Check Point CloudGuard Network for AWS
Check Point CloudGuard for AWS![]() Amazon® Web Services. Public cloud platform that offers global compute, storage, database, application and other cloud services. easily extends comprehensive Threat Prevention security to the AWS cloud and protects assets in the cloud from attacks, and at the same time enables secure connectivity.
Amazon® Web Services. Public cloud platform that offers global compute, storage, database, application and other cloud services. easily extends comprehensive Threat Prevention security to the AWS cloud and protects assets in the cloud from attacks, and at the same time enables secure connectivity.
Use CloudGuard Network to enforce consistent Security Policies![]() Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. across your entire organization. It protects data between the corporate network and the Amazon VPC. CloudGuard Network inspects data that enters and leaves the private subnet in the Amazon VPC to prevent attacks and mitigate data loss or leakage. CloudGuard Network protects services in the public cloud from the most sophisticated threats, unapproved access, and prevents application layer Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. across your entire organization. It protects data between the corporate network and the Amazon VPC. CloudGuard Network inspects data that enters and leaves the private subnet in the Amazon VPC to prevent attacks and mitigate data loss or leakage. CloudGuard Network protects services in the public cloud from the most sophisticated threats, unapproved access, and prevents application layer Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
|
|
Note - For the list of supported versions, refer to the Support Life Cycle Policy. |
Costs and Licenses
You are responsible for the cost of the AWS services that you use, when you deploy the solution described in this guide.
The AWS CloudFormation template for the Security VPC includes parameters that you can configure. Some of these settings, such as instance type have an effect on the cost of deployment. For estimated costs, see the AWS pricing calculator.
This Transit VPC - Transit Gateway solution uses Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) from the AWS Marketplace. You must subscribe to Check Point CloudGuard in the AWS Marketplace before you start the deployment.
Check Point CloudGuard Security Gateways, Check Point CloudGuard Security Management Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server., and AWS CloudFormation templates described in this guide must have a license.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server., and AWS CloudFormation templates described in this guide must have a license.
There are two licensing options:
-
Pay As You Go (PAYG)
-
Bring Your Own License (BYOL)
To buy BYOL licenses, contact Check Point Sales.
|
|
Note - With the CloudFormation template (refer to section Step 5: Deploying the CloudGuard Auto Scaling Group for more information), it is possible to launch Security Gateways based on the Bring Your Own License (BYOL) or Pay as You Go (PAYG) licensing models. For more information on how to install the Bring Your Own License (BYOL), see the CloudGuard Network Central License Management Utility guide. |
|
|
Important - Auto Scaling Group with a mixture of BYOL and PAYG Security Gateways is not supported. |
Introduction to AWS Auto Scaling Groups
Auto Scaling is a service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that helps customers automatically adjust their Amazon EC2 capacity based on the current load.
A typical use case consists of a web application served by multiple web servers that are deployed across multiple Availability Zones. An Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) distributes network traffic across this group of web servers as needed.
The Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling service increases or decreases the number of web servers based on the traffic load.
In the current cyber-landscape, it is very important that you protect these environments from attackers with a security solution that is as scalable as the resources it protects. As the number of resources you protect scales up or down, the number of Security Gateways that provide protection has to scale as well.
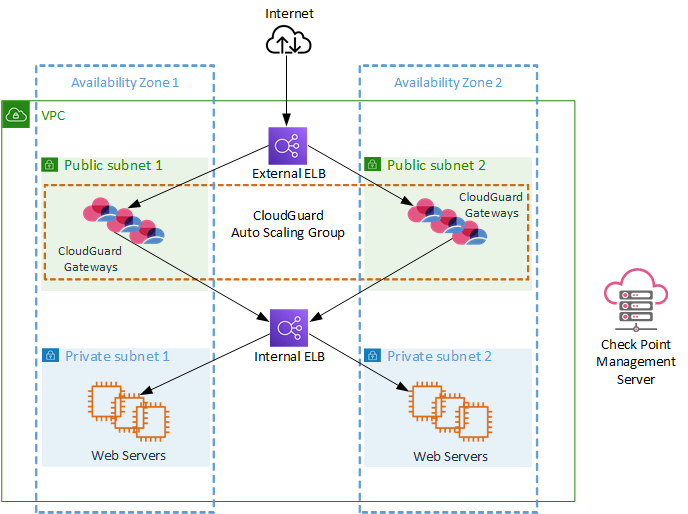
The diagram below shows the Auto Scaling Group architecture for Check Point CloudGuard Network AWS, an end-to-end solution, which includes:
-
VPC with two availability zones (Availability Zone 1 and Availability Zone 2).
-
Public and private subnet for each availability zone.
-
An External ELB to send incoming traffic to a Check Point Auto Scaling Group that resides on the two public subnets.
-
CloudGuard Network gateways in the Auto Scaling Group that inspect the traffic and, if policy allows, forward the traffic to an Internal ELB.
-
Internal ELB sends incoming traffic to a group of servers residing on the two private subnets
|
|
Note - There are few supported types of ELB, before selecting which ELB to deploy, see AWS Elastic Load Balancing. |
The Check Point Auto Scaling Group is set up to increase or decrease the number of Check Point CloudGuard Network Security Gateways that protect your environment in the group based on AWS Cloud Watch metrics.
Prerequisites
Make sure you are familiar with these topics:
If you are new to AWS, see also Getting Started with AWS.


