

In This Section: |
Deploy Check Point Security Gateways with enabled Identity Awareness Software Blade for better security for your network environment and corporate data. This section describes recommended deployments with Identity Awareness.
Important - NAT between two Identity Awareness Security Gateways that share data with each other is not supported.
You can deploy an Identity Awareness Gateway in two different network options:
IP routing mode - This is a regular and standard method used to deploy Identity Awareness Gateways. You usually use this mode when you deploy the Identity Awareness Gateway at the perimeter. In this case, the Identity Awareness Gateway behaves as an IP router that inspects and forwards traffic from the internal interface to the external interface and vice versa. Both interfaces should be located and configured using different network subnets and ranges.
Transparent mode - Known also as a "bridge mode". This deployment method lets you install the Identity Awareness Gateway as a Layer 2 device, rather than an IP router. The benefit of this method is that it does not require any changes in the network infrastructure. It lets you deploy the Identity Awareness Gateway inline in the same subnet. This deployment option is mostly suitable when you must deploy an Identity Awareness Gateway for network segregation and Data Center protection purposes.
Best Practice - If you want to evaluate how Identity Awareness operates in a Security Gateway, we recommend that you deploy it in a simple environment. The recommended test setup below gives you the ability to test all identity sources and create an identity-based Policy.
The recommendation is to install 3 main components in the setup:
Deploy the Security Gateway in front of the protected resource, the Windows server that runs IIS (web server). The user host computer will access the protected resource via the Security Gateway.
Enable and configure Identity Agents, and configure Identity Agents self-provisioning through Captive Portal.
You are redirected to the Captive Portal.
When the client is installed wait for an authentication pop-up to enter the user credentials through the client.
Security Challenge
The Security Gateway at the perimeter behaves as a main gate for all incoming and outgoing traffic to and from your corporate network. Users in internal networks access the Internet resource and applications daily. Not all Internet applications and web sites are secure and some are restricted according to corporate policy. If you block all internal access, it will affect productivity of employees that must have access as part of their daily work definition. You can control access to allowed applications with the Application Control blade. However, you require a more granular access policy for user and computer identity.
Access roles let you configure an identity aware policy with Application Control, to allow access only to specified user groups to the applications on the Internet.
Enable Identity Awareness on the perimeter Security Gateway.
Deployment scenario
Optional: You can define another internal interface, which protects DMZ servers.
Best Practice - We recommend that the Proxy server be in the DMZ network.
See the R80.20 Next Generation Security Gateway Administration Guide.
Configuration
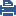
This is a sample diagram for a small to medium corporate headquarters.
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Corporate data center |
2 |
Identity Awareness Gateway protects the data center |
3 |
Perimeter Identity Awareness Gateway User IDs are sent to the gateway that protects the data center |
4 |
Internal network resources |
5 |
LDAP server (for example Active Directory) |
6 |
Internet |
Security Challenge
The Data Center contains sensitive corporate resources and information that you must securely protect from unauthorized access. You must also protect it from malwares and viruses that can harm databases and steal corporate information. Access to the Data Center and particularly to certain applications must be granted only to compliant users and computers.
Deployment Scenario
Configuration
Security Challenge
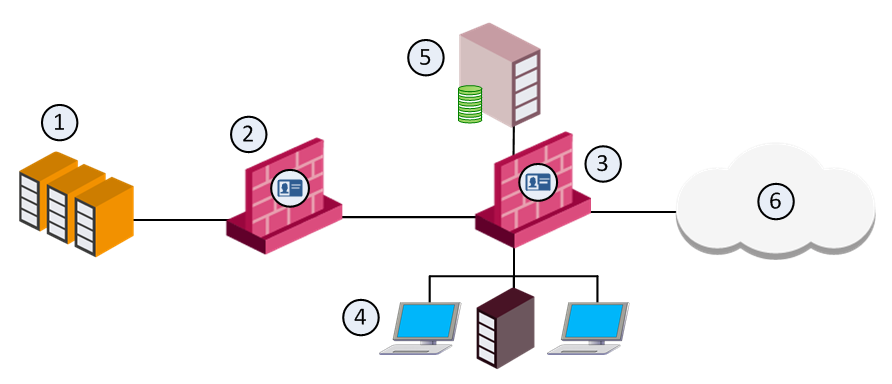
In complex large-scale enterprise networks, you must control access from the local network to the Internet and to multiple Data Center resources. The Data Center contains sensitive corporate resources and information that must be securely protected from unauthorized access. Grant access only to policy-compliant users and computers. Protect your network and Data Center from malware, bots, and viruses.
Users in the internal networks access Internet resources and applications daily. Not all Internet applications and web sites are secure, and some are restricted by the corporate policy. If you block all internal access, it will affect productivity of employees who must have access in the context of their daily work definition. You can control access to the allowed applications with the Application Control blade. If you require a granular access policy based on user and computer identity, use Access Roles with Application Control.
Deployment Scenario
Configuration
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Corporate data centers |
2 |
Identity Awareness Gateway protects the data center |
3 |
Perimeter Identity Awareness Gateway User IDs are sent to the gateways that protect the data centers |
4 |
Internal network resources |
5 |
LDAP server (for example Active Directory) |
6 |
Internet |
Best Practice - AD Query Recommended Configuration
When you enable AD Query to obtain user and computer identity, we recommend that you enable the feature on all Security Gateways that participate in the network environment. All Security Gateways should have the Active Directory domain defined with the list of all applicable domain controllers in the internal network.
Best Practice - Identity Agents Recommended Configuration
If you choose to use Identity Agents to authenticate users and computers, you have to select the Security Gateway that will be used to maintain Identity Agents.
For a single Data Center and perimeter Security Gateway, we recommend that you define Identity Agents that connect to a single Security Gateway. Then the identity obtained by the Security Gateway is shared with the other Security Gateways in the network. Select a high capacity / performance Security Gateway, which can also behave as an authentication server, and configure this Security Gateway’s IP / DNS on the Identity Agents (see Identity Agents section).
For complex multi Data Center environments, where there are several Security Gateways that protect different Data Centers and the perimeter, we recommend that you balance Identity Agents authentication using different Security Gateways. You can configure a list of Security Gateways in the Identity Agent settings, where the Identity Agent will connect to different Security Gateways. This provides load balancing across the Security Gateways. Identities learned from the agents are shared between all Security Gateways in the network.
To define a list of Security Gateways, between which identity information is shared:
Security Challenge
Networks consist of different network segments and subnets where your internal users reside. Users that connect to the network can potentially spread viruses and malwares across the network that can infect other computers and servers on the network. You want to make sure that only compliant users and computers can pass and connect across multiple network segments, as well as authenticate users connecting to the servers and the Internet.
Deployment scenario
Configuration
If there is a general domain controller that serves all users across the segments, make sure that all Security Gateways can connect to this domain controller.
If you want to share identities with one Security Gateway, for example, the perimeter Security Gateway, keep this option selected and disable Get identities from other gateways in the segment Security Gateway. Then go to the perimeter Security Gateway and select Get identities from other gateways.
Security Challenge
In distributed enterprises, there is a potential risk of malware and viruses spreading from remote branch offices over VPN links to the corporate internal networks. There is also a challenge of how to provide authorized access to users that come from remote branch offices that request and want to access the Data Center and the Internet.
Deployment Scenario
Deploy the remote branch Security Gateways in IP routing mode and have them function as a perimeter Firewall and VPN gateway, establishing a VPN link to the corporate Security Gateways.
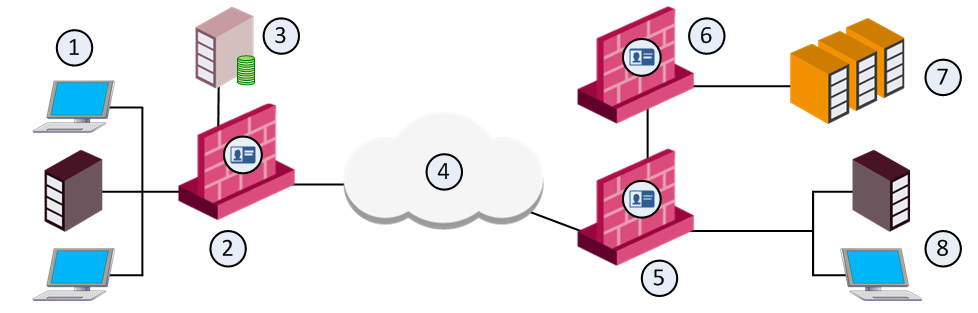
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Internal network resources - branch office |
2 |
Branch Identity Awareness Gateway User IDs are sent to the corporate gateways |
3 |
LDAP server (for example Active Directory) |
4 |
Internet |
5 |
Perimeter corporate Identity Awareness Gateway |
6 |
Identity Awareness Gateway that protects the data center |
7 |
Corporate data center |
8 |
Internal network resources - corporate office |
Configuration
Best Practice - AD Query Recommended Configuration
When you use AD Query to authenticate users from the local and branch offices, we recommend that you only configure a local domain controller list per site in the relevant Security Gateways. For example, if you have a branch office Security Gateway and a Data Center Security Gateway, enable AD Query on all Security Gateways. On the branch office Security Gateway, select the Active Directory domain controllers replications installed in the branch office only. On the Data Center Security Gateway, configure a list of domain controllers installed in the internal headquarters network.
It is not necessary to configure all domain controllers available in the network, since the identity information is shared between branch and internal Security Gateways accordingly.
Best Practice - Identity Agents Recommended Configuration
When using Identity Agents, we recommend that you configure the local branch office Security Gateway DNS/IP on the agent. The agents connect to the local Security Gateway and the user is authenticated, identities are shared with the internal headquarters Security Gateways.
Security Challenge
You use wireless networks to grant access to employees that use Wi-Fi enabled devices, guests and contractors. Guests and contractors in some cases cannot use the corporate wired network connection and must connect through WLAN. Furthermore, it is not intended for guests and contractors to install any endpoint agents on their devices.
Wireless access is also intensively used to connect mobile devices such as smartphones where agents can be installed. These devices are not part of the Active Directory domain. Wireless networks do not give a desired level of security in terms of network access.
Deployment Scenario
Configuration
Security Challenge
You have several Security Gateways that protect the Data Center or Internet access where access is based on identity acquisition. The Security Gateways run different blades and deal with heavy traffic inspection.
To avoid an impact on performance of the Security Gateways in terms of user identity acquisition and authentication, it is possible to offload this functionality to a separate Security Gateway. The dedicated Security Gateway is responsible for acquiring user identity, performing authentication and sharing learned identities with all Security Gateways in the network.
Deployment Scenario
In this deployment scenario, you have to choose an appropriate appliance to deploy as the dedicated Identity Awareness Security Gateway. All users authenticate with this Security Gateway.
If you enable AD Query, the dedicated Security Gateway should communicate with all Active Directory domain controllers over WMI.
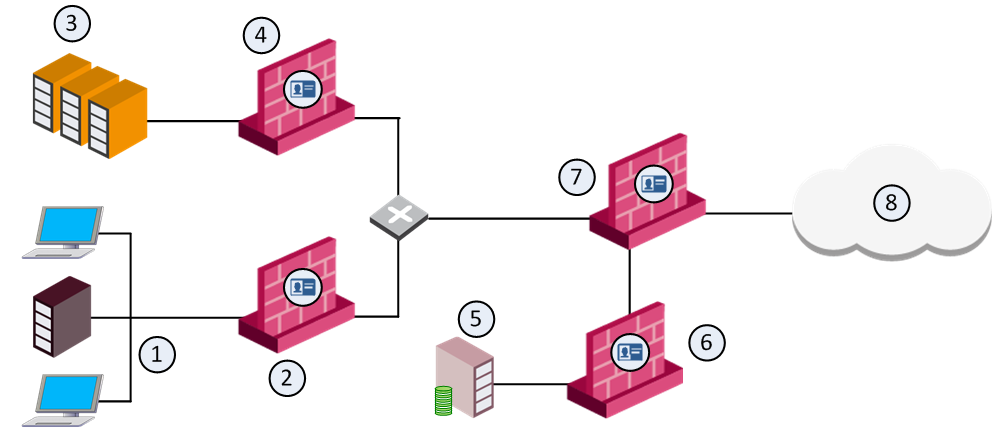
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Internal network resources |
2 |
Identity Awareness Gateway that protects the internal network User IDs are sent to the corporate gateways |
3 |
Corporate data center |
4 |
Identity Awareness Gateway that protects the data center |
5 |
LDAP server (for example Active Directory) |
6 |
Dedicated Identity Awareness Security Gateway |
7 |
Perimeter corporate Identity Awareness Gateway |
8 |
Internet |