Monitoring Traffic
Monitoring Events using SmartView Tracker
After initial configuration of IPS, monitor traffic with SmartView Tracker. The information you gain here will help you understand how to change the IPS configuration for optimal security and connectivity.
SmartView Tracker offers a number of queries that can help you focus on the events that most interest you.
- Most Important - events for protections with Severity values of High or Critical and Confidence Level values of Medium-high or High. These events typically require the most attention.
- Critical Not Prevented - events for protections with a Severity value of Critical but are set to Detect.
- All - all IPS events.
- Protocol Anomaly - events for Protocol Anomaly protections.
- Follow Up - events for protections marked for Follow Up.
- Application Control - events for Application Control protections.
Viewing IPS Events
To view the logs that result from IPS activity:
- In , select > .
- In the tab, expand > > .
- Double-click .
The events log displays all events that were generated by the IPS Blade, including information about the data, the protection and the action taken
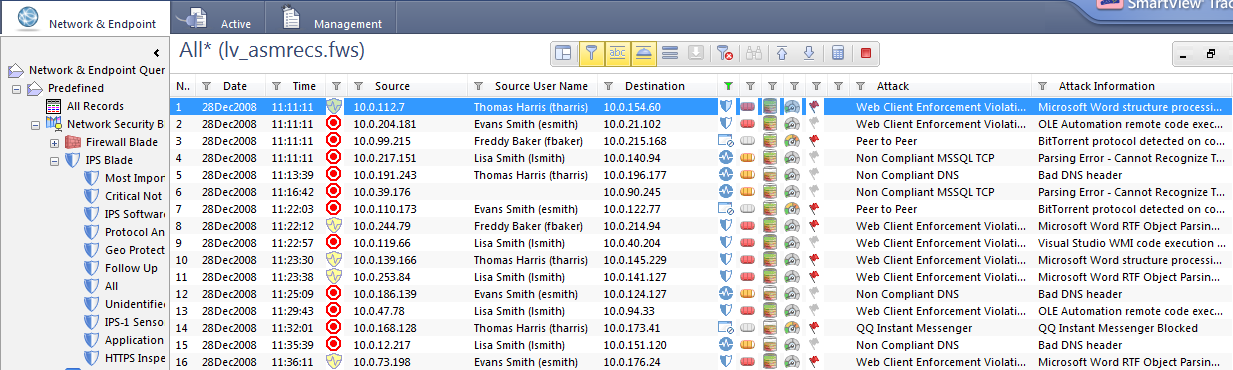
Viewing IPS Event Details
To view details about the event:
- In a records list in SmartView Tracker, double-click on the event that you want more information about.
The Record Details window opens.
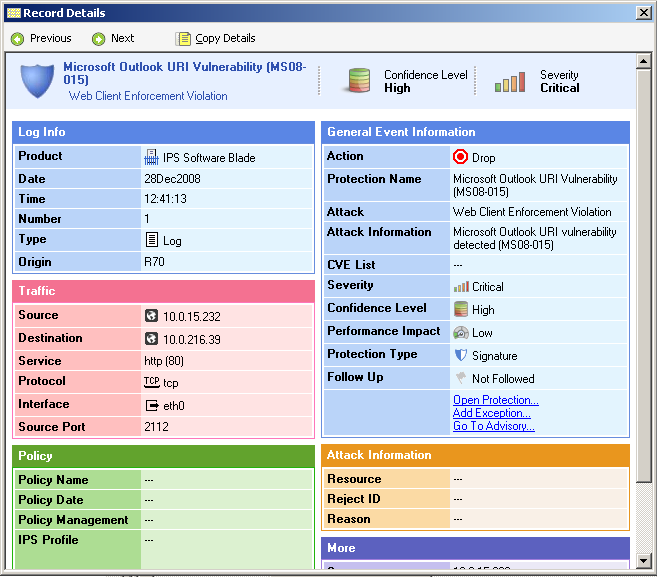
Opening Protection Settings
To open the protection from a SmartView Tracker log item:
- Right-click on the event and select Go to Protection.
SmartDashboard opens to the specific protection in the IPS tab.
Working with Packet Information
If you are familiar with network protocols, you can view packets that were tracked by IPS using an internal viewer or a third-party packet capture application. This can help you understand the nature of the attack.
Capturing a Packet for Every Log
To capture packet data for a protection for every malicious packet that is logged, turn on the packet capture option in that protection. This attaches a packet capture to every log generated by the protection.
Automatic Packet Capture in the First Log
Captured malicious traffic is automatically attached to the first log generated by a protection since policy installation, even if the packet capture option in the protection is not turned on. This is economical with system resources because only one packet capture is saved for each attack.
Attaching a Packet Capture to Every Log
A packet capture is automatically attached to the first log generated by a protection. However, if you want to capture packet data for a protection for every malicious packet that is logged, turn on the packet capture option in that protection.
To attach a packet capture to every log
- Open the protection for which you want to track the packet data.
- Make sure the protection is activated (either Detect or Prevent).
- Double-click on the profile for which you want packet capture data.
- In the Action area, select any tracking action other than None and then select Capture Packets.
Viewing Packet Capture Data in SmartView Tracker
A packet capture is automatically attached to the first packet logged by a protection since policy installation. If packet capture is turned on for a protection, a packet capture is attached to every log generated by the protection.
To view packet captures in SmartView Tracker:
- From the protection page that has selected, click .
SmartView Tracker opens. Wait until the log window for the specific protection opens.

|
Note - SmartView Tracker displays the current log file. If you have performed a log switch and the capture is in a different file, open that log file instead.
|
- If searching for automatically captured packets, make sure the column is showing.
- Locate the item
- Right-click the item in the protection's SmartView Tracker log and select .
- Select and click .
You may also use a third-party packet capture application by selecting and specifying the application in the field.
Allowing Traffic using Network Exceptions

|
Note - Network Exceptions are only supported on R70 gateways and above.
|
Viewing Network Exceptions
You can configure exceptions for a protection in order to prevent certain traffic from being identified by that specific protection. This may be useful when traffic that is legitimate for some machines or services meets the criteria set in the protection as being an attack, or when using a server that does not comply with RFC standards.
In IPS, right-click an IPS item and select Exception. The Network Exceptions window appears, displaying the exceptions that apply to that specific protection.
Configuring Network Exceptions
You can configure exact, particularized exceptions to an IPS protection on a profile or for all gateways of a similar version. This can be done from one of the following locations in SmartDashboard:
- Network Exceptions - the exception can be specified for any protection, gateway, and/or traffic definition.
- Protection - the exception can be specified for this protection, but can be applied to any gateway and/or traffic definition.
- SmartView Tracker - by right-clicking a log entry, a network exception can be made to apply to this specific traffic definition, but can be applied to any protection and/or gateway.
For example, let's assume you have created a number of profiles and activated the relevant protections. Afterwards, you decide that a specific gateway should allow instant messaging. The profile of this gateway blocks instant messaging, and other gateways have the same profile. You can make an exception for the one gateway without creating another profile or changing your requirements.
To configure an exception:
- Open the Network Exceptions page.
- Click New.
The Add/Edit Exception Rule window opens.
- From the Profile drop-down list, select an existing profile to which this exception will be added, or select Any, to apply the network exception to all profiles.
- In the Scope area, select the protection that will be affected by this exception:
- All supported protections: IPS will exclude traffic from inspection based on source, destination, or service; this effectively turns off IPS inspection for the traffic that matches the exceptions. Protections that do not support the Network Exceptions feature will not be affected.
- Single enforcement: Click Select and select a protection. This selected protection will not inspect traffic that matches the exceptions, even if it is activated in the profile.
- Define the Source and Destination:
Select Network Object and then click Manage; or select IP Address and provide the IP Address in the field.
- Define the Service:
- Leave Any selected if this exception is to be applicable to all services on provided Source or Destination.
- Click Manage and select a service to allow traffic of this service to be passed without exception.
- Select the gateways on which this exception is to be installed:
- Apply this exception on all R70 gateways (and above): The exception will be applied to all matching gateways.
- Apply this exception on: From the drop-down list of gateways of version R70 and above, select a single gateway.
- Add a comment for management and click OK.
Tip: When creating a Network Exception, you define a rule that includes Source, Destination, and Service. If you set all three of these parameters to Any, you are essentially deactivating the protection. If this is what you want, you should not create the Network Exception; you should deactivate the protection from its page. When the protection is set to Inactive from its page, it is easy to see its action mode, to understand why its traffic is not blocked, and to change the action if needed. If a protection is deactivated by a Network Exception, it may appear to be activated while not actually protecting your environment.
Tracking Protections using Follow Up
The Follow Up mark provides monitoring features for IPS protections: one-stop page for protections to monitor, quick view of protection parameters, and easy access to newly updated protections.
To view protections marked for Follow Up:
Select Follow Up in the IPS tree.
Marking Protections for Follow Up
This section covers the different ways in which to mark protections for follow up.
Marking Protections from Follow Up Page
You can mark individual protections for Follow Up, allowing you to quickly review the identified protections in the Follow Up screen. The date and time when the protection was marked for Follow Up is added to the Follow Up Comment field, but you can also edit the field to add any other significant information.
To mark more protections from the Follow Up page:
- In the Follow Up page, click Mark.
The Select Protection window opens. Here you may select a single protection; you cannot select categories or settings.
- Select the protection you want to mark for Follow Up.
- Click OK.
The Follow Up Comment window opens.
- Edit the comment, if you want. By default, it shows that the protection was marked for Follow Up (manually) on the current date and time.
- Click OK.
Marking Protections from Protection Details
As you access protection pages, you can mark a protection for Follow Up. This will ensure that the protection is listed in the Follow Up page; and for profiles that are configured to set marked protections to Detect, the protection will be in Detect mode while you monitor its effects.
To mark a protection for Follow Up from the protection details:
- In the protection details, click Follow Up.
- In the menu that appears, click Mark for Follow Up.
The Follow Up Comment window opens.
- Edit the comment, if you want. By default, it shows that the protection was marked for Follow Up (manually) on the current date and time.
- Click OK.
Automatically Marking New Protections for Follow Up
Check Point provides new and updated protections as they become available (see Updating Protections). To give you complete control over the process of integrating new IPS protections, you can have them automatically marked for Follow Up and set to Detect, giving you time to evaluate the impact the protections will have on your environment.
To have new protections automatically marked:
- In the Follow Up page, select the Mark newly downloaded protections for Follow Up checkbox.
Unmarking Protections for Follow Up
To make the Follow Up feature efficient, make sure to keep the list of marked protections as short as possible. Do mark newly downloaded protections and any protection that you want to monitor; but remember to remove protections from this list when you are more confident that you have configured them in the best way for your environment, for now. The longer the Follow Up list is, the more difficult it will be to use it as a workable task list.
Unmarking Protections from Follow Up Page
To unmark individual protections from the Follow Up page:
- In the Follow Up page, select a protection and click Unmark.
A message appears:
This action will remove the Follow Up state from <protection>. Are you sure?
- Click Yes.
To unmark all protections:
- In the Follow Up page, click View > Unmark All.
- In the confirmation dialog box that opens, click Yes.
All protections are unmarked; the Follow Up list is empty.
Unmarking Protections from Protection Details
The following are the functions that can be performed from the Protection Details window:
- Click the Unmark link to unmark a protection and remove it from the Follow Up list.
- Click the Undo link to change back to being marked.
- Click the Hide link to remove the "Follow Up Removed" banner.
HTTP Inspection on Non-Standard Ports
Applications that use HTTP normally send the HTTP traffic on TCP port 80. Some applications send HTTP traffic on other ports also. You can configure some Software Blades to only inspect HTTP traffic on port 80, or to also inspect HTTP traffic on non-standard ports.
When selected, IPS inspects all HTTP traffic, even if it is sent using non-standard ports. This option is cleared by default. You can configure this option in the Advanced section of the IPS tab.
HTTPS Inspection
You can enable HTTPS traffic inspection on Security Gateways to inspect traffic that is encrypted by the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol. SSL secures communication between internet browser clients and web servers. It supplies data privacy and integrity by encrypting the traffic, based on standard encryption ciphers.
However, SSL has a potential security gap. It can hide illegal user activity and malicious traffic from the content inspection of Security Gateways. One example of a threat is when an employee uses HTTPS (SSL based) to connect from the corporate network to internet web servers. Security Gateways without HTTPS Inspection are unaware of the content passed through the SSL encrypted tunnel. This makes the company vulnerable to security attacks and sensitive data leakage.
The SSL protocol is widely implemented in public resources that include: banking, web mail, user forums, and corporate web resources.
There are two types of HTTPS inspection:
- - To protect internal servers from malicious requests originating from the internet or an external network.
- - To protect an organization from malicious traffic being sent by an internal client to a destination outside of the organization.
The Security Gateway acts as an intermediary between the client computer and the secure web site. The Security Gateway behaves as the client with the server and as the server with the client using certificates.
All data is kept private in HTTPS Inspection logs. This is controlled by administrator permissions. Only administrators with HTTPS Inspection permissions can see all the fields in a log. Without these permissions, some data is hidden.
How it Operates
In outbound HTTPS inspection, when a client in the organization initiates an HTTPS connection to a secure site, the Security Gateway:
- Intercepts the request.
- Establishes a secure connection to the requested web site and validates the site server certificate.
- Creates a new SSL certificate for the communication between the Security Gateway and the client, sends the client the new certificate and continues the SSL negotiation with it.
- Using the two SSL connections:
- It decrypts the encrypted data from the client.
- Inspects the clear text content for all blades set in the Policy.
- Encrypts the data again to keep client privacy as the data travels to the destination web server resource.
In inbound HTTPS inspection, when a client outside of the organization initiates an HTTPS connection to a server behind the organization's gateway, the Security Gateway:
- Intercepts the request.
- Uses the server's original certificate and private key to initiate an SSL connection with the client.
- Creates and establishes a new SSL connection with the web server.
- Using the two SSL connections:
- It decrypts the encrypted data from the client.
- Inspects the clear text content for all blades set in the policy.
- Encrypts the data again to keep client privacy as the data travels to the destination server behind the gateway.
Configuring Outbound HTTPS Inspection
To enable outbound HTTPS traffic inspection, you must do these steps:
Enabling HTTPS Inspection
You must enable HTTPS inspection on each Security Gateway. From > > > Select .
The first time you enable HTTPS inspection on one of the Security Gateways, you must create an outbound CA certificate for HTTPS inspection or import a CA certificate already deployed in your organization. This outbound certificate is used by all Security Gateways managed on the Security Management Server.
Creating an Outbound CA Certificate
The outbound CA certificate is saved with a P12 file extension and uses a password to encrypt the private key of the file. The Security Gateways use this password to sign certificates for the sites accessed. You must keep the password as it also used by other Security Management Servers that import the CA certificate to decrypt the file.
After you create an outbound CA certificate, you must export it so it can be distributed to clients. If you do not deploy the generated outbound CA certificate on clients, users will receive SSL error messages in their browsers when connecting to HTTPS sites. You can configure a troubleshooting option that logs such connections.
After you create the outbound CA certificate, a certificate object named Outbound Certificate is created. Use this in rules that inspect outbound HTTPS traffic in the HTTPS inspection Rule Base.
To create an outbound CA certificate:
- In SmartDashboard, right-click the Security Gateway object and select Edit.
The Gateway Properties window opens.
- In the navigation tree, select .
- In the HTTPS Inspection page, click .
- Enter the necessary information:
- - Enter the domain name of your organization.
- - Enter the password that is used to encrypt the private key of the CA certificate.
- - Retype the password.
- - Select the date range for which the CA certificate is valid.
- Click .
- Export and deploy the CA certificate.
Exporting a Certificate from the Security Management Server
If you use more than one Security Management Server in your organization, you must first export the CA certificate using the export_https_cert CLI command from the Security Management Server on which it was created before you can import it to other Security Management Servers.
