Troubleshooting SD-WAN ""
For background information, see SD-WAN Connection Type - "Overlay".
Symptom:
After an SD-WAN link failover, the "" traffic is disconnected and stops passing.
Solution:
-
In Infinity Portal > Quantum SD-WAN application > Network view > SD-WAN Policy page:
-
In the Steering Behavior object "Overlay", make sure you selected the WAN link, to which you expected the traffic to fall back.
As a result, this "" traffic and probing traffic would match the "" steering behavior that uses the WAN link.
-
Make sure that this "" traffic and probing traffic do not match a rule with the Steering Behavior object "Breakout".
-
-
On the Security Gateway, after the SD-WAN link failover:
-
Connect to the command line on the Security Gateway.
-
Log in to the Expert mode.
-
Make sure that you have at least one VPN tunnel in the status "Up" with the VPN peer:
-
Run:
cpview -
At the top, click Advanced tab > SD-WAN page.
-
Refer to the section Overlay Probing Results > column State.
-
-
Make sure that you have at least one VPN tunnel in the status "Up" with the VPN peer:
-
Run:
cpview -
At the top, click Advanced tab > SD-WAN page.
-
Refer to the section Overlay Probing Results > column State.
-
-
Examine the routing table:
clish -c "show route"After the previously active SD-WAN interface goes down, you must make sure that there is still another active route (either the default route or a static route) that includes the destination for the "" connection.
Without such an active route, the operating system cannot route the "" traffic.
The SD-WAN selects the route to the "" destination (and not the operating system based on a static route).
This route in the operating system is necessary only for the "" traffic to flow from the inbound chain to the outbound chain, where the Security Gateway encrypts the traffic, and SD-WAN selects the best VPN transport to the VPN peer.
-
Examine the VPN connections and their VPN tunnels:
Syntax:
vpn tu conn <Source IP> <Source Port> <Destination IP> <Destination Port> <Protocol>
Note - The minus character "
-" is a wildcard "any".For more information, refer to the CLI Reference Guide for your version > Chapter "VPN Commands" > Section "vpn" > Section "vpn tu".
Example 1:
vpn tu conn - - - - -Example 2:
vpn tu conn 192.168.10.10 - 192.168.20.10 443 6
-
Symptom:
CPView > Advanced > SD-WAN page shows that the state of the "" probing is "DOWN".
Solution:
-
Make sure the nexthop device for the SD-WAN interface is up.
-
Connect to the command line on the Security Gateway.
-
Log in to the Expert mode.
-
Make sure the VPN tunnel is established and "Up" from the SD-WAN interface to the required interface on the VPN peer:
For more information about these commands, refer to the CLI Reference Guide for your version > Chapter "VPN Commands" > Section "vpn" > Section "vpn tu".
-
Run:
vpn tuand enter the digit 2 for the option "List all IPsec SAs".
-
Run:
vpn tu tlistIf the command output does not show Outbound SA or IPsec SA, then the VPN tunnel is "down".
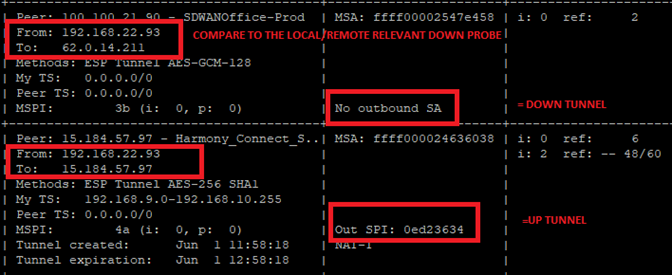
Example of a "
vpn tu tlist" output:-
The top section shows "
No outbound SA". Meaning, this VPN tunnel is "down". -
The bottom section shows a value in the "
Out SPI" field. Meaning, this VPN tunnel is "up".
