Harmony Endpoint for Linux Overview
|
|
Note - Starting in R81, the on-premises Endpoint Security Server supports Harmony Endpoint for Linux. To enable Harmony Endpoint for Linux, you must enable the Linux installation package flag as described in sk177250. |
Prerequisites
-
Available Internet access for the protected device.
-
For RHEL/CentOS, it is necessary to have access to EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository.
-
If the device has no internet access, you must enable access to certain URLs. For more information, see sk116590.
-
Ensure these directories reside on a file system mounted with executable permissions. Avoid using the
noexecoption when mounting these file systems.-
/var/lib -
/tmp
-
-
The Linux Kernel Headers package for the installed kernel must be available. This package is typically installed during the Linux distribution installation.
Key Threat Prevention Technologies
Anti-Malware
-
The Anti-Malware
 A component of the Endpoint Security client that protects against known and unknown viruses, worms, Trojan horses, adware, and keystroke loggers. security engine detects trojans, viruses, malware, and other malicious threats.
A component of the Endpoint Security client that protects against known and unknown viruses, worms, Trojan horses, adware, and keystroke loggers. security engine detects trojans, viruses, malware, and other malicious threats. -
The engine is implemented as a multi-threaded flexible scanner daemon. It is managed centrally through a web-console.
-
In addition, it supports command line utilities for on-demand file scans, access functionality, and automatic signature updates.
-
Managed centrally through a web-console and also supports Command Line Utilities for on-demand file/folder scans, detection lists and file restorations
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) / Threat Hunting
-
Harmony Endpoint for Linux, updates ThreatCloud with Indicator of Compromise (IoC) and Indicator of Attack (IoA) events.
-
Threat Hunting technology lets the administrators proactively search for cyber threats that made it through the first line of defense to the Linux Endpoint device.
-
Threat Hunting uses advanced detection capabilities, such as queries and automation, to find malicious activities and extract hunting leads of data.
-
Supporting events:
-
Process - start / stop
-
Files - create / delete / rename / open
-
Network - local connections, ports, DNS
-
Behavioral Guard
-
Dynamic analysis of malware executed on the Endpoint Client is performed based on the behavioral patterns of various attack types, including ransomware, cryptominers, and trojans.
-
Centrally managed via the web management platform.
-
Leverages a large set of constantly updated signatures to detect, prevent, and remediate modern attacks.
-
Features automatic signature updates powered by the latest intelligence, ensuring adaptation to emerging threats
Anti-Ransomware
Monitors the endpoint for signs of ransomware activity and helps prevent file encryption by malicious actors.
Forensics
Generates detailed analytics and interactive reports from threats and incidents, providing a comprehensive view of attack flows and actionable insights for effective remediation.
|
|
Note - Starting from version 1.22.x, the Forensics security blade is installed by default when the Behavioral Guard security blade is installed. |
Minimum Hardware Requirements
-
x86 processor, 64-bit (32-bit is not supported)
-
2 GHz Dual-core CPU
-
4 GB RAM
-
10 GB free disk space
Supported Linux Versions
|
Distribution / OS Version |
1.26.8 |
1.24.02 |
1.22.18 |
1.22.16 |
1.22.12 |
1.20.7 |
1.18.16 |
1.18.12 |
1.15.10 |
1.15.7 |
1.13.3 |
1.13.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ubuntu 24.04 (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Ubuntu 22.04 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 22.04 - 22.04.3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Ubuntu 20.04 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 20.04 - 20.04.6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Ubuntu 18.04* (64-bit) (Supported versions: 18.04 - 18.04.6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Ubuntu 16.04 (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Alma Linux 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alma Linux 9.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alma Linux 9.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alma Linux 9 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 9.0 - 9.3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Alma Linux 8 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 8.9 and 8.10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Amazon Linux 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Amazon Linux 2 (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
CentOS 8* (64-bit) (Supported versions : 8.0 - 8.5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
CentOS 7 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 7.8 - and 7.9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Debian Linux 13 (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Debian Linux 12 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 12.0 - 12.5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Debian Linux 11* (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
| Debian Linux 10* (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
| Debian Linux 9* (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Fedora 39¹ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Fedora 38¹ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Fedora 37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Fedora 36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Fedora 35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Fedora 34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Mint 22.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mint 22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mint 21.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSUSE Leap 16.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSUSE Leap 15.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OpenSUSE 15.4 and OpenSUSE 15.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
OpenSUSE 42.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Oracle Linux 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Linux 9.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Linux 9.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Linux 9.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Linux 8 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 8.0 - 8.10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Linux 7.9 (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 10.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 10 (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9.6 (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9 ¹ (64-bit) (Supported versions: 9.0 - 9.5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 8.0 - 8.9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8.10 (64-bit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 7.8 and 7.9) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Rocky 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rocky 9.5 |
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Rocky 8.10 |
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 15 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 15SP2 and 15SP3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 12 (64-bit) (Supported versions: 12SP5) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|
¹ Only Anti-Malware support.
Linux Kernel Support
Harmony Endpoint for Linux supports the general-purpose Linux kernels included in standard Linux distributions. These kernels come by default with Linux distribution.
This excludes kernels that are:
-
Non default kernels
-
Unbreakable kernels
-
Appliance, for example, Exadata
-
Community based, for example, ELRepo
-
Custom Compiled kernels
-
Desktop and Gaming kernels
Installation on Semi-Isolated Environments with Super Node Proxy
Prerequisite
-
Make sure that Harmony Endpoint for Linux version 1.22.12 or higher is installed on client devices.
-
Make sure that Harmony Endpoint for Windows version E88.70 or higher is installed on super node devices.
-
The Linux devices must be able to resolve the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the Windows super node machine. This can be achieved through an organizational name server.
|
|
Notes:
|
Installation Procedure
-
Export and Download the Offline Package: Download the appropriate universal offline package (rpm or deb) that matches your distribution. Transfer the package to all endpoint devices.
-
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), run this command before installing the package:
subscription-manager config --rhsm.manage_repos=0 -
Run the installation package.
-
Verify communication with the Management Server:
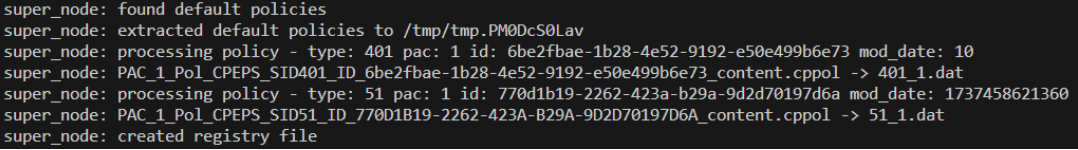
-
To verify the status, run:
cpla info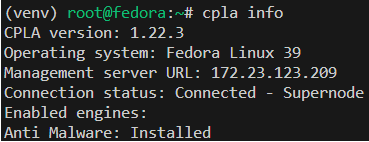
The output displays:
Connection status: Connected - SupernodeThe client appears in the server's asset information.
-
|
|
Note - If communication is not established, perform these:
|