Usage:
export_https_cert [-local] | [-s server] [-f certificate file name under FWDIR/tmp][-help]
To export the CA certificate:
Exporting and Deploying the Generated CA
To prevent users from getting warnings about the generated CA certificates that HTTPS inspection uses, install the generated CA certificate used by HTTPS inspection as a trusted CA. You can distribute the CA with different distribution mechanisms such as Windows GPO. This adds the generated CA to the trusted root certificates repository on client computers.
When users do standard updates, the generated CA will be in the CA list and they will not receive browser certificate warnings.
To distribute a certificate with a GPO:
- From the window of the Security Gateway, click .
Or
From the > pane in a supported blade, click .
- Save the CA certificate file.
- Use the Group Policy Management Console to add the certificate to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities certificate store.
- Push the Policy to the client computers in the organization.
Note - Make sure that the CA certificate is pushed to the client computer organizational unit.
- Test the distribution by browsing to an HTTPS site from one of the clients and verifying that the CA certificate shows the name you entered for the CA certificate that you created in the field.
Deploying Certificates by Using Group Policy
You can use this procedure to deploy a certificate to multiple client machines by using Active Directory Domain Services and a Group Policy object (GPO). A GPO can contain multiple configuration options, and is applied to all computers that are within the scope of the GPO.
Membership in the local Administrators group, or equivalent, is necessary to complete this procedure.
To deploy a certificate using Group Policy:
- Open the Group Policy Management Console.
- Find an existing GPO or create a new GPO to contain the certificate settings. Make sure the GPO is associated with the domain, site, or organization unit whose users you want affected by the policy.
- Right-click the GPO and select .
The Group Policy Management Editor opens and shows the current contents of the policy object.
- Open > > > .
- Click > .
- Do the instructions in the to find and import the certificate you exported from SmartDashboard.
- In the navigation pane, click and repeat steps 5-6 to install a copy of the certificate to that store
Importing an Outbound CA Certificate
You can import a CA certificate that is already deployed in your organization or import a CA certificate created on one Security Management Server to use on another Security Management Server.

|
Note - It is recommended that you use private CA Certificates.
|
For each Security Management Server that has Security Gateways enabled with HTTPS inspection, you must:
- Import the CA certificate.
- Enter the password the Security Management Server uses to decrypt the CA certificate file and sign the certificates for users. This password is only used when you import the certificate to a new Security Management Server.
To import a CA certificate:
- If the CA certificate was created on another Security Management Server, export the certificate from the Security Management Server on which it was created.
- In SmartDashboard, right-click a Security Gateway object, select > >
Or
From the > Gatewayspane of a supported blade, click the arrow next to Create Certificate and select .
The Import Outbound Certificate window opens.
- Browse to the certificate file.
- Enter the .
- Click .
- If the CA certificate was created on another Security Management Server, deploy it to clients.
Configuring Inbound HTTPS Inspection
To enable inbound HTTPS traffic inspection:
- Set the Security Gateway for HTTPS Inspection. From > > , select .
- Import server certificates for servers behind the organization Security Gateways.
- Generate an HTTPS inspection policy. Define relevant rules in the HTTPS inspection Rule Base.
- Configure the relevant server certificate in the HTTPS inspection Rule Base.
Server Certificates
When a client from outside the organization initiates an HTTPS connection to an internal server, the Security Gateway intercepts the traffic. The Security Gateway inspects the inbound traffic and creates a new HTTPS connection from the gateway to the internal server. To allow seamless HTTPS inspection, the Security Gateway must use the original server certificate and private key.
To enable inbound HTTPS inspection:
- Add the server certificates to the Security Gateway. This creates a server certificate object.
- Add the server certificate object to the column in the HTTPS Inspection Policy, to enforce it in rules.
The Server Certificates window in SmartDashboard has these options:
- - Import a new server certificate. Enter a name for the server certificate, optional comment and import the P12 certificate file.
- - Delete a previously added server certificate. This option does not delete the server certificate option. It only removes it from the Server Certificate list.
- - Enter a key word to search for a server certificate in the list.
Adding a Server Certificate
When you import a server certificate, enter the same password that was entered to protect the private key of the certificate on the server. The Security Gateway uses this certificate and the private key for SSL connections to the internal servers.
After you import a server certificate (with a P12 file extension) to the Security Gateway, make sure you add the object to the HTTPS Inspection Policy.
Do this procedure for all servers that receive connection requests from clients outside of the organization.
To add a server certificate:
- In SmartDashboard, open > .
- Click .
The Import Certificate window opens.
- Enter a and a (optional).
- Browse to the certificate file.
- Enter the .
- Click .
The Successful Import window opens the first time you import a server certificate. It shows you where to add the object in the HTTPS Inspection Rule Base. Click if you do not want to see the window each time you import a server certificate and .
The HTTPS Inspection Policy
The HTTPS inspection policy determines which traffic is inspected. The primary component of the policy is the Rule Base. The rules use the categories defined in the Application Database, network objects and custom objects (if defined).
The HTTPS Rule Base lets you inspect the traffic on other network blades. The blades that HTTPS can operate on are based on the blade contracts and licenses in your organization and can include:
- Application Control
- URL Filtering
- IPS
- DLP
- Threat Prevention
If you enable Identity Awareness on your Security Gateways, you can also use Access Role objects as the source in a rule. This lets you easily make rules for individuals or different groups of users.
To access the HTTPS inspection Rule Base:
In SmartDashboard, open the Policy page from the specified blade tab:
- For Application Control and URL Filtering, Anti-Bot, Anti-Virus, and IPS - Select > > .
- For DLP - Select > >.
Predefined Rule
When you enable HTTPS inspection, a predefined rule is added to the HTTPS Rule Base. This rule defines that all HTTPS and HTTPS proxy traffic from any source to the internetis inspected on all blades enabled in the Blade column. By default, there are no logs.

Parts of the Rule
The columns of a rule define the traffic that it matches and if that traffic is inspected or bypassed. When traffic is bypassed or if there is no rule match, the traffic continues to be examined by other blades in the Security Gateway.
Number (No.)
The sequence of rules is important because the first rule that matches is applied.
For example, if the predefined rule inspects all HTTPS traffic from any category and the next rule bypasses traffic from a specified category, the first rule that inspects the traffic is applied.
Name
Give the rule a descriptive name. The name can include spaces.
Double-click in the Name column of the rule to add or change a name.
Source
The source is where the traffic originates. The default is Any.

|
Important - A rule that blockstraffic, with the and parameters defined as , also blocks traffic to and from the Captive Portal.
|
Put your mouse in the column and a plus sign shows. Click the plus sign to open the list of network objects and select one or multiple sources. The source can be an Access Role object, which you can define when Identity Awareness is enabled.
Destination
Choose the destination for the traffic. The default is the , which includes all traffic with the destination of DMZ or external. If you delete the destination value, the rule changes to , which applies to traffic going to all destinations

|
Important - A rule that blockstraffic, with the and parameters defined as , also blocks traffic to and from the Captive Portal.
|
To choose other destinations, put your mouse in the column and a plus sign shows. Click the plus sign to open the list of network objects and select one or multiple destinations.
Services
By default, HTTPS traffic on port 443 and HTTP and HTTPS proxy on port 8080 is inspected. You can include more services and ports in the inspection by adding them to the services list.
To select other HTTPS/HTTP services, put your mouse in the column and a plus sign shows. Click the plus sign to open the list of services and select a service. Other services, such as SSH are not supported.
Site Category
The Site Category column contains the categories for sites and applications that users browse to and you choose to include. One rule can include multiple categories of different types.

|
Important -
- A valid URL Filtering blade contract and license are necessary on the relevant Security Gateways to use the Site Category column.
- To perform categorization correctly, a single connection to a site must be inspected in some cases regardless of the HTTPS inspection policy. This maps the IP address of a site to the relevant domain name.
|
You can also include custom applications, sites, and hosts. You can select a custom defined application or site object with the Custom button or create a new host or site with the New button at the bottom of the page.

|
Note - You can only use custom objects that specify the domain name or host part of a URL. URLs that contain paths are not supported. For example, you can use an object defined as ww.gmail.com but not www.gmail.com/myaccount.
|
To add site categories to a rule:
Put your mouse in the column and a plus sign shows. Click the plus sign to open the Category viewer. For each category, the viewer shows a description and if there are applications or sites related with it.
- To filter the Available list by categories or custom-defined sites, click the specified button in the toolbar of the viewer. The Available list opens in the left column and then you can add items to the rule.
- To add a category object to the rule, click the checkbox in the Available list.
- To see the details of category without adding it to the rule, click the name of the item in the Available list.
- You can only select a category to add to the rule from the Available list.
- If a category is already in a rule, it will not show in the Category viewer.
- If you know the name of a category, you can search for it. The results will show in the Available list.
- You can add a new host site with the New button.
Adding a New Host Site
You can create a new host site object to use in the HTTPS Rule Base if there is no corresponding existing category. Only the domain name part or hosts part of the URL is supported.
To create a new host site:
- Click the plus icon in the Site Category column.
- In the Category viewer, select .
The window opens.
- Enter a name for the host site.
- Set a color for the host site icon (optional).
- Enter a comment for the host site (optional).
- In , enter a valid URL and click .
- If you used a regular expression in the URL, click .
- Click .
The new host site is added to the list and can be added to the Rule Base.
Action
The action is what is done to the traffic. Click in the column to see the options and select one to add to the rule.
- - The traffic is inspected on the blades set in the column.
- - The traffic of source and destination traffic in rules that include the bypass action are not decrypted and inspected. You can bypass HTTPS inspection for all Check Point objects. This is recommended for Anti-Bot, Anti-Virus, URL Filtering, and IPS updates. Other HTTPS protections that already operate on traffic will continue to work even when the HTTPS traffic is not decrypted for inspection.
Track
Choose if the traffic is logged in SmartView Tracker or if it triggers other notifications. Click in the column and the options open. The options include:
- - Does not record the event
- - Records the event details in SmartView Tracker. This option is useful for obtaining general information on your network traffic. There is one or more log for each session depending on the suppression option.
- - Logs the event and executes a command, such as display a popup window, send an email alert or an SNMP trap alert, or run a user-defined script as defined in >>>
- - Sends an email to the administrator, or runs the mail alert script defined in >>>
- - Sends a SNMP alert to the SNMP GUI, or runs the script defined in >>>
- - Sends one of three possible customized alerts. The alerts are defined by the scripts specified in >>>
Blade
Choose the blades that will inspect the traffic. Click in the column and the options open. The options include:
- Application Control
- Data Loss Prevention
- IPS
- URL Filtering
- Anti-Virus
- Anti-Bot

|
Important - The blade options you see are based on the blade contracts and licenses in your organization.
|
Install On
Choose which Security Gateways the rule will be installed on. The default is All, which means all Security Gateways that have HTTPS inspection enabled. Put your mouse in the column and a plus sign shows. Click the plus sign to open the list of available Security Gateways and select.
Certificate
Choose the certificate that is applicable to the rule. The Security Gateway uses the selected certificate for communication between the Security Gateway and the client.
- - choose the object (default) that reflects the CA certificate you created/imported and deployed on the client machines in your organization.
- - choose the server certificate applicable to the rule. Put your mouse in the column and a plus sign shows. Click the plus sign to open the list of available server certificates and select one. When there is a match to a rule, the Security Gateway uses the selected server certificate to communicate with the source client. You can create server certificates from > > .
Bypassing HTTPS Inspection for Software Update Services
Check Point dynamically updates a list of approved domain names of services from which content is always allowed. This option makes sure that Check Point updates or other 3rd party software updates are not blocked. For example, updates from Microsoft, Java, and Adobe.
To bypass HTTPS inspection for software updates:
- In the HTTPS Inspection > Policy pane, select. This option is selected by default.
- Click to see the list of approved domain names.
Enhanced HTTPS Inspection Bypass
Enhanced HTTPS Inspection Bypass lets the gateway bypass traffic to servers that require client certificate authentication and bypass non-browser applications.
This feature is supported on R77.30 and higher gateways.
To enable enhanced HTTPS inspection:
- In the
$FWDIR/boot/modules/fwkern.conf file on the gateway, add:
enhanced_ssl_inspection=1 - Reboot.
You can configure this feature without changing the configuration file, but it does not survive reboot:
In expert mode, run: fw ctl set int enhanced_ssl_inspection 1
Gateways Pane
The pane lists the gateways with HTTPS Inspection enabled. Select a gateway and click Edit to edit the gateway properties. You can also search, add and remove Security Gateways from here.
For each gateway, you see the gateway name, IP address and comments.
In the CA Certificate section, you can the certificate validity date range if necessary and it for distribution to the organization client machines.
If the Security Management Server managing the selected Security Gateway does not have a generated CA certificate installed on it, you can add it with .
- You can import a CA certificate already deployed in your organization.
- You can import a CA certificate from another Security Management Server. Before you can import it, you must first export it from the Security Management Server on which it was created.
Adding Trusted CAs for Outbound HTTPS Inspection
When a client initiates an HTTPS connection to a web site server, the Security Gateway intercepts the connection. The Security Gateway inspects the traffic and creates a new HTTPS connection from the Security Gateway to the designated server.
When the Security Gateway establishes a secure connection (an SSL tunnel) to the designated web site, it must validate the site server certificate.
HTTPS Inspection comes with a preconfigured list of trusted CAs. This list is updated by Check Point when necessary and is automatically downloaded to the Security Gateway. The system is configured by default to notify you when a Trusted CA update file is ready to be installed. The notification in SmartDashboard shows as a pop-up notification or in the window in the Automatic Updates section. After you install the update, make sure to install the policy. You can choose to disable the automatic update option and manually update the Trusted CA list.
If the Security Gateway receives a non-trusted server certificate from a site, by default the user gets a self-signed certificate and not the generated certificate. A page notifies the user that there is a problem with the website security certificate, but lets the user continue to the website.
You can change the default setting to block untrusted server certificates.
The trusted CA list is based on the Microsoft Root Certificate Program.
Automatically Updating the Trusted CA List and Certificate Blacklist
Updates for the trusted CA list and Certificate Blacklist will be published from time to time on the Check Point web site. They are automatically downloaded to the Security Management Server by default. When you are sent a notification that there is an update available, install it and do the procedure. The first notification is shown in a popup balloon once and then in the notification line under > . You can disable automatic updates if necessary.
To update the Trusted CA list and Certificate Blacklist:
- In SmartDashboard, select > .
- In the section, click .
You see the certificates that will be added or removed to the lists and the validity date range of the certificates added to the Trusted CA list.
- Click to confirm the update.
The certificates will be added or removed respectively from the lists.
- Install the Policy.
To disable automatic updates:
- In SmartDashboard, select > .
- In the section, clear the checkbox.
Manually Updating a Trusted CA
To add a trusted CA manually to the Security Gateway, you must export the necessary certificate from a non-trusted web site and then import it into SmartDashboard.
To export a CA certificate to add to the Trusted CAs list:
- Temporarily disable HTTPS inspection on the Security Gateway.
- Install the security policy.
- Browse to the site to get the certificate issued by the CA.
- Go to the Certification Path of the certificate.
- Select the root certificate (the top most certificate in the list).
- In Internet Explorer and Chrome:
- Click .
- From the Details tab, click .
- Follow the wizard steps.
- In Firefox, export the certificate.
To import a CA certificate to the Trusted CAs list:
- In SmartDashboard, open >.
- Click ,browse to the location of the saved certificate and click .
The certificate is added to the trusted CAs list.
- Install the security policy on Security Gateways enabled with HTTPS Inspection.
Saving a CA Certificate
You can save a selected certificate in the trusted CAs list to the local file system.
To export a CA certificate:
- In SmartDashboard, open > .
- Click > .
- Browse to a location, enter a file name and click .