-
-
Run:
vpn tu conn <Source IP Address> – <Destination IP Address> – 1
Note - The minus character "
-" is a wildcard "any" because ICMP does not use traffic ports.Example:
vpn tu conn 192.168.3.57 – 172.16.4.68 – 1Run this command with the IP addresses of the overlay probing connection that is down.
The connection must be encrypted and must pass through a VPN tunnel that is "up".
-
-
If the VPN tunnel is "down", then understand why:
-
Examine the Security Gateway logs in SmartConsole / SmartView.
Filter for the applicable Source IP address, Destination IP address, and Ports 500 (IKE) and 4500 (NAT-T).
Determine whether the VPN peers send and respond to the IKE negotiation traffic.
-
Capture the traffic on the Security Gateway with FW Monitor (sk30583).
Filter for the applicable Source IP address, Destination IP address, and Ports 500 (IKE) and 4500 (NAT-T).
Determine whether the VPN peers send and respond to the IKE negotiation traffic.
-
Examine the Security Gateway logs in SmartConsole / SmartView.
Filter for the action "
Key Install".Determine the reason for the failure. For example, an invalid IPsec certificate. The Source IP address of a VPN Gateway is not known to its VPN peer (Invalid ID).
For additional information, see: sk164840, sk88780, sk112054.
-
Collect the VPN debug as described in sk180488.
-
Contact Check Point Support and include the CLI outputs, VPN debug outputs, and log files.
-
-
If VPN tunnel is "up", but CPView shows it as "down", then the Security Gateway does not receive the ICMP Replies from the VPN peer.
-
Make sure the Security Policy on each VPN peer explicitly allows the ICMP Echo Request traffic between these VPN peers on their external interfaces.
-
Make sure the SD-WAN Policy:
-
Matches the ICMP Echo Request traffic between these VPN peers on the "" steering object.
-
Has all available WAN interfaces selected.
-
-
Make sure the Encryption Domain of the Security Gateway does not include the subnets of the SD-WAN peer.
If the Encryption Domain contains the VPN peer subnets, the Security Gateway does not encrypt the traffic it sends to the VPN peer.
-
Capture the traffic on the Security Gateway with FW Monitor (sk30583).
Use the "
-F" parameter to filter for the ICMP package between the Security Gateway and its VPN peer.Example syntax (port "
0" means "any"):fw monitor -F "192.168.22.33,0,141.10.60.1,0,1" -F "172.20.44.55,0,192.168.22.33,0,1"The FW Monitor traffic capture must show:
-
The ICMP Echo Request traffic from the Security Gateway (encrypted in the Pre-Outbound chain "
oE") to the VPN peer. -
The ICMP Echo Reply traffic from the VPN peer to the Security Gateway (decrypted in the Pre-Inbound chain "
iD").
If this ICMP traffic is not encrypted, then:
-
In SmartConsole, examine the Access Control policy.
Make sure there is an explicit rule to accept this ICMP traffic.
-
Open the Security Gateway object > expand Network Management > click VPN Domain.
Make sure you did not exclude the external interface that establish the VPN tunnel from the VPN Domain.
-
Make sure you did not exclude this ICMP traffic in the
crypt.deffile (see sk25675). -
Make sure you did not exclude this ICMP traffic in the corresponding VPN Community object on the Excluded Services page.
If the ICMP Echo Reply traffic from the VPN peer to the Security Gateway does not get to the Post-Inbound chain "
I", then determine why the Security Gateway drops it:-
Examine the Security Gateway logs in SmartConsole / SmartView.
-
Collect the kernel debug:
For more information about the kernel debug procedure on a Security Gateway, see the Security Gateway Guide for your version > chapter "Kernel Debug".
fw ctl zdebug -m fw + drop | grep 'value'
-
-
Symptom:
CPView > Advanced > SDWAN > Probing > the section "Steering Objects Results" does not show the "" steering objects.
Cause:
This is by design.
CPView shows only the "Local Breakout" and "Backhaul" steering objects.
Symptom:
FW Monitor (sk30583) traffic capture of the "" traffic between a client and a server does not show the expected outbound interface on Post-Outbound chain "O".
