

In This Section |
When dealing with mission-critical applications, an enterprise requires its network to be highly available.
Clustering provides redundancy, and thus, High Availability, at the Security Gateway level. Without Bonding, redundancy of Network Interface Cards (NICs) or of the switches on either side of the Security Gateway are only possible in a cluster, and only by failover of the Security Gateway to another Cluster Member.
You can have redundancy of clustering without Bonding. If a switch or Cluster Member fails, a High Availability cluster solution provides system redundancy. For example, you can have a redundant system with two synchronized Cluster Members deployed in a simple redundant topology.
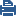
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Cluster Member GW1 with interfaces connected to the external switches (items 5 and 6) |
2 |
Cluster Member GW2 with interfaces connected to the external switches (items 5 and 6) |
3 |
Interconnecting network C1 |
4 |
Interconnecting network C2 |
5 |
Switch S1 |
6 |
Switch S2 |
If Cluster Member GW1 (item 1), its NIC, or switch S1 (item 5) fails, Cluster Member GW2 (item 2) becomes the only Active member, connecting to switch S2 (item 6) over network C2 (item 4). If any component fails (Cluster Member, NIC, or switch), the result of the failover is that no further redundancy exists. A further failure of any active component completely stops network traffic through this cluster.
The Bonding High Availability mode, when deployed with ClusterXL, enables a higher level of reliability by providing granular redundancy in the network. This granular redundancy is achieved by using a fully meshed topology, which provides for independent backups for both NICs and switches.
A fully meshed topology further enhances the redundancy in the system by providing a backup to both the interface and the switch, essentially backing up the cable. Each Cluster Member has two external interfaces, one connected to each switch.
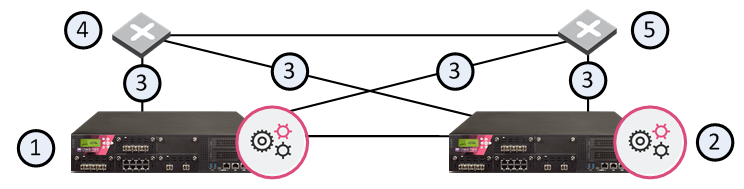
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Cluster Member GW1 with interfaces connected to the external switches (items 4 and 5) |
2 |
Cluster Member GW2 with interfaces connected to the external switches (items 4 and 5) |
3 |
Interconnecting network |
4 |
Switch S1 |
5 |
Switch S2 |
In this scenario:
If any of the interfaces on a Cluster Member that connect to an external switch fails, the other interface continues to provide the connectivity.
If any Cluster Member, its NIC, or switch fails, the other Cluster Member, connecting to switch S2 over network C2. If any component fails (Cluster Member , NIC, or switch), the result of the failover is that no further redundancy exists. A further failure of any active component completely stops network traffic.
Bonding provides High Availability of NICs. If one fails, the other can function in its place.
In Bonding High Availability mode, when the Security Gateway is part of a cluster, bond internal failover can occur in one of these cases:
Either of these failures will induce a failover within the interface bond, or between Cluster Members, depending on the circumstances.
When a failure is detected, a log is recorded. You can see it in SmartConsole > Logs & Monitor > Logs.
Follow the instructions in the R80.10 Gaia Administration Guide - Chapter Network Management - Section Network Interfaces - Section Bond Interfaces (Link Aggregation).
Make sure that the bond interface is UP, by displaying the bond information.
cphaprob -am if
Make sure that the bond status is reported as UP.
cphaconf show_bond <Name of Bond>
Check that the bond is correctly configured.
In Bonding High Availability mode, ClusterXL monitors VLAN IDs for connectivity failure or miscommunication, and initiate a failover when a failure is detected.
In a VLAN-enabled switched environment, ClusterXL monitors the VLAN with the lowest ID number. The monitoring is conducted by sending ClusterXL Control Protocol (CCP) packets on round-trip paths at a set interval. The lowest VLAN ID indicates the status of the physical connection. This VLAN ID is always monitored, and a connectivity failure causes ClusterXL to initiate a failover. ClusterXL will not detect a VLAN configuration problem on the switch.
The use of more than one physical synchronization interface (1st sync, 2nd sync, 3rd sync) for synchronization redundancy is not supported.
For synchronization redundancy, you can use bond interfaces.
Requirements and Limitations:
To configure bond interfaces for sync High Availability:
cphaprob -am if