Multi-Domain Security Management Overview
Multi-Domain Security Management is a centralized management solution for large-scale, distributed environments with many different network Domains. This best-of-breed solution is ideal for enterprises with many subsidiaries, branches, partners and networks. Multi-Domain Security Management is also an ideal solution for managed service providers, cloud computing providers, and data centers.
Centralized management gives administrators the flexibility to manage polices for many diverse entities. Security policies should be applicable to the requirements of different departments, business units, branches and partners, balanced with enterprise-wide requirements.
Glossary
This glossary includes product-specific terms used in this guide.
Term
|
Description
|
Administrator
|
Security administrator with permissions to manage the Multi-Domain Security Management deployment.
|
Global Policy
|
Policies that are assigned to all Domains, or to specified groups of Domains.
|
Global Objects
|
Network objects used in global policy rules. Examples of global objects include hosts, global Domain Management Servers, and global VPN communities.
|
Internal Certificate Authority (ICA)
|
Check Point component that authenticates administrators and users. The ICA also manages certificates for Secure Internal Communication (SIC) between Security Gateways and Multi-Domain Security Management components.
|
Multi-Domain Security Management
|
Check Point centralized management solution for large-scale, distributed environments with many different network Domains.
|
Domain
|
A network or group of networks belonging to a specified entity, such as a company, business unit or organization.
|
Multi-Domain Server
|
Multi-Domain Security Management server that contains all system information and security policy databases for individual Domains.
|
Domain Management Server
|
Virtual Security Management Server that manages Security Gateways for one Domain.
|
Multi-Domain Log Servers
|
Physical log server that hosts the log database for all Domains.
|
Domain Log Server
|
Virtual log server for a specified Domain.
|
Primary Multi-Domain Server
|
The first Multi-Domain Server that you define and log into in a High Availability deployment.
|
Permissions Profile
|
Predefined group of SmartConsole access permissions that you assign to Domains and administrators. This lets you manage complex permissions for many administrators with one definition.
|
Secondary Multi-Domain Server
|
Any subsequent Multi-Domain Server that you define in a High Availability deployment.
|
Active Multi-Domain Server
|
The only Multi-Domain Server in a High Availability deployment from which you can add, change or delete global objects and global policies. By default, this is the primary Multi-Domain Server. You can change the active Multi-Domain Server.
|
Standby Multi-Domain Server
|
All other Multi-Domain Servers in a High Availability deployment, which cannot manage global policies and objects. Standby Multi-Domain Servers are synchronized with the active Multi-Domain Server.
|
Active Domain Management Server
|
In a High Availability deployment, the only Domain Management Server that can manage a specific Domain.
|
Standby Domain Management Server
|
In a High Availability deployment, any Domain Management Server for a specified Domain that is not designated as the active Domain Management Server.
|
Key Features
Centralized Management
|
Administrators with applicable permissions can manage multiple Domains from a central console. Global policies let administrators define security rules that apply to all Domains or to groups of Domains.
|
Domain Security
|
Virtual IP addresses for each Domain Management Server make sure that there is total segregation of sensitive data for each Domain. Although many Domains are hosted by one server, access to data for each Domain is permitted only to administrators with applicable permissions.
|
High Availability
|
Multi-Domain Security Management High Availability features make sure that there is uninterrupted service throughout all Domains. All Multiple Multi-Domain Servers are synchronized and can manage the deployment at any time. Multiple Domain Management Servers give Active/Standby redundancy for individual Domains.
|
Scalability
|
The Multi-Domain Security Management modular architecture seamlessly adds new Domains, Domain Management Servers, Security Gateways, and network objects into the deployment. Each Multi-Domain Server supports up to 250 Domains.
|
Basic Architecture
Multi-Domain Security Management uses tiered architecture to manage Domain network deployments.
- The Security Gateway enforces the security policy to protect network resources.
- A Domain is a network or group of networks belonging to a specified entity, such as a company, business unit, department, branch, or organization. For a cloud computing provider, one Domain can be defined for each customer.
- A Domain Management Server is a virtual Security Management Server that manages security policies and Security Gateways for a specified Domain.
- The Multi-Domain Server is a physical server that hosts the Domain Management Server databases and Multi-Domain Security Management system databases.
- The SmartDomain Manager is a management client that administrators use to manage domain security and the Multi-Domain Security Management system.
The Multi-Domain Servers and SmartDomain Manager are typically located at central Network Operation Centers (NOCs). Security Gateways are typically located together with protected network resources, often in another city or country.
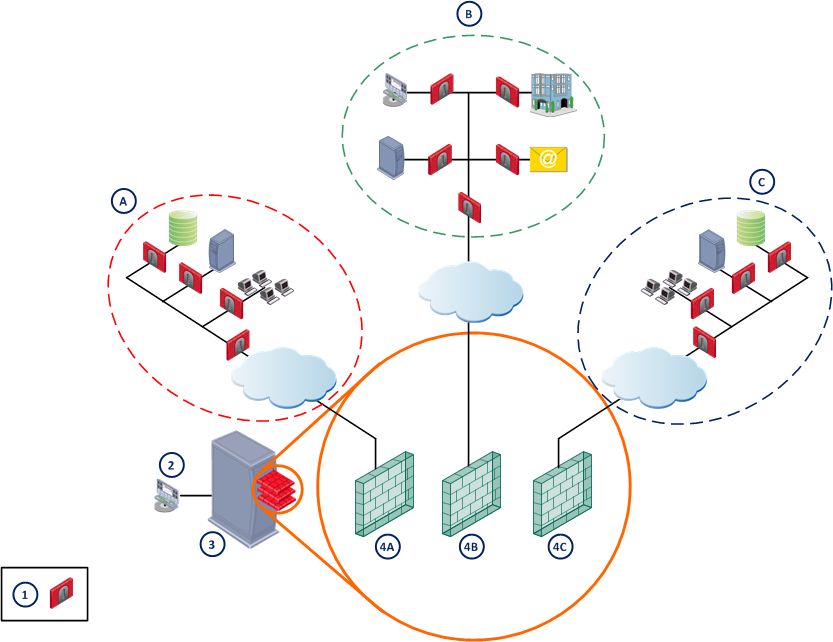
Item
|
Description
|
|
|
USA Development Domain
|
|
|
Headquarters Domain
|
|
|
UK Development Domain
|
|
|
Security Gateway
|
|
|
Network Operation Center
|
|
|
Multi-Domain Server
|
|
|
USA Development Domain Management Server
|
|
|
Headquarters Domain Management Server
|
|
|
UK Development Domain Management Server
|
The Multi-Domain Server
The Multi-Domain Server is a physical computer that hosts Domain Management Servers, system databases, and the Multi-Domain Log Server. The system databases include Multi-Domain Security Management network data, administrators, Global Policies, and domain management information.
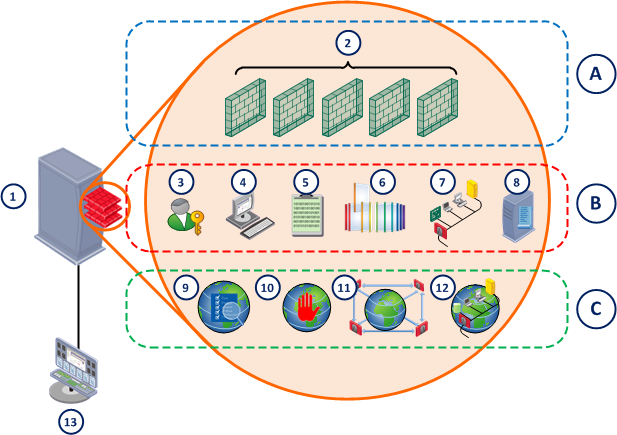
Item
|
Description
|
|
|
Domain Management Server database
|
|
|
Global objects database
|
|
|
Multi-Domain Security Management System database
|
|
|
Multi-Domain Server
|
|
|
Domain Management Servers
|
|
|
Administrators and permissions
|
|
|
GUI clients
|
|
|
Licenses
|
|
|
Software packages
|
|
|
Network objects
|
|
|
Multi-Domain Log Server
|
|
|
Global policies
|
|
|
Global IPS
|
|
|
Global VPN communities
|
|
|
Other Global objects
|
|
|
SmartDomain Manager in Network Operations Center
|
A Multi-Domain Server can host a large amount of network and policy data on one server. To increase performance in large deployments, distribute traffic load, and configure high availability, you can use multiple Multi-Domain Servers.
Domain Management Servers
A Domain Management Server is the Multi-Domain Security Management functional equivalent of a Security Management Server. Administrators use Domain Management Servers to define, change and install Domain security policies to Domain Security Gateways. A Domain can have multiple Domain Management Servers in a high availability deployment. One Domain Management Server is active, while the other, fully synchronized, Domain Management Servers are standbys. You can also use a Security Management Server as a backup for the Domain Management Server.
Typically, a Domain Management Server is located on the Multi-Domain Server in the Network Operations Center network.

