 12417720320 Active Virtual Memory (Bytes): 3741556736 Total Real Memory (Bytes): 8231063552 Active Real Memory (Bytes): 3741556736 Free Real Memory (Bytes): 4489506816 Memory Swaps/Sec: - Memory To Disk Transfers/Sec: - CPU User Time (%): 3 CPU System Time (%): 0 CPU Idle Time (%): 97 CPU Usage (%): 3 CPU Queue Length: - CPU Interrupts/Sec: 140 CPUs Number: 8 Disk Servicing Read\Write Requests Time: - Disk Requests Queue: - Disk Free Space (%): 61 Disk Total Free Space (Bytes): 12659716096 Disk Available Free Space (Bytes): 11606188032 Disk Total Space (Bytes): 20477751296
[Expert@MyGW:0]# |
To stop and start one member of a cluster from SmartView Monitor:
VPN Tunnels are secure links between Security Gateways. These Tunnels ensure secure connections between gateways of an organization and remote access clients.
When Tunnels are created and put to use, you can keep track of their normal function, so that possible malfunctions and connectivity problems can be accessed and solved as soon as possible.
To ensure this security level, SmartView Monitor constantly monitor and analyze the status of an organization's Tunnels to recognize malfunctions and connectivity problems. With the use of Tunnel views, you can generate fully detailed reports that include information about the Tunnels that fulfill the specific Tunnel views conditions. With this information you can monitor Tunnel status, the Community with which a Tunnel is associated, the gateways to which the Tunnel is connected, and so on. These are the Tunnel types:
Permanent tunnels are constantly monitored. Therefore, each VPN tunnel in the community can be set as a Permanent tunnel. A log, alert or user defined action can be issued when the VPN tunnel is down.
Permanent tunnels can only be established between Check Point gateways. The configuration of Permanent tunnels takes place on the community level and:
This table shows the possible Tunnel states and their significance to a Permanent or Regular Tunnel.
State |
Permanent Tunnel |
Regular Tunnel |
|---|---|---|
Up |
The tunnel works and the data can flow with no problems. |
IDE SA (Phase 1) and IPSEC SA (Phase 2) exist with a peer gateway. |
Destroyed |
The tunnel is destroyed. |
The tunnel is destroyed. |
Up Phase1 |
Irrelevant |
Tunnel initialization is in process and Phase 1 is complete (that is, IKE SA exists with cookies), but there is no Phase 2. |
Down |
There is a tunnel failure. You cannot send and receive data to or from a remote peer. |
Irrelevant. |
Up Init |
The tunnel is initialized. |
Irrelevant. |
Gateway not Responding |
The gateway is not responding. |
The gateway is not responding. |
If a Tunnel is deleted from SmartConsole, the Tunnel Results View shows the deleted Tunnel for an hour after it was deleted.
If a community is edited, the Results View shows removed tunnels for an hour after they were removed from the community.
When a Tunnel view runs the results show in the SmartView Monitor client. A Tunnel view can run:
A Tunnels view can be created and run for:
Down Tunnel view results list all the Tunnels that are currently not active.
To run a down tunnel view:
A list of all the Down Tunnels associated with the selected view properties shows.
Permanent Tunnel view results list all of the existing Permanent Tunnels and their current status.
A Permanent Tunnel is a Tunnel that is constantly kept active.
To run a permanent tunnel view:
A list of the Permanent Tunnels related to the selected view properties shows.
Tunnels on Community view results list all the Tunnels related to a selected Community.
To run a tunnels on community view:
A list of all Communities shows.
A list of all the Tunnels related to the selected Community shows.
Tunnels on Gateways view results list all of the Tunnels related to a selected Gateway.
To run tunnels on Gateway view:
A list of the gateways shows.
A list of the Tunnels related to the selected gateway shows.
SmartView Monitor provides tools that enable you to know traffic related to specified network activities, server, and so on, and the status of activities, hardware and software use of different Check Point products in real-time. With this knowledge you can:
SmartView Monitor delivers a comprehensive solution to monitor and analyze network traffic and network usage. You can generate fully detailed or summarized graphs and charts for all connections intercepted and logged when you monitor traffic, and for numerous rates and figures when you count usage throughout the network.
Traffic Monitoring provides in-depth details on network traffic and activity. As a network administrator you can generate traffic information to:
Network traffic patterns help administrators determine which services demand the most network resources.
Monitoring traffic can provide information on how the use of network resources is divided among corporate users and departments. Reports that summarize customer use of services, bandwidth and time can provide a basis to estimate costs for each user or department.
A Traffic view can be created to monitor the Traffic types listed in the following table.
