MGCP-Based VoIP
Introduction to MGCP
MGCP is a protocol for controlling telephony gateways from external call control devices called Call Agents (also known as Media Gateway Controllers).
MGCP is a master-slave protocol, with the Call Agent as master and endpoints as slaves. (SIP and H.323 are peer-to-peer protocols.)
The MGCP protocol assumes call control devices, or Call Agents, synchronize with each other to send commands to the devices (Media Gateways) they control. Call Agents also connect directly to IP Phones. The Media Gateways or IP Phones are run commands sent by the Call Agents. The figure shows the MGCP elements and call control actions.
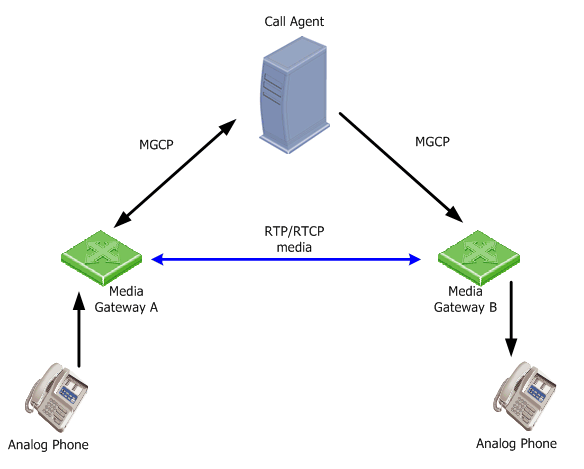
Media Gateways and MGCP IP phones usually support features such as conference calls, 3-way brokering and supervisor inspection.
MGCP Supported Deployments and NAT Support
The Security Gateway supports the MGCP deployments listed in the table. It is possible to configure NAT (Hide or Static) for the phones in the internal network.
NAT is not supported on IP addresses behind an external Check Point gateway interface.
The SmartDashboard configuration depends on the topology.
Supported MGCP Topology
|
No NAT
|
NAT for Internal Phones -
Hide/Static NAT
|
Call Agent in external network
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Call Agent in DMZ
|
Yes
|
No
|
Call Agent to Call Agent
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
|
|
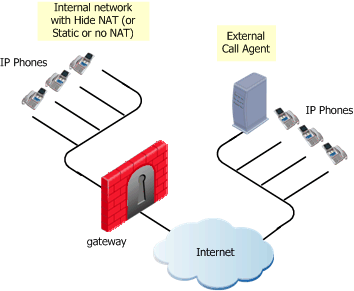
Call Agent in external network
|
The IP Phones use the services of a Call Agent on the external side of the gateway. This topology enables using the services of a Call Agent that is maintained by another organization. It is possible to configure Hide NAT (or Static NAT or no NAT) for the phones on the internal side of the gateway.
|
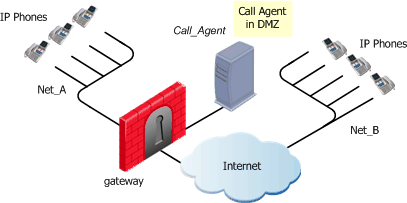
Call Agent in the DMZ
|
The same Call Agent controls both endpoint domains. This topology makes it possible to provide Call Agent services to other organizations.
|
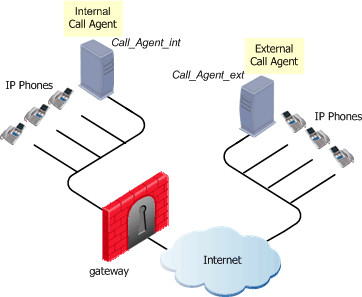
Call Agent to Call Agent
|
Each Call Agent controls a separate endpoint domain.
Where there is one or more Call Agents, the signaling passes through each Call Agent. Once the call has been set up, the media can pass endpoint to endpoint.
|
Additional Conditions for Using NAT in MGCP Networks
You can use MGCP with Network Address Translation (NAT), but:
- Manual NAT rules are not supported. Use Automatic NAT.
- Calls cannot be made from an external source to two endpoints on the trusted side of a gateway if one of the endpoints is NATed and the other is not.
- Bidirectional NAT of VoIP calls is not supported.

|
Important - Hide NAT can be used for all types of calls (incoming, outgoing, internal and external). For security reasons, when using Hide NAT for incoming calls, the of the VoIP call in the Rule Base cannot be .
|
Hide NAT for MGCP traffic
Enabling the option configures the gateway to do Hide NAT on the:
- IP address of the MGCP endpoint phones
- Source port of the MGCP endpoint phones.
Find the option on the:
tab tab.
With this option disabled, the gateway performs Hide NAT only on the IP address of the MGCP endpoint phones. This option must be selected in environments where:
- The gateway is configured (in SmartDashboard) to do Hide NAT on the internal IP addresses of the endpoints.
- The MGCP server can register only one endpoint with a given IP address and port combination.
MGCP Packet before NAT
The packet capture shown here shows an MGCP packet from a phone with IP address 194.90.147.53, and source port 2427 (the default MGCP port).
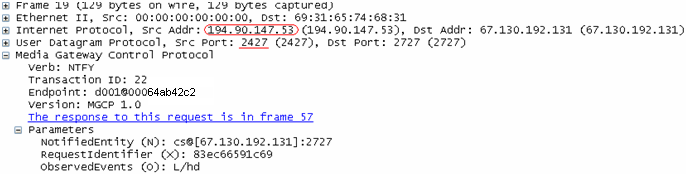
Packet after Hide NAT when Option is Disabled
The packet capture shown here shows the MGCP packet after Hide NAT, with the Hide NAT changes source port for MGCP option disabled. The IP address is translated to the Hide NAT address of 194.90.147.14, but the source port 2427 is unchanged.
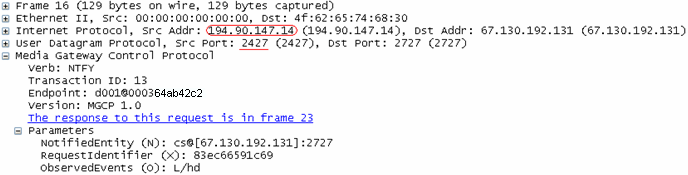
In this environment, all the internal phones are registered with the same Source IP (for example 194.90.147.14) and the default MGCP source port (2427).
Some MGCP servers can register a phone with only one IP address and port combination. As a result, only one of the phones behind that IP address will be registered successfully on the server.
Packet after NAT when Option is Enabled
This packet capture shows the MGCP packet after Hide NAT, with the option enabled.
- The IP address is translated to the Hide NAT address of 194.90.147.14.
- The source port is also translated to an allocated port of 10416.
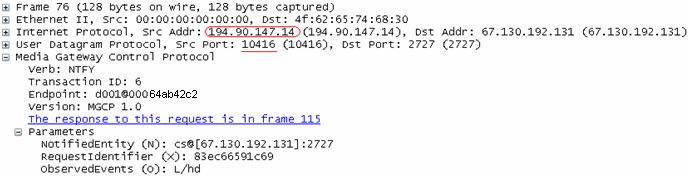
In this environment, a different port is allocated for each internal phone. All phones are registered with a different Source IP: port combination. For example:
- One phone with source IP 194.90.147.14 and source port 10416 (as shown in the packet capture), and
- Another phone with source IP 194.90.147.14 and source port 10417.
As a result, all internal phone are registered successfully on the server.
Rule Base Configuration for MGCP
This section explains how to configure Security Rule Base Rules so that the gateway allows MGCP calls.
MGCP-Specific services
These predefined MGCP services are available:
Predefined MGCP-Specific Services
Service
|
Purpose
|
UDP:mgcp_CA
|
Used for MGCP over UDP, for connections using the well known port is the Call-Agent port (2727).
|
UDP:mgcp_MG
|
Used for MGCP over UDP, and whose well known port is the Media Gateway port (2427).
|
Other:MGCP_dynamic_ports
|
Allows a MGCP connection to be opened on a dynamic port and not on the MGCP well-known port.
|
MGCP Rules for a Call Agent in the External Network
An MGCP topology with a Call Agent in the external network is shown in the figure.
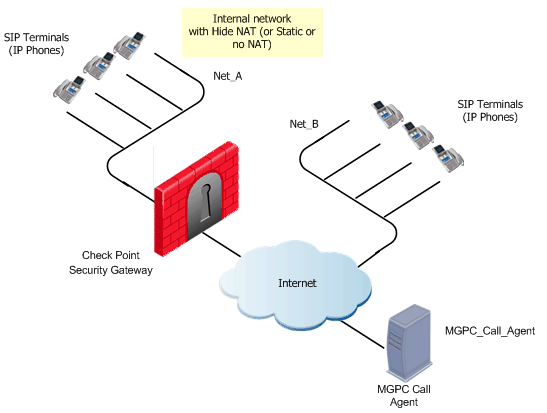
This procedure explains how to:
- Allow bidirectional calls between the MGCP phones in the internal network (Net_A) and phones in an external network (Net_B)
- Define NAT for the internal phones
To define an MGCP rule for a call agent in the external network:
- Define the network objects (Nodes or Networks) for IP Phones managed by the MGCP Call Agent, and their calls subject to gateway inspection.
For the example in the figure, these are Net_A and Net_B.
- Define the network object for the Call Agent (MGCP_Call_Agent).
- Define this security rule:
Source
|
Destination
|
Service
|
Action
|
MGCP_Call_Agent
Net_A
|
Net_A
MGCP_Call_Agent
|
mgcp_CA or mgcp_MG or mgcp_dynamic_ports
|
Accept
|
To define Hide NAT (or Static NAT) for the phones in the internal network, edit the network object for Net_A.
- On the tab, select .
- Select the method (Hide or Static).
- Install the security policy.
MGCP Rules for Call Agent in DMZ
The figure illustrates an MGCP-based VoIP topology where a Call Agent is installed in the DMZ.
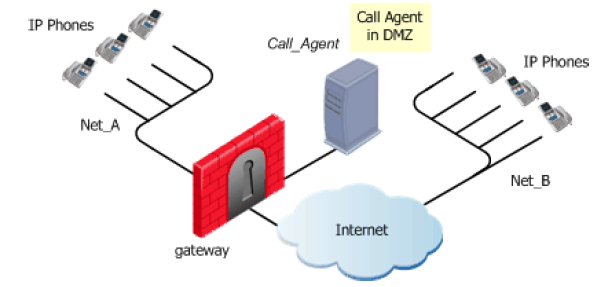
To enable bidirectional calls between phones in internal and external networks (Net_A and Net_B):
- Define the Network objects (nodes or networks) for the phones that are permitted to make calls, and their calls subject to gateway inspection. In the figure, these are Net_A and Net_B.
- Define the Network object for the Call Agent (Call_Agent).
- Define this security rule:
Source
|
Destination
|
Service
|
Action
|
Comment
|
Net_A
Net_B
Call_Agent
|
Net_A
Net_B
Call_Agent
|
mgcp_CA
or
mgcp-MG
|
Accept
|
Bidirectional calls.
|
- Install the security Policy.
MGCP Rules for Call Agent to Call Agent
The figure illustrates a Call Agent-to-Call Agent topology with the Call Agents on opposite sides of the gateway.
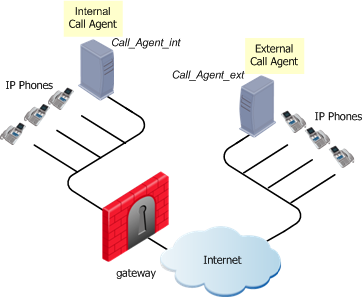
To enable bidirectional calls between phones in internal and external networks:
- Define the Network object for the Proxy objects (Call_Agent_Int and Call_Agent_Ext).
- Define this security rule:
Source
|
Destination
|
Service
|
Action
|
Comment
|
Call_Agent_Int
Call_Agent_Ext
|
Call_Agent_Ext
Call_Agent_Int
|
mgcp_CA
or
mgcp-MG
|
Accept
|
Bidirectional calls.
|
- Install the security Policy.
|