Item
|
Description
|
|
|
USA Development Domain
|
|
|
Headquarters Domain
|
|
|
UK Development Domain
|
|
|
Security Gateway
|
|
|
Network Operation Center
|
|
|
Headquarters Domain Management Server
|
|
|
USA Development Domain Management Server
|
|
|
Headquarters Domain Management Server
|
|
|
UK Development Domain Management Server
|
After you define a Domain Management Server, you define Security Gateways, network objects, and security policies using the basic procedures in the R76 Security Management Administration Guide. You manage Security Gateways using the Domain Management Server SmartDashboard.
You must define routers to communicate between Domain Security Gateways and Domain Management Servers. Traffic must be allowed between the Multi-Domain Servers, network, Security Gateways and Domain Security Gateways. It should also be allowed for SmartConsole Client applications and Domain Management Server connections. Access rules must be set up as appropriate in Domain Security Gateway rule base.
If you are using Logging or High Availability Domain network, you must configure routing to support these functions.
Log Servers
This section shows how log servers operate in a Multi-Domain Security Management deployment.
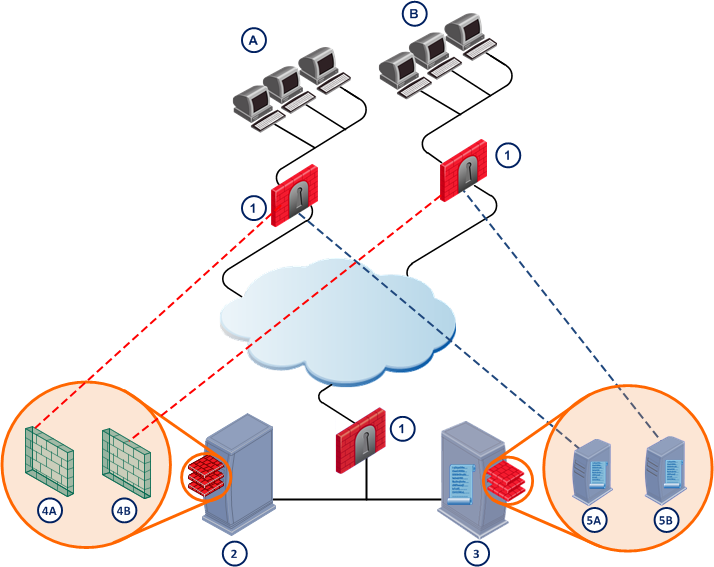
Item
|
Description
|
|
|
Domain A
|
|
|
Domain B
|
|
|
Security Gateway
|
|
|
Multi-Domain Server
|
|
|
Multi-Domain Log Server
|
|
|
Domain Management Server - Domain A
|
|
|
Domain Management Server - Domain B
|
|
|
Domain Log Server - Domain A
|
|
|
Domain Log Server - Domain B
|
Multi-Domain Log Server
A Multi-Domain Log Server hosts log files for multiple Domains. Typically, the Multi-Domain Log Server is hosted on a Multi-Domain Server dedicated for log traffic. This improves performance by isolating log traffic from management traffic.
You can optionally install a Multi-Domain Log Server on a Multi-Domain Server together with the Domain Management Servers and system databases. This option is appropriate for deployments with lighter traffic loads. You can also create a redundant log infrastructure by defining the Multi-Domain Log Server as the primary log server and the Multi-Domain Server as a backup.
You can have multiple Multi-Domain Log Servers in a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. You use the SmartDomain Manager to manage your Domain Log Servers with a different log repository for each Domain.
Domain Log Server
A Domain Log Server is a virtual log server for a single Domain. Typically, Domain Log Servers are virtual components installed on a Multi-Domain Log Server. You can also configure Domain Log Servers to monitor specified Domain Security Gateways.
Security Policies
A Security Policy is a set of rules that are enforced by Security Gateways. In a Multi-Domain Security Management deployment, administrators use Domain Management Servers to define and manage security policies for Security Gateways included in Domains.
Global Policies
