SD-WAN Connection Type - "Internet"
The connection (Steering Behavior) type "Internet" has these routing preference modes:
-
Local Breakout Only
-
Backhaul Only
-
Prioritize Local Breakout
Routing Preference "Local Breakout Only"
This connection type represents a direct WAN Link to the Internet.

Offices with multiple direct WAN Links to the Internet.
Example:
-
A Security Gateway with two ISPs.
-
The Zoom application traffic must go over an ISP Link with lower latency.
-
The backup transfer traffic must go over an ISP Link with higher latency.
Example of an SD-WAN Policy rule:
Traffic, using the "YouTube" services, must go from any source behind the Security Gateway to the Internet.
The Security Gateway sends the traffic through the WAN Links configured in the Steering Behavior, if the Access Control Policy allows this traffic.
|
|
Important:
|
The Security Gateway sends the traffic directly to the Internet, based on the Services & Applications column of the SD-WAN Policy.
In the section Steering Candidates, configure the applicable settings:
-
All Relevant WAN Links - To use all available WAN Links.
-
Specific WAN Links - To use only the selected WAN Links.
Routing Preference "Backhaul Only"
This connection sends traffic from VPN spoke sites to the Internet through the Central VPN hub site.
This connection type enables the VPN spoke site to use the Public lines / Private lines to reach the Internet through the Headquarters.

Branch offices with a direct WAN Link to the Internet and with a direct WAN Link to the Headquarters.
Branch offices must send specific traffic to the Internet through the Headquarters Security Gateway.
Example:
-
A branch Security Gateway with two ISPs.
-
Regular web traffic must go over a direct WAN Link to the Internet.
-
Email traffic must go through the Headquarters Security Gateway for deep inspection.
Example topology:
-
User ---> Branch Gateway ---> ISP1 ---> (Internet) -
User ---> Branch Gateway ---> ISP2 ---> HQ Gateway ---> (Internet)
Example of an SD-WAN Policy rule:
|
|
Important:
|
-
The Branch Security Gateway creates a Site-to-Site VPN tunnel with the Headquarters Security Gateway.
-
The Branch Security Gateway encrypts the traffic and sends the traffic directly to the Headquarters Security Gateway.
-
The Headquarters Security Gateway decrypts the traffic.
-
The Headquarters Security Gateway forwards the traffic to the Internet.
-
The response arrives from the Internet to the Headquarters Security Gateway.
-
The Headquarters Security Gateway inspects the traffic.
-
The Headquarters Security Gateway encrypts the traffic and sends the traffic directly to the Branch Security Gateway.
-
The Branch Security Gateway decrypts the traffic.
In the section Steering Candidates, configure the applicable settings:
-
All Relevant WAN Links
The Security Gateway uses all available WAN Links.
-
Specific WAN Links
The Security Gateway uses only the selected WAN Links.
-
Use the same settings for Branch to HQ connection
Controls which WAN Links the Security Gateway uses to connect from a Branch office to the Headquarters ("All Relevant WAN Links" or "Specific WAN Links").
Routing Preference "Prioritize Local Breakout"
This connection type gives priority to the direct WAN Link (not through the Headquarters) to send all traffic directly to the Internet.
If all direct WAN Links to the Internet are down, the Security Gateway uses the direct WAN Link with encrypted traffic to the Headquarters to connect to the Internet.
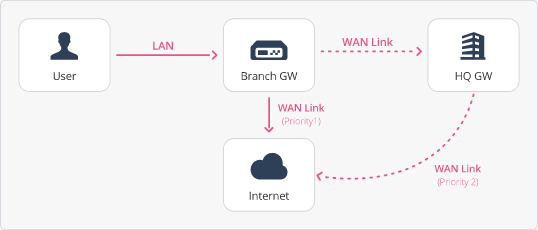
Example:
-
A branch Security Gateway with two ISPs.
-
All traffic must go over a direct WAN Link to the Internet (denoted "ISP1" below).
-
When the direct WAN Link to the Internet is down (denoted "ISP1" below), the Security Gateway connects to the Internet through the other WAN Link with encrypted traffic to the Headquarters (denoted "ISP2" below).
Example topology:
-
User ---> Branch Gateway ---> ISP1 ---> (Internet) -
User ---> Branch Gateway ---> ISP2 ---> HQ Gateway ---> (Internet)
Special scenario:
To send one traffic type directly to the Internet, and send another traffic type to the Internet through the Headquarters, configure two Steering objects and two rules in the SD-WAN Policy (rule numbers below are only for convenience):
Example:
-
If at least one direct WAN Link to the Internet is up, the Security Gateway uses the "Local Breakout Only" connection:
The Security Gateway sends the traffic directly to the Internet, based on the Services & Applications column of the SD-WAN Policy.
-
If all direct WAN Links to the Internet are down, the Security Gateway uses the "Backhaul Only" connection:
-
The Branch Security Gateway creates a Site-to-Site VPN tunnel with the Headquarters Security Gateway.
-
The Branch Security Gateway encrypts the traffic and sends the traffic directly to the Headquarters Security Gateway.
-
The Headquarters Security Gateway decrypts the traffic.
-
The Headquarters Security Gateway forwards the traffic to the Internet.
-
The response arrives from the Internet to the Headquarters Security Gateway.
-
The Headquarters Security Gateway inspects the traffic.
-
The Headquarters Security Gateway encrypts the traffic and sends the traffic directly to the Branch Security Gateway.
-
The Branch Security Gateway decrypts the traffic.
-
|
|
Important:
|
In the section Steering Candidates, configure the applicable settings:
-
All Relevant WAN Links
The Security Gateway uses all available WAN Links.
-
Specific WAN Links
The Security Gateway uses only the selected WAN Links.
-
Use the same settings for Branch to HQ connection
Controls which WAN Links the Security Gateway uses to connect from a Branch office to the Headquarters ("All Relevant WAN Links" or "Specific WAN Links").

