

Identity Agents are dedicated client agents that are installed on user endpoint computers. These Identity Agents acquire and report identities to the Identity Awareness Gateway. As the administrator, you, not the users, configure these Identity Agents.
There are three types of Identity Agents - Full, Light and Custom:
Identity Agent |
Description |
|---|---|
Full |
Predefined Identity Agent that includes packet tagging and computer authentication. |
Light |
Predefined Identity Agent that does not include packet tagging and computer authentication. |
Custom |
Configure custom features for all computers that use this Identity Agent, such as MAD services and packet tagging. |
Note - Make sure to use the correct Identity Agent for your environment.
This table shows the similarities and differences of the Light and Full Identity Agent types.
|
Identity Agent Light |
Identity Agent Full |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Installation Elements |
Identity Agent format |
Resident application |
Resident application + service + driver |
|||
Installation permissions |
None |
administrator |
||||
Upgrade permissions |
None |
None |
||||
Security Features |
User identification |
SSO |
SSO |
|||
Computer identification |
No |
Yes |
||||
IP change detection |
Yes |
Yes |
||||
Packet tagging |
No |
Yes |
||||
The installation file size is 7MB for both types. The installation takes less than a minute.
Using Identity Agents gives you:
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
User identification |
Users that log in to the Active Directory domain are transparently authenticated (with SSO) and identified when using an Identity Agent. |
Computer identification |
You get computer identification when you use the Full Identity Agent, as it requires installing a service. |
Seamless connectivity |
Transparent authentication using Kerberos Single Sign-On (SSO), when users are logged in to the domain. |
IP change detection |
When an endpoint IP address changes (interface roaming, or DHCP assigns a new IP address), the Identity Agent automatically detects the change and reconnects. |
Added security |
You can use the patented packet tagging technology to prevent IP Spoofing. |
Packet tagging |
A technology that prevents IP spoofing is available only for the Full Identity Agent, as it requires installing a driver. |
IP Spoofing happens when an unauthorized user assigns an IP address of an authenticated user to an endpoint computer. By doing so, the user bypasses identity access enforcement rules. It is also possible to poison ARP tables that let users do ARP "man-in-the-middle attacks" that keep a continuous spoofed connectivity status.
To protect packets from IP spoofing attempts, you can enable Packet Tagging. Packet Tagging is a patent pending technology that prevents spoofed connections from passing through the Identity Awareness Gateway. This is done by a joint effort between the Identity Agent and the Identity Awareness Gateway that uses a unique technology that sign packets with a shared key.
To see Packet Tagging logs in SmartConsole:
blade:"Identity Awareness"
You can also click Queries > Predefined > Access > Identity Awareness Blade > All.
The Successful status indicates that a successful key exchange happened.
Note - Packet Tagging can only be set on computers installed with the Full Identity Agent.
To enable IP Spoofing protection:
Users download the Identity Agent from the Captive Portal and then authenticate to the Identity Awareness Gateway.
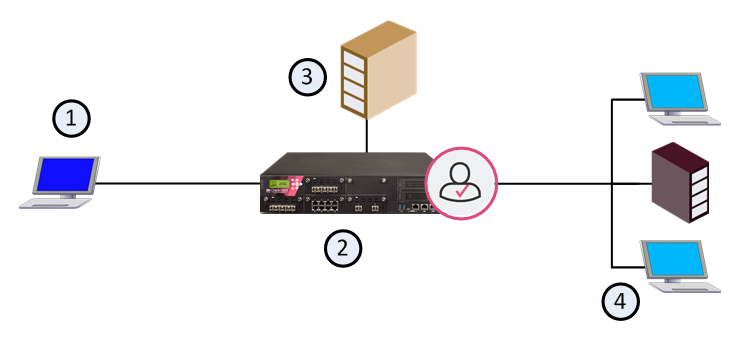
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
User that is trying to connect to the internal network |
2 |
Identity Awareness Gateway |
3 |
Active Directory domain controller |
4 |
Internal network |
This is a high-level overview of the Identity Awareness authentication process:
Note - If SSO with Kerberos is configured, the user is automatically connected.