Global policies are a collection of rules and objects that are assigned to all Domains, or to specified groups of Domains. This is an important time saver because it lets administrators assign rules to any or all Domain Security Gateways without having to configure them individually.
The Management Model
Introduction to the Management Model
The Multi-Domain Security Management model is granular and lets you assign a variety of different access privileges to administrators. These privileges let administrators do specified management tasks for the entire deployment or for specified Domains.
Management Tools
The SmartDomain Manager
Administrators use the SmartDomain Manager to manage the Multi-Domain Security Management and to open the SmartConsole client applications for specific Domains. The SmartDomain Manager has many views to let administrators see information and do various tasks.
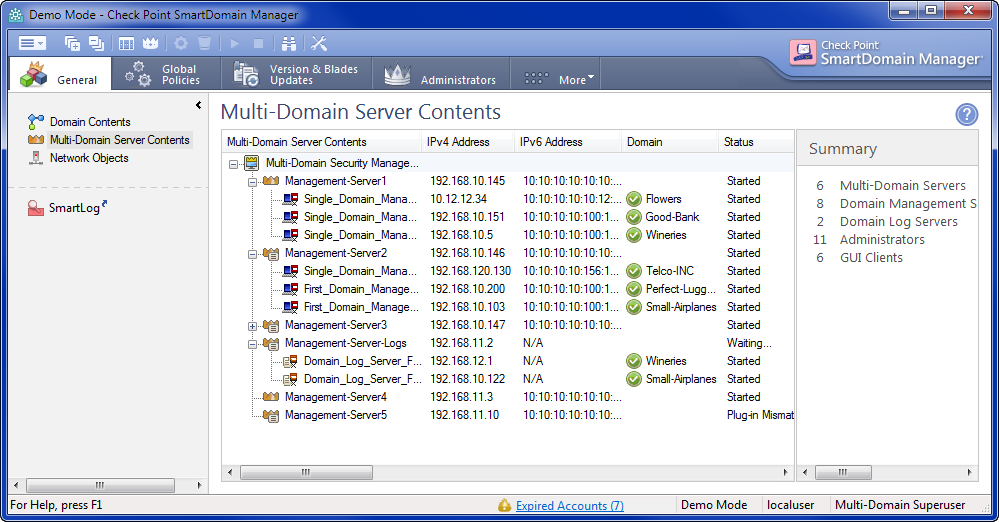
SmartConsole Client Applications
Administrators use SmartConsole clients to configure, manage and monitor security policies. SmartConsole clients include all the following:
- SmartDashboard lets administrators define and manage security policies.
- SmartView Tracker lets administrators see, manage and track log information.
- SmartUpdate lets administrators manage and maintain the license repository, as well as to update Check Point software.
- SmartView Monitor lets administrators monitor traffic on Multi-Domain Servers, Security Gateways, and QoS Security Gateways. They can also see alerts and test the status of various Check Point components throughout the system.
- SmartReporter lets administrators generate reports for different aspects of network activity.
- SmartProvisioning lets administrators manage many SmartProvisioning Security Gateways.
SmartDashboard Toolbar
You can use the SmartDashboard toolbar to do these actions:
Icon
|
Description
|

|
Open the SmartDashboard menu. When instructed to select menu options, click this button to show the menu.
For example, if you are instructed to select > , click this button to open the Manage menu and then select the option.
|

|
Save current policy and all system objects.
|

|
Open a policy package, which is a collection of Policies saved together with the same name.
|

|
Refresh policy from the Security Management Server.
|

|
Open the Database Revision Control window.
|

|
Change global properties.
|

|
Verify Rule Base consistency.
|

|
Install the policy on Security Gateways or VSX Gateways.
|

|
Open SmartConsole.
|
High Availability

|
Note - The current version supports multiple Domain Management Servers for each Domain.
|
Multi-Domain Security Management High Availability gives uninterrupted management redundancy for all Domains. Multi-Domain Security Management High Availability operates at these levels:
You can also use ClusterXL to give High Availability redundancy to your Domain Security Gateways. You use SmartDashboard to configure and manage Security Gateway High Availability for Domain Management Servers.
|
|