Traffic Type |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Services |
Shows the current status view about Services used through the selected gateway. |
IPs/Network Objects |
Shows the current status view about active IPs/Network Objects through the selected gateway. |
Security Rules |
Shows the current status view about the most frequently used Firewall rules. The Name column in the legend states the rule number as previously configured in SmartConsole. |
Interfaces |
Shows the current status view about the Interfaces associated with the selected gateway. |
Connections |
Shows the current status view about current connections initiated through the selected gateway. |
Tunnels |
Shows the current status view about the Tunnels associated with the selected gateway and their usage. |
Virtual Link |
Shows the current traffic status view between two gateways (for example, Bandwidth, Bandwidth Loss, and Round Trip Time). |
Packet Size Distribution |
Shows the current status view about packets according to the size of the packets. |
QoS |
Shows the current traffic level for each QoS rule. |
The values that you see in the legend depend on the Traffic view that you run.
All units in the view results show in configurable Intervals.
Monitoring System Counters provides in-depth details about Check Point Software Blade usage and activities. As a network administrator you can generate system status information about:
When a Traffic or System Counters view runs, the results show in the SmartView Monitor client. A Traffic or System Counter view can run:
To run a Traffic or System Counters view:
A list of available gateways shows.
The results of the selected view show in the SmartView Monitor client.
You can save a record of the Traffic or System Counter view results.
To record a traffic or counter view:
A Save As window shows.
The word Recording shows below the Traffic or Counter toolbar. The appearance of this word signifies that the view currently running is recorded and saved.
A record of the view results is saved in the directory you selected in step 3 above.
After you record a view, you can play it back. You can select Play or Fast Play, to see results change faster.
To play the results:
The Select Recorded File window shows.
The results of the selected recorded view start to run. The word Playing shows below the toolbar.
The User Monitor is an administrative feature. This feature lets you to keep track of Endpoint Security VPN users currently logged on to the specific Security Management Servers. The User Monitor provides you with a comprehensive set of filters which makes the view definition process user-friendly and highly efficient. It lets you to easily navigate through the obtained results.
With data on current open sessions, overlapping sessions, route traffic, connection time, and more, the User Monitor gives detailed information about connectivity experience of remote users. This SmartView Monitor feature lets you view real-time statistics about open remote access sessions.
If specific data are irrelevant for a given User, the column shows N/A for the User.
When you run a Users view, the results show in the SmartView Monitor client:
A Users view can be created and run for:
To run a user view for a specified user:
The User DN Filter window opens.
The view results show in the Results View.
To run a user view for all users or Mobile Access users:
The view results show in the Results View.
To run a user view for a specified Gateway:
The Select Gateway window shows.
The view results show in the Results View.
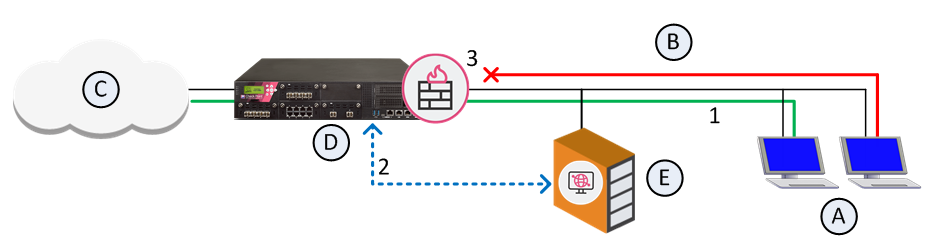
Cooperative Enforcement works with Check Point Endpoint Security Management Servers. This feature utilizes the Endpoint Security Management Server compliance function to make sure connections that come from different hosts across the internal network.
Endpoint Security Management Server is a centrally managed, multi-layered endpoint security solution that employs policy based security enforcement for internal and remote PCs. The Endpoint Security Management Server mitigates the risk of hackers, worms, spyware, and other security threats.
Features such as policy templates and application privilege controls enable administrators to easily develop, manage, and enforce Cooperative Enforcement.
With Cooperative Enforcement, a host that initiates a connection through a gateway is tested for compliance. This increases the integrity of the network because it prevents hosts with malicious software components to access the network.
Cooperative Enforcement acts as a middle-man between hosts managed by an Endpoint Security Management Server and the Endpoint Security Management Server itself. It relies on the Endpoint Security Management Server compliance feature. It defines if a host is secure and can block connections that do not meet the defined prerequisites of software components.
|
Unauthorized |
|
|
Authorized |
|
If the client is non-compliant and Cooperative Enforcement is not in Monitor-only mode, the connection is closed.
Cooperative Enforcement is not supported by all the NAT configurations.
For Cooperative Enforcement to work in a NAT environment, the gateway and the Endpoint Security Server must recognize the same IP address of a client. If NAT causes the IP address received by gateway to be different than the IP address received by the Endpoint Security Server, Cooperative Enforcement will not work.
To configure Cooperative Enforcement:
From the gateway Cooperative Enforcement page, click Authorize clients using Endpoint Security Server to enable Cooperative Enforcement.
If Monitor Only is not selected, Cooperative Enforcement works in Enforcement mode. The Endpoint Security Firewall blocks non-compliant host connections. For HTTP connections, the client is notified that its host is non-compliant. The user can change the computer to make compliant. For example, the user can upgrade the version of the Endpoint Security client.
The Non-Compliant Hosts by Gateway view lets you to see Host IPs by Endpoint Security Management Server compliance: