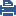


AD Query is an easy to deploy, clientless identity acquisition tool. It is based on Active Directory integration, and it is completely transparent to the user.
AD Query works when:
The technology is based on querying the Active Directory Security Event Logs and extracting the user and computer mapping to the network address from them. It is based on Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), a standard Microsoft protocol. The Identity Awareness Gateway communicates directly with the Active Directory domain controllers and does not require a separate server.
No installation is necessary on the clients, or on the Active Directory server.
AD Query extracts user and computer identity information from the Active Directory Security Event Logs. The system generates a Security Event Log entry when a user or a computer accesses a network resource. For example, this occurs when a user logs in, unlocks a screen, or accesses a network drive. Security Event Logs are not generated when a user logs out because Active Directory cannot detect this action.
When you work with AD Query, it is important that you understand and comply with these limitations:
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Identity Awareness Gateway |
2 |
Active Directory Domain Controller |
3 |
User with Active Directory credentials |
4 |
Network resources |
Flow of events:
@domain), computer name and source IP address).