A CER file is created.
HTTPS Validation
Server Validation
When a Security Gateway receives an untrusted certificate from a web site server, the settings in this section define when to drop the connection.
When selected, traffic from a site with an untrusted server certificate is immediately dropped. The user gets an error page that states that the .
When cleared, a self-signed certificate shows on the client machine when there is traffic from an untrusted server. The user is notified that there is a problem with the website's security certificate, but lets the user continue to the website (default).
When selected, the Security Gateway validates that each server site certificate is not in the Certificate Revocation List (CRL) (default).
If the CRL cannot be reached, the certificate is considered trusted (this is the default configuration). An HTTPS Inspection log is issued that indicates that the CRL could not be reached. This setting can be changed with GuiDBedit. Select > > and change the attribute drop_if_crl_cannot_be_reached from to .
To validate the CRL, the Security Gateway must have access to the internet. For example, if a proxy server is used in the organizational environment, you must configure the proxy for the Security Gateway.
To configure the proxy:
- From the tab, double-click the Security Gateway that requires proxy configuration.
- Select > .
- Select and and enter the proxy IP address.
- Optionally, you can use the default proxy settings.
- Click .
When cleared, the Security Gateway does not check for revocations of server site certificates.

|
Important - Make sure that there is a rule in the Rule Base that allows outgoing HTTP from the Security Gateway.
|
- When selected, the Security Gateway drops the connection if the server certificate has expired.
- When cleared, the Security Gateway creates a certificate with the expired date. The user can continue to the website (default).
Choose if the server validation traffic is logged in SmartView Tracker or if it triggers other notifications. The options include:
- - Does not record the event.
- - Records the event details in SmartView Tracker
- - Logs the event and executes a command, such as shows a popup window, send an email alert or an SNMP trap alert, or run a user-defined script as defined in >>>
- - Sends an email to the administrator, or runs the mail alert script defined in >>>
- - Sends an SNMP alert to the SNMP GUI, or runs the script defined in >>>
- - Sends one of three possible customized alerts. The alerts are defined by the scripts specified in >>>
- When selected, intermediate CA certificates issued by trusted root CA certificates that are not part of the certificate chain are automatically retrieved using the information on the certificate (default).
- When cleared, a web server certificate signed by an intermediate CA and not sent as part of the certificate chain, is considered untrusted.
Certificate Blacklisting
You can create a list of certificates that are blocked. Traffic from servers using the certificates in the blacklist will be dropped. If a certificate in the blacklist is also in the Trusted CAs list, the blacklist setting overrides the Trusted CAs list.
- - Lets you add a certificate. Enter the certificate serial number (in hexadecimal format HH:HH) and a comment that describes the certificate.
- - Lets you change a certificate in the blacklist.
- - lets you delete a certificate in the blacklist.
- - Lets you search for a certificate in the blacklist.
Choose if the dropped traffic is logged in SmartView Tracker or if it triggers other notifications. The options include:
- - Does not record the event.
- - Records the event details in SmartView Tracker
- - Logs the event and executes a command, such as shows a popup window, send an email alert or an SNMP trap alert, or run a user-defined script as defined in >>>
- - Sends an email to the administrator, or runs the mail alert script defined in >>>
- - Sends an SNMP alert to the SNMP GUI, or runs the script defined in >>>
- - Sends one of three possible customized alerts. The alerts are defined by the scripts specified in >>>
Troubleshooting
Secure connections between a client and server with no traffic create logs in SmartView Tracker labeled as "Client has not installed CA certificate". This can happen when an application or client browser fails to validate the server certificate. Possible reasons include:
- The generated CA was not deployed on clients.
- The DN in the certificate does not match the actual URL (for example, when you browse to https://www.gmail.com, the DN in the certificate states mail.google.com).
- Applications (such as Firefox and anti-viruses) that use an internal trusted CA list (other than Windows). Adding the CA certificate to the Windows repository does not solve the problem.
The option in the HTTPS Validation pane:
- When selected, logs are recorded for secure connections between a client and server with no traffic in SmartView Tracker (default). Logs are recorded only when a server certificate is trusted by the Security Gateway. If the server certificate is untrusted, a self-signed certificate is created and always results in a log labeled as "Client has not installed CA certificate".
- When cleared, logs are not recorded for secure connections without traffic that can be caused by not installing the CA certificate on clients or one of the above mentioned reasons.
HTTP/HTTPS Proxy
You can configure a gateway to be an HTTP/HTTPS proxy. When it is a proxy, the gateway becomes an intermediary between two hosts that communicate with each other. It does not allow a direct connection between the two hosts.
Each successful connection creates two different connections:
- One connection between the client in the organization and the proxy.
- One connection between the proxy and the actual destination.
Proxy Modes
Two proxy modes are supported:
- - All HTTP traffic on specified ports and interfaces is intercepted and sent to a proxy. No configuration is required on the clients.
- - All HTTP/HTTPS traffic on specified ports and interfaces directed to the gateway is sent to a proxy. Configuration of the proxy address and port is required on client machines.
Access Control
You can configure one of these options for forwarding HTTP requests:
- - HTTP/HTTPS traffic from all internal interfaces is forwarded by proxy.
- - HTTP/HTTPS traffic from interfaces specified in the list is forwarded by proxy.
Ports
By default, traffic is forwarded only on port 8080. You can add or edit ports as required.