Cause:
FW Monitor shows the outbound interface based on the routing table.
This does not mean that it was the actual interface that routed the packet.
Solution:
To see the real interface that routed the traffic, do one of these:
-
In the applicable Security Gateway logs, examine the "SD-WAN" section.
-
Capture the ESP / NAT-T traffic with the CPPCAP tool (sk141412) in the Expert mode:
cppcap -i <Name of Interface> -f "esp or port 4500" -o /var/log/cppcap_ESP_NATT.cap -
Examine the VPN connections and their VPN tunnels:
Syntax:
vpn tu conn <Source IP> <Source Port> <Destination IP> <Destination Port> <Protocol>
Note - The minus character "
-" is a wildcard "any".For more information, refer to the CLI Reference Guide for your version > Chapter "VPN Commands" > Section "vpn" > Section "vpn tu".
Example 1:
vpn tu conn - - - - -Example 2:
vpn tu conn 192.168.10.10 - 192.168.20.10 443 6
Environment:
-
Product: Quantum Security Gateway / Quantum Spark
-
Features:
-
SD-WAN (Site-to-Site VPN over multiple transports)
-
IPsec VPN (Domain-Based or Route-Based VPN)
-
Symptom:
-
Some or all connections do not pass over a Site-to-Site VPN between SD-WAN peers.
-
Applications that should use (encrypted via SD-WAN transports) fail, or time out.
-
SD-WAN transports appear configured, but specific connections do not work as expected.
Troubleshooting:
Run the following checks on both peers, filtering the same connection on both sides.
-
Check Packet Path with fw monitor
On each gateway, run:
fw monitor -F "192.168.1.1,0,192.168.2.1,0,0" -F "192.168.2.1,0,192.168.1.1,0,0"(Replace IPs with your actual source and destination.)
Interpret the inspection points:
i– packet entering from NIC (pre-inbound)I– packet after inbound chain (post-inbound)o– packet before outbound chain (pre-outbound)O– packet leaving NIC (post-outbound – should beOefor encrypted traffic)
Symptom:
-
CPView > Advanced > SDWAN > Probing > the section "Overlay Probing Results" does not show the expected VPN Transports to VPN peers.
-
Infinity Portal > Quantum SD-WAN > Monitor view > Dashboard page > Overlay Tunnels Monitoring tab does not shows the expected VPN transports to VPN peers.
For example, there are no VPN transports to a specific VPN Peer, or to a specific interface of a VPN peer.
The kernel debug "
fw ctl zdebug -m fw + drop" on the Security Gateway (see Troubleshooting SD-WAN with Kernel Debug) may show these traffic drops between the IP addresses of the interfaces on the local Security Gateway and the IP addresses of the interfaces on the VPN Peer Security Gateway:
fw_log_drop_ex: Packet proto=1 <Local IP Address>:0 -> <Peer IP Address>:<Port> dropped by vpn_encrypt_chain Reason: encrypt drop; sdwan_get_vpn_transport_id: Could not find transport id, vpn_transport=[<Peer IP Address>, 12, <Peer IP Address>] kiss_htab_bl_get_ret_val=-1 (_set1); vpn_sdwan_get_transport: Could not find transport entry in defaults transports for peer gateway <Peer IP Address>, conn=<dir 1, <Local IP Address>:0 -> <Peer IP Address>:<Port>IPP 1> rule_uuid=<UUID>.;
Solution:
-
In SmartConsole, make sure the names of interfaces in the object of each involved VPN Peer Security Gateway match the names of interfaces in the Operating System.
-
In the object for a Security Gateway that runs the Gaia OS, go to the page Network Management.
-
In the object for a Quantum Spark Gateway that runs the OS, go to the page Topology.

Important - In a cluster object, the names of the Cluster Virtual Interfaces must be identical to the corresponding physical / virtual interfaces on the cluster members. For example, if you paired the interfaces on cluster members with the names "
eth1", then the Cluster Virtual Interface must also have the name "eth1". -
-
In SmartConsole, make sure the involved VPN Peer Security Gateways / Clusters participate in the correct VPN Community.
