Command Line Interface
QoS Commands
QoS Command Names
QOS Command
|
Description
|
etmstart
|
Starts QoS
|
etmstop
|
Stops QoS
|
fgd50
|
QoS daemon
|
Setup
cpstart and cpstop
Generally, to stop and start the QoS gateway you are required to stop the
Firewall using the cpstop and cpstart commands. In the event that you would like to stop the QoS gateway only, you can use the QoS specific etmstart and etmstop commands. For more on cpstop and cpstart, see the R76 Security Management Administration Guide.
etmstart
etmstart loads the QoS gateway, starts the QoS daemon (fgd50), and retrieves the last policy that was installed on the QoS gateway.
etmstop
etmstop kills the QoS daemon (fgd50) and then unloads the QoS policy and gateway.
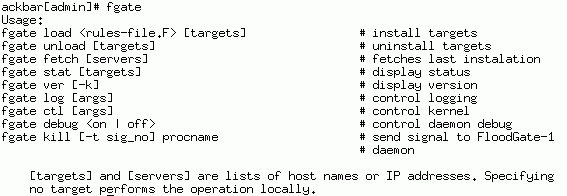
fgate Menu
The following menu is displayed when typing fgate from the command line.
Control
fgate
The fgate program is used to manage QoS. Its specific action is determined by the first command line argument, as described in the following sections:
fgate load
fgate load runs a verifier on the policy file. If the policy file is valid, fgate compiles and installs a QoS Policy to the specified QoS gateways. It can only be run from the Security Management Server.
- Syntax
fgate load <rule-file.F> [targets]
|
If targets is not specified, the QoS Policy is installed on the local host.
fgate unload
fgate unload uninstalls a QoS Policy from the specified QoS gateways. It can only be run from both the Security Management Server and localhost.
- Syntax
If targets is not specified, the QoS Policy is uninstalled from the local host.
fgate fetch
fgate fetch retrieves the QoS Policy that was last installed on the local host. You must specify the machine where the QoS Policy is found. Use "localhost" in case there is no Security Management Server or if the Security Management Server is down. You may specify a list of Security Management Servers, which will be searched in the order listed.
fgate fetch -f attempts to retrieve policies from all management stations, one after the other until it succeeds. If the gateway fails to retrieve a policy from a Security Management Server, it tries to retrieve one from itself.
Syntax
fgate fetch [-f | servers]
|
Examples
fgate fetch localhost
fgate fetch -f
fgate fetch mgmt_server_name
|
Monitor
fgate stat
fgate stat displays the status of target hosts in various formats. If this command is launched from a Security Management Server, it can be run on an array of gateways. If this command is launched from a gateway, the status of the gateway is returned.
Usage
The default format displays the following information for each host: product, version, build number, policy name (Express or Traditional), install time and interfaces number.
If no target is specified, the status of localhost is shown. Example:
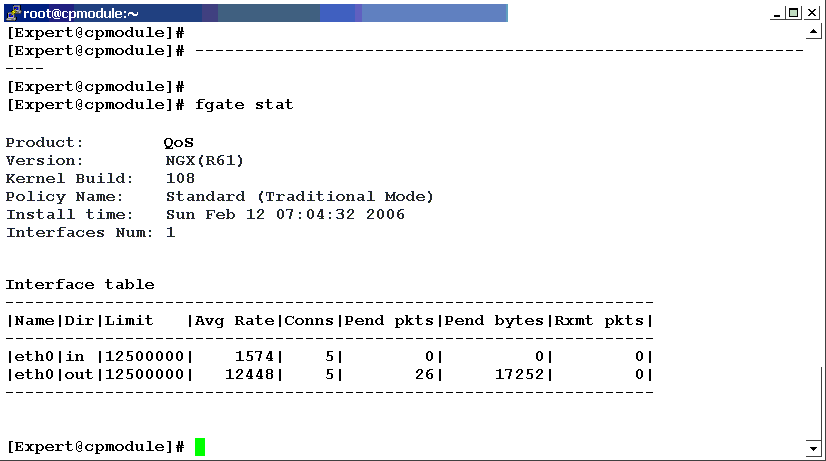
Examples
fgate stat
fgate stat gateway1 gateway2
|
fgate ver
fgate ver displays the QoS version number. If the -k option is included, both the kernel version build number and QoS executable version build number are returned. Without the -k, only the QoS executable version is specified.
Syntax
Utilities
fgate log
fgate log turns logging on or off in the kernel. It can be used in order to save resources without reinstalling your QoS policy. The stat option returns the current state of logging.
Syntax
fgate log < on | off | stat >
|
By default, fgate log is turned on.
fgate ctl
fgate ctl sends control information to the QoS kernel gateway.
Syntax
Parameter
|
Meaning
|
etmreg
|
etmreg is for Unix platforms only. fgate ctl turns on or off the QoS kernel.
|
fgate debug
fgate debug turns on a debug flag which sends additional debugging information to the fgd log file: $FGDIR/log/fgd.elg. The default is off.
Syntax
fgate kill
fgate kill sends a signal to a QoS daemon. The Security Management Server does not run the QoS daemon therefore this command is valid only on gateways.
Syntax
fgate kill [-t sig_no] proc-name
|
Parameter
|
Meaning
|
[-t sig_no] proc-name
|
If the file $FWDIR/tmp/<proc-name>.pid exists, send sig_no to the PID in the file.
If no signal is specified, signal 15 (sigterm) is sent.
|
The QoS daemon writes the PIDs to files in the log directory upon startup. These files are named $FWDIR/tmp/<daemon_name>.pid. For example, the file containing the PID of the QoS SNMP daemon is $FWDIR/log/snmpd.pid.
Examples
The following command:
sends signal 15 to the QoS fgd daemon.
The following command:
sends signal 1 to the QoS fgd daemon.
|