Advanced
By default, the HTTP header contains the proxy related header. You can remove this header with the option.
You can also use the Advanced option to configure the that contains the IP address of the client machine. It is not added by default because it reveals the internal client IP.
Logging
The Security Gateway opens two connections, but only the Firewall blade can log both connections. Other blades show only the connection between the client and the gateway. The Destination field of the log only shows the gateway and not the actual destination server. The Resource field shows the actual destination.
To configure a Security Gateway to be an HTTP/HTTPS proxy:
- From the window of a Security Gateway object, select from the tree.
- Select .
- Select the or proxy mode.
Note - If you select mode, make sure to configure the clients to work with the proxy.
- Select to forward HTTP requests from one of these options:
- - Click the plus sign to add specified interfaces or the minus sign to remove an interface.
- To enter more ports on which to forward traffic, select .
- To include the actual source IP address in the HTTP header, select > .
The X-Forward-For header must be configured if traffic will be forwarded to Identity Awareness Security Gateways that require this information for user identification.
- Click .
Security Gateway Portals
The Security Gateway runs a number of web-based portals over HTTPS:
- Mobile web access portal
- SecurePlatform WebUI
- Gaia WebUI
- Identity Awareness (Captive Portal)
- DLP portal
- SSL Network Extender portal
- UserCheck portal
- Endpoint Security portals (CCC)
All of these portals can resolve HTTPS hosts to IPv4 and IPv6 addresses over port 443.
These portals (and HTTPS inspection) support the latest versions of the TLS protocol. In addition to SSLv3 and TLS 1.0 (RFC 2246), the Security Gateway supports:
- TLS 1.1 (RFC 4346)
- TLS 1.2 (RFC 5246)
Support for TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2 is enabled by default but can be disabled in SmartDashboard (for web-based portals) or GuiDBedit (for HTTPS Inspection).
To configure TLS protocol support for portals:
- In , open .
- In the section, click .
The window opens.
- On the page, set minimum and maximum versions for SSL and TLS protocols.
To Configure TLS Protocol Support for HTTPS inspection:
- In , on the tab, select .
- In the column, select .
- In the column, select the minimum and maximum TLS version values in these fields:
- (default = TLS 1.2)
- (default = SSLv3)
HTTPS Inspection in SmartView Tracker
Logs from HTTPS Inspection are shown in SmartView Tracker. There are two types of predefined queries for HTTPS Inspection logs in SmartView Tracker:
- HTTPS Inspection queries
- Blade queries - HTTPS Inspection can be applied to these blades:
- Application Control
- URL Filtering
- IPS
- DLP
- Anti-Virus
- Anti-Bot
To open SmartView Tracker:
- From the SmartDashboard toolbar, click > .
- With SmartDashboard active, press Control +Shift +.
HTTPS Inspection Queries
These are the predefined queries in > > .
Blade Queries
When applying HTTPS Inspection to a specified blade:
- There is an for each of the blades that can operate with HTTPS Inspection. The query shows all traffic of the specified blade that passed through HTTPS inspection.
- The log in the blade queries includes an . The field value can be inspect or bypass. If the traffic did not go through HTTPS inspection, the field does not show in the log.
Permissions for HTTPS Logs
An administrator must have HTTPS inspection permissions to see classified data in HTTPS inspected traffic.
To set permissions for an administrator in a new profile:
- In the Users and Administrators tree, select an administrator > Edit.
- In the > page in the field, click .
- In the window:
- Enter a for the profile.
- Select and click .
The window opens.
- In the tab, select for permission to see the classified information in the HTTPS Inspection logs.
- Click on all of the open windows.
To edit an existing permissions profile:
- From the SmartDashboard toolbar, select >.
- Select a profile and click .
- Follow the instructions above from step 3.
HTTPS Inspection in SmartEvent
Events from HTTPS Inspection are shown in SmartEvent. There are two types of predefined queries for HTTPS Inspection events in SmartEvent:
- HTTPS Inspection queries for HTTPS validations
- Blade queries - HTTPS Inspection can be applied to these blades:
- Application Control
- URL Filtering
- IPS
- DLP
- Anti-Virus
To open SmartEvent:
- From the SmartDashboard toolbar, click > .
- With SmartDashboard active, press Control +Shift +.
Event Analysis in SmartEvent
SmartEvent supplies advanced analysis tools with filtering, charts, reporting, statistics, and more, of all events that pass through enabled Security Gateways. SmartEvent shows all HTTPS Inspection events.
You can filter the HTTPS Inspection information for fast monitoring on HTTPS Inspection traffic.
- Real-time and history graphs of HTTPS Inspection traffic.
- Graphical incident timelines for fast data retrieval.
- Easily configured custom views to quickly view specified queries.
- Incident management workflow.
SmartEvent shows information for all Software Blades in the environment.
Viewing Information in SmartEvent
There are two types of predefined queries for HTTPS Inspection events in SmartEvent:
- HTTPS Inspection queries
- Blade queries
HTTPS Inspection Queries
- Go to >>> to show the SSL validation events that occurred.
- The and in the event record show if the traffic was detected or rejected due to SSL Validation settings.
Blade Queries
- There is an for each of the blades that can operate with HTTPS Inspection. The query shows all traffic of the specified blade that passed through HTTPS inspection.
- The in the event record in the blade queries includes an . The field value can be inspect or bypass. If the traffic did not go through HTTPS inspection, the field does not show in the event record.
|