-
Make sure the involved VPN Peer Security Gateways / Cluster Members have SD-WAN enabled and the Nano-Agent is running and communicating with the Internet:

Note - In a cluster, run these commands on each cluster member.
-
Run:
cpsdwan statThe output must show the SD-WAN policy is installed.
-
Run:
cpnano -sThe output must show the SD-WAN Nano-Services are running, and the connectivity to the Internet did not fail.
-
-
If you recently made changes in the objects of the involved VPN Peer Security Gateways / Clusters, then install the Access Control policy on each VPN Peer Security Gateway / Cluster.
-
On each VPN Peer Security Gateway / Cluster Member, run:
jq . $FWDIR/state/local/SDWAN/sdwan_steering_policy.jsonThe output must show the relevant Security Gateway / each relevant Cluster Member in the section "
sdwan_steering_vpn_peers".-
If the VPN peer does not appear in the output at all, it most probably means one of these (other causes are also possible):
-
The local Security Gateway / Cluster does not have the SD-WAN information about that VPN peer from Infinity Portal.
-
The local Security Gateway / Cluster does not participate in the same VPN community with this VPN peer.
-
-
If the VPN peer appears in the output, then in the section of this VPN peer, the sub-section "
interfaces" must show the configured interfaces and must show the "Circuit ID" number for each interface.
Important - Make sure the same interface name appears in all these places:
-
In the Gaia operating system on the Security Gateway / each Cluster Member.
-
In SmartConsole > Security Gateway / Cluster object > Network Management page.
-
In the
sdwan_steering_policy.jsonfile > in the section "interfaces" > in the "name" value.
-
-
In the upper section of the output, the section "
sdwan_steering_vpn_local" must show the configured interfaces and must show the "Circuit ID" number for each interface for the local Security Gateway / Cluster Member. -
When the VPN Peer Security Gateways / Clusters are managed by the same Security Management Server / Domain Management Server:
-
The section "
sdwan_steering_vpn_local" and the section "sdwan_steering_vpn_peers" must show the same "Domain UUID" value. If the value is not the same in these sections, then these VPN Peers behave if they are managed by different Management Servers. -
If you configured a Global VPN Community on a Multi-Domain Security Management Server, and the VPN Peer Security Gateways / Cluster are managed by different Domain Management Servers:
-
The section "
sdwan_steering_vpn_local" and the section "sdwan_steering_vpn_peers" will show different "Domain UUID" values. -
The section "
sdwan_steering_vpn_peers" will show the names of interfaces on the VPN peers managed as "ifc-<Number>".
Support for "" in a Global VPN Community is available in:
-
R82 and higher
-
R81.20 Jumbo Hotfix Accumulator Take 79 and higher
-
-

Important:
-
If the "
Circuit ID" numbers for the local Security Gateway / Cluster Member and for the VPN Peer are different, then the VPN Transport cannot be created between them. This is by design. -
It is not supported to use a dummy object that represents a Management Server.
For example, in the Security Gateway / Cluster object properties > on the Fetch Policy page.
-
-
Examine the
$FWDIR/log/sdwan_steering.elgfile for errors about the VPN Peer. -
Examine the VPN tunnel details with dedicated tools:
-
Run:
vpn tu tlistThe output must show tunnels with "
From:" and "To:" fields indicating the SD-WAN interfaces on the local Security Gateway / Cluster Member and on the VPN Peer. -
Run:
vpn tu conn - - - - -The output must show connections that are passing between these:
-
Encryption Domain of the local Security Gateway / Cluster Member
-
Encryption Domain of the VPN Peer
The output must show connections with "
From:" and "To:" fields indicating the SD-WAN interfaces on the local Security Gateway / Cluster Member and on the VPN Peer. -
If the above dedicated tools show the VPN tunnels and VPN connections, then this may be a display issue in the CPView tool.
-
-
If the issue persists, then contact Check Point Support and include these files from each the involved Security Gateway:
-
CPinfo file (sk92739)
-
$FWDIR/log/sdwan_steering.elg -
$FWDIR/log/cpsdwan.elg -
$FWDIR/state/local/SDWAN/sdwan_steering_policy.json -
/var/log/nano_agent/cp-nano-sdwan.dbg -
/var/log/nano_agent/cp-nano-orchestration.dbg -
Run this command and include the output file "
/var/log/vpn_tu_tlist.txt":vpn tu tlist >> /var/log/vpn_tu_tlist.txt -
Run this command and include the output file "
/var/log/vpn_tu_conn.txt":vpn tu conn - - - - - >> /var/log/vpn_tu_conn.txt -
Screenshot from CPView:
-
Run:
cpview -
At the top, click Advanced > SDWAN > Probing.
-
If needed, scroll to down to the relevant section.
-
Take a screenshot - press the "C" key.
-
Press the CTRL+C keys to exit the CPView tool.
-
Include the screenshot file "
cpview_<PID>.cap<Number>"This file is created in the current working directory, in which you ran the
cpviewcommand.Example:
cpview_25117.cap0
-
-
Symptoms:
After enabling SD-WAN "" on a Security Gateway, or after adding multiple SD-WAN VPN Peers:
-
Output of the "
top" command shows significant increase in the CPU load in the processes "fw_worker".CPView (sk101878) > CPU > Overview shows significant increase in the CPU load in the "
CoreXL_FW" instances. -
Output of the "
fw tab -t connections -u -s" command (see sk65133) shows significant increase in the number of concurrent connections (the#VALScolumn). -
Output of the "
fwaccel conns" command shows that ICMP connections are forwarded to the Firewall kernel.
Cause:
-
Each SD-WAN "" Peer sends ICMP Echo Request packets to probe the configured next hop (see SD-WAN Probing and Configuring Steering Behavior).
-
When the value of the kernel parameter "
fw_allow_simultaneous_ping" is set to "1" (one), the Security Gateway handles each ICMP Echo Request packet as a new ICMP connection. Therefore, the Security Gateway does not accelerate these ICMP connections in SecureXL, but forwards them to the Firewall kernel for complete inspection.
|
|
Important - Understand why the value of this kernel parameter was set to "1". There are cases when this value is required, so traffic sent directly to Cluster Members over a Site to Site VPN tunnel can reach them. See sk26874. |
Solution:
-
Connect to the command line on the Security Gateway.
-
Log in to Gaia Clish or the Expert mode.
-
Get the current value of the kernel parameter "
fw_allow_simultaneous_ping":fw ctl get int fw_allow_simultaneous_ping -
If the current value of this kernel parameter is "1" (one), then set its value to "0" (zero) temporarily:
fw ctl set int fw_allow_simultaneous_ping 0 -
Examine the CPU load in one of these ways:
-
Run "
cpview" > go to CPU > Overview > examine the CPU load in the "CoreXL_FW" instances. -
Run "
top" > examine the CPU load in the processes "fw_worker".
-
-
To set the value of this kernel parameter to "0" (zero) permanently, run:
fw ctl set -f int fw_allow_simultaneous_ping 0
Symptoms:
-
Traffic that should be routed through the VTI is not encrypted and is sent in clear-text.
-
Local outgoing connections from the SD-WAN Security Gateway's VTI to the remote VPN peer's VTI (for example, BGP traffic) are not encrypted and are sent in clear-text.
-
Kernel debug on the SD-WAN Security Gateway may show this message (when the debug flag "
fw ctl debug -m VPN + policy" is enabled):init_encryption_params: Traffic accepted by a breakout rule - change to clear
Cause:
The traffic is matching a Local Breakout rule, which by design disables VPN encryption.
Solution:
Make sure that all VPN traffic matches an SD-WAN rule with the "Overlay" behavior and not with the "Internet > Local Breakout Only" behavior.
