Introduction to Quantum SD-WAN
With Quantum SD-WAN you can configure your Security Gateway / Cluster to steer traffic dynamically between the configured WAN Links based on the measured ISP link quality. This does not require dynamic routing configuration on your Security Gateway / Cluster.
With Quantum SD-WAN customers get the most efficient use of high-cost Wide Area Network connections and best user experience for consuming cloud-hosted services in branch offices.
The Security Gateway / Cluster sends different types of traffic through different Internet Service Providers (ISPs) based on application / identity and dynamic measurement of WAN Link characteristics.
The Security Gateway / Cluster applies the configured SD-WAN rules only if the Security Policy allows this traffic.
After you install the SD-WAN Policy, it becomes the main decision maker for traffic paths, traffic priorities, and so on for WAN connections. The SD-WAN policy makes these decisions based on the settings you configure in Infinity Portal.
For additional information, see sk180605.
SD-WAN Use Case
A Security Gateway is connected to two Internet Service Providers.
Traffic from the Zoom application goes to the Internet through ISP #1.
Traffic from the Outlook 365 application goes to the Internet through ISP #2.
Basic SD-WAN Action
You can use SD-WAN for:
-
Local breakout – to control the steering and select the best path for outbound traffic to the Internet.
-
Overlay – to control the best VPN path between VPN peers, for routing internal traffic between the organization sites, either from VPN Spokes to the Hub (Satellites to Center), or between VPN sites in a mesh topology.
-
Backhaul - to route Internet traffic on VPN spoke sites through the Headquarters over the VPN tunnel. This connection uses the overlay-based connection from the Branch to the Center, and a Breakout-based connection from the Center to the Internet.
The Security Gateway uses the WAN Links you configured as SD-WAN interfaces, for Breakout (public SD-WAN interfaces) and for Overlay VPN (all SD-WAN interfaces).
SD-WAN Policy
The SD-WAN Policy contains these ordered rules:
-
Classification of traffic:
-
Source and Destination – IP address, Network address, User / Computer Identity.
-
Service or Application -
Zoom,Teams,https,ftp(see Objects Supported in SD-WAN Policy).
Note - The Security Gateway uses these heuristics to identify connections on the first packet:
-
DNS heuristic – The Security Gateway saves the DNS domains during the DNS query phase and associates the connection that follows with the applicable DNS domain.
-
SNI heuristic – The Security Gateway learns about HTTPS connections and applies the learned data to subsequent connections.
-
DPI heuristic – The Security Gateway applies Deep Packet Inspection to subsequent connections.
As a result of these multiple heuristics, the Security Gateway might not detect the application on the first packet of its connection. For example, when two applications are hosted on the same server.

Best Practice - Use Updatable Objects in the "Destination" column of the SD-WAN Policy. This allows matching of application connections on the first packet and most accurate traffic steering.
-
 Example of an SD-WAN Policy
Example of an SD-WAN Policy
-
Rule #1 - For all traffic from the network 192.168.20.0/24 to the Internet, from the application with the signature of
Microsoft Teams, apply the steering behavior "Aggregate". -
Rule #2 - For all traffic from the network 192.168.20.0/24 to IP addresses that are resolved from the Updatable object "
Zoom Services", from any application, apply the steering behavior "Prioritize_WAN2". -
Rule #3 - For all traffic from users (IP addresses) determined by the Access Role "SalesRole" to the Internet, from the application with the signature of "
YouTube", apply the steering behavior "High_Quality".
-
-
Steering Behavior:
Steering tactics include a measurement target and a steering decision to select a WAN Link.
-
Connection Type (Steering Behavior):
-
 "Internet" with "Local Breakout Only"
"Internet" with "Local Breakout Only"
See Routing Preference "Local Breakout Only".
This connection type represents a direct WAN Link to the Internet.

-
 "Internet" with "Backhaul Only"
"Internet" with "Backhaul Only"
See Routing Preference "Backhaul Only".
This connection sends traffic from VPN spoke sites to the Internet through the Central VPN hub site.
This connection type enables the VPN spoke site to use the Public lines / Private lines to reach the Internet through the Headquarters.

-
 "Internet" with "Prioritize Local Breakout"
"Internet" with "Prioritize Local Breakout"
See Routing Preference "Prioritize Local Breakout".
This connection type gives priority to the direct WAN Link (not through the Headquarters) to send all traffic directly to the Internet.
If all direct WAN Links to the Internet are down, the Security Gateway uses the direct WAN Link with encrypted traffic to the Headquarters to connect to the Internet.
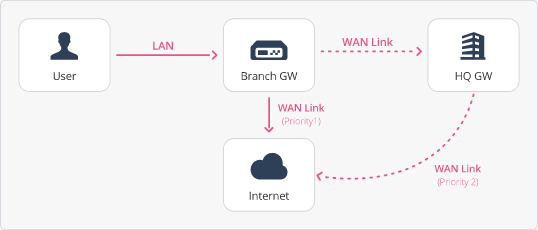
-
 ""
""
See SD-WAN Connection Type - "Overlay".
This connection type represents a direct WAN Link with encrypted traffic to the Headquarters.
The direct WAN Link with encrypted traffic to the Headquarters provides redundancy.

-
-
Steering Criteria:
-
Select a better ISP Link based on Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss.
-
Select a better ISP Link based on WAN Link utilization.
You also configure the Quality Check methods to measure the ISP link quality.
-
-
Basic Workflow
To steer traffic with SD-WAN, you configure the required settings:
-
On the Security Gateway / each Cluster Member - The SD-WAN interfaces and the Nano-Agent.
-
In SmartConsole - The required objects and the connection to your account in Infinity Portal.
In Smart-1 Cloud - The required objects.
-
In Infinity Portal - The required SD-WAN objects, WAN Link settings, and SD-WAN Policy.
