

Included Topics |
You can use one of these procedures to define a cluster object and its members:
The Cluster Gateway Properties window lets you:
This version includes two wizards:
The Small Appliance Wizard is recommended for these Check Point appliances:
To create a new cluster with the Small Appliance Wizard:
After you finish the wizard, we recommend that you open the cluster object and manually do these steps:
The Check Point Appliance or Open Server Wizard is recommended for enterprise grade appliances and open server platforms.
To create a new cluster with the Appliance or Open Server Wizard:
Important: You must define a corresponding IPv4 address for every IPv6 address. This release does not support pure IPv6 addresses.
Note: Make sure that you do not define IPV6 address for sync interfaces. The wizard does not let you define an interface with an IPv6 address as a sync interface.
The wizard automatically calculates the subnet for each network and assigns it to the applicable interface on each member. The calculated subnet shows in the upper section of the window.
The available network objectives are:
This option is recommended for the management interface.
After you finish the wizard, we recommend that you open the cluster object and do these procedures:
The Cluster Gateway Properties window contains many different ClusterXL properties as well as other properties related to Security Gateway and Software Blade functionality. This section includes only the properties and procedures directly related to ClusterXL. See the applicable Administration Guides for these non-ClusterXL properties.
Configuration Steps |
To configure the general properties of a cluster:
To configure a cluster member:
Important - You must define a corresponding IPv4 address for every IPv6 address. This release does not support the configuration of only IPv6 addresses.
IPv6 Considerations
To activate IPv6 functionality for an interface, define an IPv6 address for the applicable interface on the cluster and on each member. All interfaces configured with an IPv6 address must also have a corresponding IPv4 address. If an interface does not require IPv6, only the IPv4 definition address is necessary.
|
Note - You must configure synchronization interfaces with an IPv4 address only. This is because the synchronization mechanism works using IPv4 only. All IPv6 information and states are synchronized using this interface. |
To open the In the Topology page, click Edit Topology. The Edit Topology window opens.
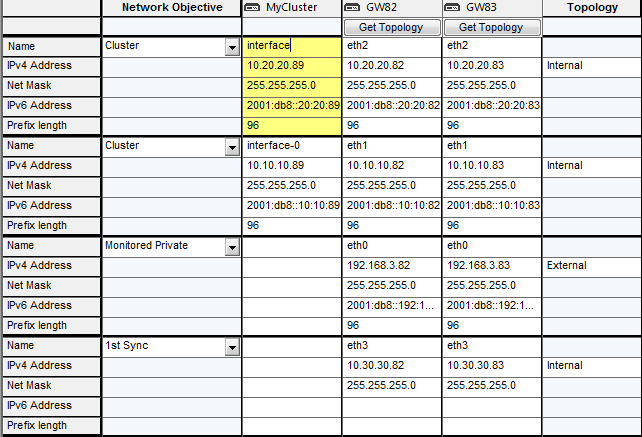
This window is a table that shows topology information for all detected interfaces in the cluster object and its related members. The rows show the interfaces. The columns contain these information categories for each interface:
If you used the Cluster Properties window to manually create a cluster, an empty table shows. You manually add and configure the interfaces in the table.
If you created the cluster using one of the wizards, the topology is calculated automatically and shows in the Edit Topology window. You can change the IP addresses and other properties directly in this window.
To configure cluster virtual interface Properties:
Note: Make sure that you do not define IPV6 address for sync interfaces. The wizard does not let you define an interface with an IPv6 address as a sync interface.
Important: You must define a corresponding IPv4 address for every IPv6 address. This release does not support pure IPv6 addresses.
Cluster members can be located on a different subnet than the cluster virtual IP address. When this occurs, use this tab to map the member IP address to the cluster virtual IP address. This advanced option is explained in Configuring Cluster Addresses on Different Subnets.
To define a new network, click Add Network.
The available network objectives are:
Enter the cluster virtual IPv4 and IPv6 addresses for each network (internal or external). These addresses must be located in the calculated subnet.
This option is recommended for the management interface.
To change the synchronization interface on your cluster members:
You can configure cluster gateways for bridge mode in different deployments Active/Standby mode or Active/Active mode.
|
Item |
Description |
1 and 2 |
Switches |
|
|
Security Gateway Firewall bridging Layer-2 traffic |
|
3 |
eth1 |
|
4 |
eth2 |
|
5 |
eth3 - the ClusterXL Sync interface |
This is the preferred mode in topologies that support it.
In Active-Standby mode, ClusterXL decides the cluster state. The standby member drops all packets. It does not pass any traffic, including STP/RSTP/MSTP. If there is a failover, the switches are updated by the Security Gateway to forward traffic to the new active member.
If you use this mode, it is best to disable STP/RSTP/MSTP on the adjacent switches.
To configure Active/Standby mode:
cpconfig8ycphaprob stateThe output should be similar to:
Cluster Mode: High Availability (Active Up, Bridge Mode) with IGMP Membership
Number Unique Address Firewall State (*)
1 (local> 2.2.2.3 Active
2 2.2.2.2 Standby
When you define a bridge interface on a Security Gateway cluster, Active/Active mode is activated by default.
Before you begin, install ClusterXL High Availability on a Gaia appliance or open server.
To configure Active/Active mode, do these steps on each member of the cluster:
Do not configure an IP address on the newly created bridge interface.
Bridge port topology cannot be defined. It is external by default.
cphaprob statThe output should be similar to:
Cluster Mode: High Availability (Active Up, Bridge Mode) with IGMP MembershipNumber Unique Address Firewall State (*)1 (local> 2.2.2.3 Active2 2.2.2.2 Active
After you configure Active/Active mode, the output for chpaprob stateFirewall State is Active/Active
To confirm the High Availability configuration:
You can configure a bridged cluster between four switches, in Active/Active mode.
Active/Standby mode is not supported.
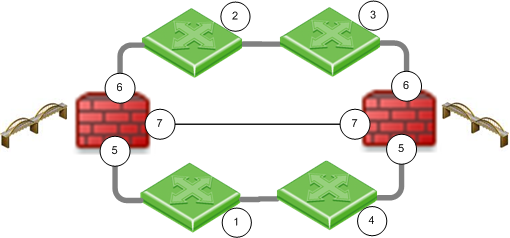
Item |
Description |
1, 2, 3, 4 |
Switches |
|
Security Gateway Firewall bridging Layer-2 traffic |
5 |
eth1 |
6 |
eth2 |
7 |
eth3 - the ClusterXL Sync interface |
See also: Link Aggregation with ClusterXL in Layer-2
You can bind two ports together, so that when the link state for one port goes down, the other port also goes down. This lets a switch detect and react to a link failure on the other side of a bridge or another part of the network.
This feature is available in one of these modes:
Link state propagation is supported on these Check Point appliance line cards:
For example:fw_lsp_pair1=”eth1,eth2"
|
Note - You can add up to four lines to this file, one for each pair. |
Note: The below procedures are applicable to R77.20 and higher.
To configure Link State Propagation for automatic port detection:
FWDIR/modules/fwkern.confIf there is no fwkern.conf
fw_link_state_propagation_enabled=1
To create port pairs automatically:
FWDIR/modules/fwkern.confIf there is no fwkern.conf
fw_link_state_propagation_enabled=1
fw_manual_link_state_propagation_enabled=1
fw_lsp_pair<1-4>=”<interface_name1,interface_name2>”
|
Note - Link State Propagation is a Firewall Software Blade feature. It is supported for Security Gateways and clusters. You must configure Link State Propagation for each cluster member. |