

In This Section: |
Security Gateways enforce Security Policies on traffic that passes through the Security Gateways in the network. Remote clients are located outside of the protected network and traffic to the remote clients does not pass through the Security Gateways. Therefore remote clients are vulnerable to attack.
Attackers can also use unprotected remote access clients to access the protected network, through the VPN tunnel.
Check Point clients that include Desktop Security, such as Endpoint Security VPN, enforce a Desktop Security Policy on the client to give it Firewall protection. The administrator defines the Desktop Security Policy in the Desktop Rule Base in SmartDashboard. You can assign rules to specified user groups or to all users.
The Security Management Server downloads the Desktop Security Policy to a Policy Server, which is a feature that you enable on the Remote Access Security Gateway. Remote Access Client computers download their Desktop Security Policies from the Policy Server when they connect to the Security Gateway.
Clients enforce the Desktop Policy to accept, encrypt, or drop connections based on the Source, Destination, and Service.
Note - If you use Endpoint Security VPN as part of the Check Point Endpoint Security Suite, you can configure if your client Firewall comes from Desktop Security in SmartDashboard or SmartEndpoint.
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
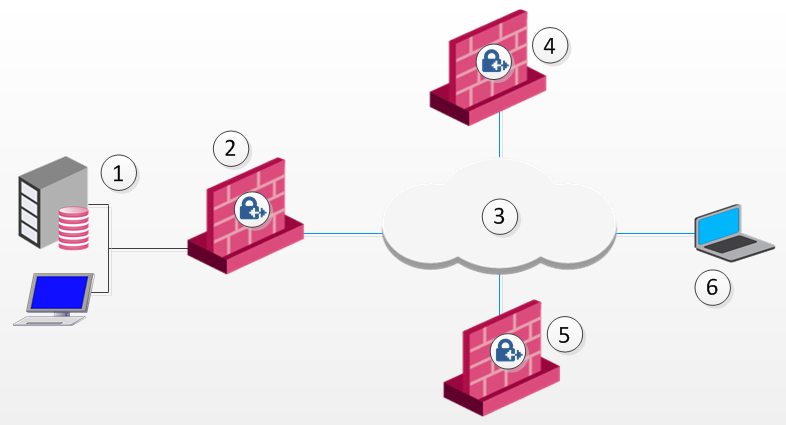
1 |
Security Management Server |
2 |
Firewall |
3 |
Internet |
4 |
Gateway and policy server |
5 |
Security Gateway |
6 |
Remote Access Client |
The Desktop Security Policy has Inbound and Outbound rules.
Each rule defines traffic by source, destination, and service. The rule defines what action to enforce on traffic that matches.
Connections to computers inside of the organization, for example, all of the machines in the VPN domain of the Security Gateway, are automatically encrypted, even if the rule that lets them pass is an Accept rule.
In addition to the rules that you define, the Desktop Security Policy has implicit rules added to the end of the inbound and outbound policies.
You can define different rules for remote users based on locations and user groups.
Rules apply to user groups, not individual users. The client does not identify user groups, so it must get group definitions from the gateway when it connects. The gateway resolves the user groups of the authenticated user and sends this information to the client. The client enforces the rules that apply to the user, based on the user groups.
Rules can also be applied to radius groups on the RADIUS server.
When a client is started, and before it connects to the Policy Server, it enforces a "default policy," which consists of the rules defined for all users in the last policy downloaded from the Policy Server. This is because at this point, the client does not know to which groups the user belongs. The default policy is enforced until the user downloads an updated policy (and the current user's group information) from a Policy server.
If a client loses its connection to the Policy Server, it enforces the default policy until the connection is restored and a Policy is downloaded.
To enable the gateway to be a Policy Server for Desktop Security:
The gateway window opens and shows the General Properties page.
To activate the Desktop Security policy:
The policy window opens.
To configure the Desktop Policy rules:
SmartDashboard opens and shows the Desktop tab.
In inbound rules, the client computer (the desktop) is the destination. Select user groups to which the rule applies.
In outbound rules, the client computer (the desktop) is the source. Select user groups to which the rule applies.
Make sure that you install the Advanced Security policy on the Security Gateways and the Desktop Security policy on your Policy Servers.
Define the Desktop Security Policy. Rules are managed in order: what is blocked by a previous rule cannot be allowed later.
The right-click menus of the Rule Base include these options:
If clients use active FTP, you must add a rule to the Desktop Security Policy to specifically allow the service that you need. Select be one of the active FTP services that is not ftp-pasv.
To add the Active FTP Rule:
A Policy Server is installed on a Security Gateway, when you enable it in the Gateway General Properties > Network Security tab. It serves as a repository for the Desktop Security Policy. Client machines download their Desktop Security Policies from the Policy Server.
When the client computer connects or re-authenticates to the site, it automatically checks the Policy Server for updates and downloads them.
Location-based policies add location awareness support for the Desktop Firewall using these policies:
disconnected_in_house_fw_policy_mode property). Location-Based Polices for Desktop Firewall are disabled by default.
The Location Awareness configuration is based on these properties in the client configuration file:
Possible values are:
Possible values are:
To enable Location Awareness for desktop firewall:
$FWDIR/conf/trac_client_1.ttm.disconnected_in_house_fw_policy_enabled entry to the file::disconnected_in_house_fw_policy_enabled ( :gateway (disconnected_in_house_fw_policy_enabled :default (true) ) ) |
To configure the location based policy:
$FWDIR/conf/trac_client_1.ttm.disconnected_in_house_fw_policy_mode entry to the file: :disconnected_in_house_fw_policy_mode ( :gateway (disconnected_in_house_fw_policy_mode :default (encrypt_to_allow) ) ) |
Note - It is highly recommended to configure default values for these properties in trac_client_1.ttm for all gateways.
Desktop Security logs are saved locally on the client computer in:
C:\Program Files\CheckPoint\Endpoint Connect\trac_fwpktlog.log C:\Program Files(x86)\CheckPoint\Endpoint Connect\trac_fwpktlog.log Alerts are saved and uploaded to the Security Management Server when the client connects. You can see alerts in the Logs tab in the SmartConsole Logs & Monitor view.
By default, the desktop firewall allows IPv6 traffic to the client.
To block IPv6 traffic to the client:
$FWDIR/conf/trac_client_1.ttm
:allow_ipv6 ( :gateway (allow_ipv6 :default (false) ) ) |
Desktop Policy can support wireless hotspots.
A proxy might be required.
Plan your Desktop Security policy to balance considerations of security and convenience. You want to let users work as freely as possible, but at the same time, make it hard to attack the remote user's computer. Important points: