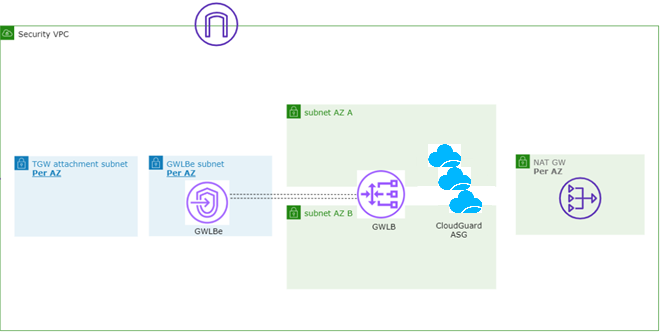
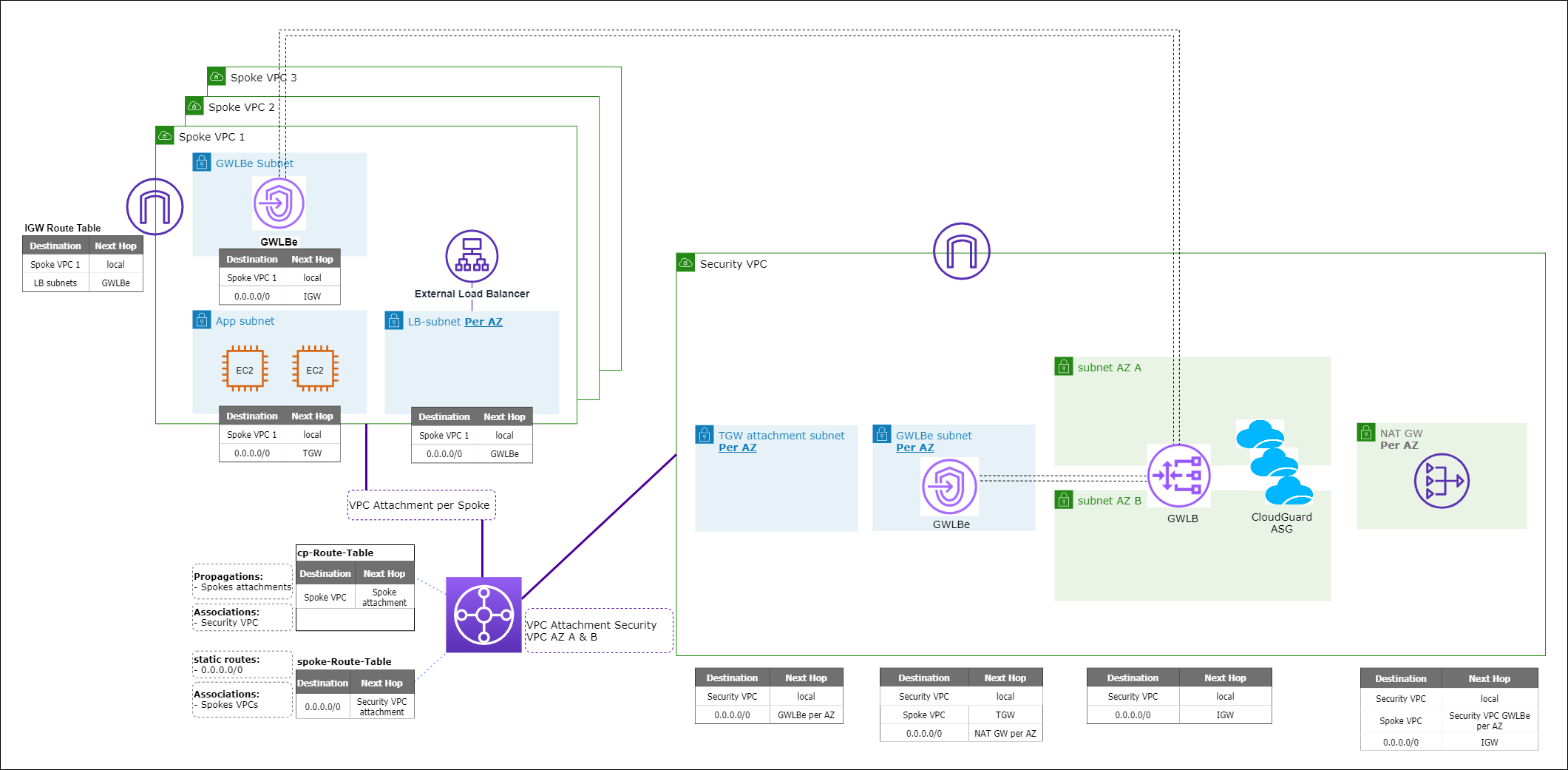
Deploying a GWLB Security VPC for Transit Gateway
This section describes the steps to deploy a CloudGuard Network Security VPC with the Gateway Load Balancer for theTransit Gateway.
Steps 1-8 describe how to configure a GWLB Security VPC for TGW east-west and outbound traffic inspection. To add inbound inspection to your Spoke VPCs with GWLB, see (Optional) Configure Inbound Traffic to Spoke VPCs.
The Security VPC CloudFormation Template for Transit Gateway deploys a CloudGuard Network Auto Scaling Group, a Gateway Load Balancer, Gateway Load Balancer Endpoints, NAT Gateways for each AZ, and an optional Security Management Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. into a new VPC.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. into a new VPC.
Step 1: Prepare your AWS Account
To prepare your AWS account:
-
If you do not have an AWS
 Amazon® Web Services. Public cloud platform that offers global compute, storage, database, application and other cloud services. account, create one.
Amazon® Web Services. Public cloud platform that offers global compute, storage, database, application and other cloud services. account, create one. -
Use the region selector in the navigation bar to select the AWS region where you want to deploy Check Point CloudGuard Network Auto Scaling on AWS.
-
Create a key pair in your preferred region.
-
Request a service limit increase for the AWS resources you plan to use, if necessary.
By default, this Deployment Guide uses:
-
c5.xlarge instances for Security Gateways
-
m5.xlarge instances for the Security Management Server
 Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server..
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server..
-
Minimum Permissions for Deployment
Configure the relevant IAM policy with the minimum permissions for a successful deployment, as shown below.
In the AWS VPC![]() AWS Virtual Private Cloud. A private cloud that exists in the public cloud of Amazon. It is isolated from other Virtual Networks in the AWS cloud. Console, navigate to the IAM service, select the relevant IAM policy, copy the required permissions from this guide (see below) and paste them into the policy:
AWS Virtual Private Cloud. A private cloud that exists in the public cloud of Amazon. It is isolated from other Virtual Networks in the AWS cloud. Console, navigate to the IAM service, select the relevant IAM policy, copy the required permissions from this guide (see below) and paste them into the policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Permissions",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"SNS:CreateTopic",
"SNS:DeleteTopic",
"SNS:GetTopicAttributes",
"SNS:Subscribe",
"autoscaling:CreateAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:DeleteAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:DeletePolicy",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:DescribePolicies",
"autoscaling:DescribeScalingActivities",
"autoscaling:PutNotificationConfiguration",
"autoscaling:PutScalingPolicy",
"autoscaling:SetInstanceProtection",
"autoscaling:UpdateAutoScalingGroup",
"cloudformation:CreateStack",
"cloudformation:DeleteStack",
"cloudformation:DescribeStacks",
"cloudformation:ListStackResources",
"cloudformation:ValidateTemplate",
"cloudwatch:DeleteAlarms",
"cloudwatch:PutMetricAlarm",
"ec2:AllocateAddress",
"ec2:AssociateAddress",
"ec2:AssociateRouteTable",
"ec2:AttachInternetGateway",
"ec2:AttachNetworkInterface",
"ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress",
"ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress",
"ec2:CreateInternetGateway",
"ec2:CreateLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:CreateLocalGatewayRouteTable",
"ec2:CreateNetworkInterface",
"ec2:CreateRoute",
"ec2:CreateRouteTable",
"ec2:CreateSecurityGroup",
"ec2:CreateSubnet",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"ec2:CreateVpc",
"ec2:CreateVpcEndpointServiceConfiguration",
"ec2:DeleteInternetGateway",
"ec2:DeleteLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:DeleteNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DeleteRoute",
"ec2:DeleteRouteTable",
"ec2:DeleteSecurityGroup",
"ec2:DeleteSubnet",
"ec2:DeleteVpc",
"ec2:DeleteVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DescribeAccountAttributes",
"ec2:DescribeAddresses",
"ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceAttribute",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypes",
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeInternetGateways",
"ec2:DescribeKeyPairs",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplateVersions",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplates",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkAcls",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces",
"ec2:DescribeRegions",
"ec2:DescribeRouteTables",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ec2:DescribeSubnets",
"ec2:DescribeTags",
"ec2:DescribeVolumes",
"ec2:DescribeVpcAttribute",
"ec2:DescribeVpcClassicLink",
"ec2:DescribeVpcClassicLinkDnsSupport",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServicePermissions",
"ec2:DescribeVpcs",
"ec2:DetachInternetGateway",
"ec2:DetachNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DisassociateAddress",
"ec2:DisassociateRouteTable",
"ec2:ModifyNetworkInterfaceAttribute",
"ec2:ModifySubnetAttribute",
"ec2:ModifyVpcAttribute",
"ec2:ReleaseAddress",
"ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupEgress",
"ec2:RunInstances",
"ec2:TerminateInstances",
"elasticloadbalancing:AddTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateListener",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateLoadBalancer",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteListener",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteLoadBalancer",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListeners",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroupAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroups",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetHealth",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyTargetGroupAttributes",
"iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile",
"iam:AttachRolePolicy",
"iam:CreateInstanceProfile",
"iam:CreatePolicy",
"iam:CreateRole",
"iam:DeleteInstanceProfile",
"iam:DeletePolicy",
"iam:DeleteRole",
"iam:DeleteRolePolicy",
"iam:DetachRolePolicy",
"iam:GetInstanceProfile",
"iam:GetPolicy",
"iam:GetPolicyVersion",
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:ListAttachedRolePolicies",
"iam:ListInstanceProfilesForRole",
"iam:ListPolicyVersions",
"iam:ListRolePolicies",
"iam:PutRolePolicy",
"iam:RemoveRoleFromInstanceProfile"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "IAMPassRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PassRole",
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"iam:PassedToService": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Permissions",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"SNS:CreateTopic",
"SNS:DeleteTopic",
"SNS:GetTopicAttributes",
"SNS:Subscribe",
"autoscaling:CreateAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:DeleteAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:DeletePolicy",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:DescribePolicies",
"autoscaling:DescribeScalingActivities",
"autoscaling:PutNotificationConfiguration",
"autoscaling:PutScalingPolicy",
"autoscaling:SetInstanceProtection",
"autoscaling:UpdateAutoScalingGroup",
"cloudformation:CreateStack",
"cloudformation:DeleteStack",
"cloudformation:DescribeStacks",
"cloudformation:ListStackResources",
"cloudformation:ValidateTemplate",
"cloudwatch:DeleteAlarms",
"cloudwatch:DescribeAlarms",
"cloudwatch:ListTagsForResource",
"cloudwatch:PutMetricAlarm",
"ec2:AllocateAddress",
"ec2:AssociateAddress",
"ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress",
"ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress",
"ec2:CreateLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:CreateNetworkInterface",
"ec2:CreateRoute",
"ec2:CreateSecurityGroup",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"ec2:CreateVpcEndpointServiceConfiguration",
"ec2:DeleteLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:DeleteNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DeleteSecurityGroup",
"ec2:DeleteVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DescribeAddresses",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceAttribute",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypes",
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeKeyPairs",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplateVersions",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplates",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ec2:DescribeSubnets",
"ec2:DescribeTags",
"ec2:DescribeVolumes",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServicePermissions",
"ec2:DescribeVpcs",
"ec2:DescribeRegions",
"ec2:DetachNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DisassociateAddress",
"ec2:ModifyNetworkInterfaceAttribute",
"ec2:ReleaseAddress",
"ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupEgress",
"ec2:RunInstances",
"ec2:TerminateInstances",
"elasticloadbalancing:AddTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateListener",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateLoadBalancer",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteListener",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteLoadBalancer",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListeners",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroupAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroups",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetHealth",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyTargetGroupAttributes",
"iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile",
"iam:AttachRolePolicy",
"iam:CreateInstanceProfile",
"iam:CreatePolicy",
"iam:CreateRole",
"iam:DeleteInstanceProfile",
"iam:DeletePolicy",
"iam:DeleteRole",
"iam:DeleteRolePolicy",
"iam:DetachRolePolicy",
"iam:GetInstanceProfile",
"iam:GetPolicy",
"iam:GetPolicyVersion",
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:ListAttachedRolePolicies",
"iam:ListInstanceProfilesForRole",
"iam:ListPolicyVersions",
"iam:ListRolePolicies",
"iam:PutRolePolicy",
"iam:RemoveRoleFromInstanceProfile"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "IAMPassRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PassRole",
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"iam:PassedToService": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Permissions",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"SNS:CreateTopic",
"SNS:DeleteTopic",
"SNS:GetTopicAttributes",
"SNS:Subscribe",
"autoscaling:CreateAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:DeleteAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:DeletePolicy",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:DescribePolicies",
"autoscaling:DescribeScalingActivities",
"autoscaling:PutNotificationConfiguration",
"autoscaling:PutScalingPolicy",
"autoscaling:SetInstanceProtection",
"autoscaling:UpdateAutoScalingGroup",
"cloudformation:CreateStack",
"cloudformation:DeleteStack",
"cloudformation:DescribeStacks",
"cloudformation:ListStackResources",
"cloudformation:ValidateTemplate",
"cloudwatch:DeleteAlarms",
"cloudwatch:DescribeAlarms",
"cloudwatch:ListTagsForResource",
"cloudwatch:PutMetricAlarm",
"ec2:AllocateAddress",
"ec2:AssociateAddress",
"ec2:AssociateRouteTable",
"ec2:AttachInternetGateway",
"ec2:AttachNetworkInterface",
"ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress",
"ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress",
"ec2:CreateInternetGateway",
"ec2:CreateLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:CreateLocalGatewayRouteTable",
"ec2:CreateNatGateway",
"ec2:CreateNetworkInterface",
"ec2:CreateRoute",
"ec2:CreateRouteTable",
"ec2:CreateSecurityGroup",
"ec2:CreateSubnet",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"ec2:CreateVpc",
"ec2:CreateVpcEndpoint",
"ec2:CreateVpcEndpointServiceConfiguration",
"ec2:DeleteInternetGateway",
"ec2:DeleteLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:DeleteNatGateway",
"ec2:DeleteNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DeleteRoute",
"ec2:DeleteRouteTable",
"ec2:DeleteSecurityGroup",
"ec2:DeleteSubnet",
"ec2:DeleteVpc",
"ec2:DeleteVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DeleteVpcEndpoints",
"ec2:DescribeAccountAttributes",
"ec2:DescribeAddresses",
"ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceAttribute",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypes",
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeInternetGateways",
"ec2:DescribeKeyPairs",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplateVersions",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplates",
"ec2:DescribeNatGateways",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkAcls",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces",
"ec2:DescribePrefixLists",
"ec2:DescribeRegions",
"ec2:DescribeRouteTables",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ec2:DescribeSubnets",
"ec2:DescribeTags",
"ec2:DescribeVolumes",
"ec2:DescribeVpcAttribute",
"ec2:DescribeVpcClassicLink",
"ec2:DescribeVpcClassicLinkDnsSupport",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServicePermissions",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpoints",
"ec2:DescribeVpcs",
"ec2:DetachInternetGateway",
"ec2:DetachNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DisassociateAddress",
"ec2:DisassociateRouteTable",
"ec2:ModifyNetworkInterfaceAttribute",
"ec2:ModifySubnetAttribute",
"ec2:ModifyVpcAttribute",
"ec2:ReleaseAddress",
"ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupEgress",
"ec2:RunInstances",
"ec2:TerminateInstances",
"elasticloadbalancing:AddTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateListener",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateLoadBalancer",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteListener",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteLoadBalancer",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListeners",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroupAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroups",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetHealth",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyTargetGroupAttributes",
"iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile",
"iam:AttachRolePolicy",
"iam:CreateInstanceProfile",
"iam:CreatePolicy",
"iam:CreateRole",
"iam:DeleteInstanceProfile",
"iam:DeletePolicy",
"iam:DeleteRole",
"iam:DeleteRolePolicy",
"iam:DetachRolePolicy",
"iam:GetInstanceProfile",
"iam:GetPolicy",
"iam:GetPolicyVersion",
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:ListAttachedRolePolicies",
"iam:ListInstanceProfilesForRole",
"iam:ListPolicyVersions",
"iam:ListRolePolicies",
"iam:PutRolePolicy",
"iam:RemoveRoleFromInstanceProfile"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "IAMPassRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PassRole",
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"iam:PassedToService": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Permissions",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"SNS:CreateTopic",
"SNS:DeleteTopic",
"SNS:GetTopicAttributes",
"SNS:Subscribe",
"autoscaling:CreateAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:DeleteAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:DeletePolicy",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:DescribePolicies",
"autoscaling:DescribeScalingActivities",
"autoscaling:PutNotificationConfiguration",
"autoscaling:PutScalingPolicy",
"autoscaling:SetInstanceProtection",
"autoscaling:UpdateAutoScalingGroup",
"cloudformation:CreateStack",
"cloudformation:DeleteStack",
"cloudformation:DescribeStacks",
"cloudformation:ListStackResources",
"cloudformation:ValidateTemplate",
"cloudwatch:DeleteAlarms",
"cloudwatch:DescribeAlarms",
"cloudwatch:ListTagsForResource",
"cloudwatch:PutMetricAlarm",
"ec2:AllocateAddress",
"ec2:AssociateAddress",
"ec2:AssociateRouteTable",
"ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupEgress",
"ec2:AuthorizeSecurityGroupIngress",
"ec2:CreateLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:CreateNatGateway",
"ec2:CreateNetworkInterface",
"ec2:CreateRoute",
"ec2:CreateRouteTable",
"ec2:CreateSecurityGroup",
"ec2:CreateSubnet",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"ec2:CreateVpcEndpoint",
"ec2:CreateVpcEndpointServiceConfiguration",
"ec2:DeleteLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:DeleteNatGateway",
"ec2:DeleteNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DeleteRouteTable",
"ec2:DeleteSecurityGroup",
"ec2:DeleteSubnet",
"ec2:DeleteVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DeleteVpcEndpoints",
"ec2:DescribeAddresses",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceAttribute",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypes",
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeKeyPairs",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplateVersions",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplates",
"ec2:DescribeNatGateways",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces",
"ec2:DescribePrefixLists",
"ec2:DescribeRouteTables",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ec2:DescribeSubnets",
"ec2:DescribeTags",
"ec2:DescribeVolumes",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServicePermissions",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpoints",
"ec2:DescribeVpcs",
"ec2:DescribeRegions",
"ec2:DetachNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DisassociateAddress",
"ec2:DisassociateRouteTable",
"ec2:ModifyNetworkInterfaceAttribute",
"ec2:ReleaseAddress",
"ec2:RevokeSecurityGroupEgress",
"ec2:RunInstances",
"ec2:TerminateInstances",
"elasticloadbalancing:AddTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateListener",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateLoadBalancer",
"elasticloadbalancing:CreateTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteListener",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteLoadBalancer",
"elasticloadbalancing:DeleteTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListeners",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroupAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroups",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetHealth",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyLoadBalancerAttributes",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyTargetGroup",
"elasticloadbalancing:ModifyTargetGroupAttributes",
"iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile",
"iam:AttachRolePolicy",
"iam:CreateInstanceProfile",
"iam:CreatePolicy",
"iam:CreateRole",
"iam:DeleteInstanceProfile",
"iam:DeletePolicy",
"iam:DeleteRole",
"iam:DeleteRolePolicy",
"iam:DetachRolePolicy",
"iam:GetInstanceProfile",
"iam:GetPolicy",
"iam:GetPolicyVersion",
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:ListAttachedRolePolicies",
"iam:ListInstanceProfilesForRole",
"iam:ListPolicyVersions",
"iam:ListRolePolicies",
"iam:PutRolePolicy",
"iam:RemoveRoleFromInstanceProfile"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "IAMPassRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PassRole",
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"iam:PassedToService": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}Step 2: Subscribe to Check Point CloudGuard Network Security
To deploy the Check Point GWLB solution, do these steps:
-
Log in to the AWS Marketplace.
-
Search for "CloudGuard Network Security".
-
Select one of these licensing options for the CloudGuard Network Security for Gateway Load Balancer:
-
CloudGuard Network Security with Threat Prevention & SandBlast BYOL
-
CloudGuard Network Security Next-Gen Firewall with Threat Prevention
-
CloudGuard Network Security with Threat Prevention and SandBlast
Or one of these licensing options for a Check Point CloudGuard Security Management Server:
-
-
Select Continue to subscribe.
-
Select Accept Terms to confirm that you accept the AWS Marketplace license agreement.
Step 3: Deploy the Check Point Security Management Server
Use one of these options to deploy the Check Point Security Management Server:
-
Deploying a New SMS with a Management CloudFormation Template
-
Using the Existing On-Premises SMS or the SMS in AWS
-
Deploying a Dedicated SMS as Part of the Security VPC
-
Deploy the Security Management Server separately as described in sk130372 > Installing Check Point Security Management Server section.
-
Create an IAM role with read and write permissions as described in the section below or deploy the IAM role and attach it to the Security Management Server that manages the GWLB Auto Scale solution.
You can use an existing on premises or AWS Security Management Server instance.
In AWS VPC Console, configure the required permissions for the Security Management Server:
{
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetHealth",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTargetGroups",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeTags",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeRules",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeLoadBalancers",
"elasticloadbalancing:DescribeListeners",
"ec2:DescribeVpcs",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpoints",
"ec2:DescribeVpcEndpointServiceConfigurations",
"ec2:DescribeSubnets",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ec2:DescribeRouteTables",
"ec2:DescribeRegions",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces",
"ec2:DescribeInternetGateways",
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "*"
}
],
"Version": "2012-10-17"
}With the Solution CloudFormation Template, you can create a dedicated Security Management Server as part of the deployment.
Step 4: Deploy the GWLB Security VPC for Transit Gateway
This step details the necessary procedure for deploying the Check Point CloudGuard Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. Auto Scaling Group configured for Gateway Load Balancer in a Centralized Security VPC for Transit Gateway.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. Auto Scaling Group configured for Gateway Load Balancer in a Centralized Security VPC for Transit Gateway.
To deploy the Auto Scaling group configured for GWLB, select a CloudFormation template for a new or existing VPC. Then, follow the instructions in this section on how to deploy the solution. Finally, examine and test the deployment.
|
CloudFormation (CFT) Template |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Creates a new VPC and deploys a Gateway Load Balancer, Check Point CloudGuard Security Gateway Auto Scaling Group, Gateway Load Balancer Endpoints, NAT Gateways for each AZ, and an optional Security Management Server to the new VPC. |
|
|
Auto Scaling group for Gateway Load Balancer into existing VPC |
Deploys a Gateway Load Balancer, Check Point CloudGuard Security Gateway Auto Scaling Group, Gateway Load Balancer Endpoints, NAT Gateways for each AZ, and an optional Security Management Server to the existing VPC. |
Parameters for Deploying an Auto Scaling Group with a GWLB to a New VPC for Transit Gateway
|
Parameter Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Requires input |
Select, at minimum, two Availability Zones (AZs) for the VPC subnets. |
|
|
2 |
Specify the number of AZs to use in the VPC. This must align with the number of AZs selected for the Availability Zones parameter. |
|
|
10.0.0.0/16 |
Configure the CIDR block for the VPC |
|
|
10.0.10.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the public subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.20.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the public subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.30.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the public subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.40.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the public subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.12.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the TGW subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.22.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the TGW subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.32.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the TGW subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.42.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the TGW subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.13.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the NAT subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.23.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the NAT subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.33.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the NAT subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.43.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the NAT subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.14.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the GWLBe subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.24.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the GWLBe subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.34.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the GWLBe subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
|
|
10.0.44.0/24 |
Specify a CIDR block for the GWLBe subnet. Use this format: x.x.x.x/16-28 |
General Settings:
|
Parameter Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Requires input |
Specify an EC2 key pair to enable SSH access to the instances created by this stack. |
|
|
True |
Enable or disable instance volume encryption with the default AWS Key Management Service (KMS) key. |
|
|
100 |
Set the root volume size in GB. |
|
|
gp3 |
Select the General Purpose SSD volume type. |
|
|
False |
Enable or disable protection against accidental instance termination. |
|
|
False |
Enable or disable establishing SSH connections through the AWS web console. |
|
|
True |
Enable or disable automatic download of Software Blade |
|
|
gwlb-management server |
Provide a name for the Security Management Server in the automatic provisioning configuration. |
|
|
gwlb-ASG-configuration |
Specify a name for a Security Gateway configuration template in the automatic provisioning configuration. |
|
|
Optional |
(Optional) Provide an email address to receive AWS notifications about scaling events. |
|
|
/etc/cli.sh |
Select the admin shell to enable advanced command line configuration for Security Gateways and Security Management Server. |
Gateway Load Balancer Configuration:
|
Parameter Name |
Default Value |
Description |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gateway Load Balancer |
gwlb1 |
Provide a unique name for the Gateway Load Balancer. The name can have a maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters and hyphens.
|
||
|
|
tg1 |
Specify a unique name for the target group. The name can have a maximum of 32 alphanumeric characters and hyphens.
|
||
|
|
True |
Enable or disable Cross-AZ Load Balancing.
|
Check Point CloudGuard Network Security Gateways Auto Scaling Group Configuration:
|
Parameter Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Check Point Gateway |
Provide a name tag for the Security Gateway instances. |
|
|
c5.xlarge |
Select the EC2 instance type for Security Gateways. |
|
|
2 |
Set the minimum number of Security Gateways in the Auto Scaling Group. |
|
|
10 |
Set the maximum number of Security Gateways in the Auto Scaling Group. |
|
|
R81.20-BYOL |
Select the version and license type for Security Gateways. |
|
|
Optional |
(Optional) Provide the admin user's password hash (use the command " |
|
|
Optional |
(Optional) Check Point recommends to set the admin user's password and maintenance-mode password for recovery purposes (use command |
|
|
Requires input |
Enter a SIC |
|
|
Private |
Select if provisioned Security Gateways use private or public addresses. |
|
|
False |
Enable or disable allocation of public IP addresses for Security Gateways. |
|
|
False |
Enable or disable support for IPv6 traffic inspection. |
|
|
False |
Enable or disable reporting of Check Point-specific CloudWatch metrics. |
|
|
Optional |
Provide an optional script with semicolon-separated commands to run on initial boot. |
|
|
Note - For more information on how to use Check Point metrics to trigger AWS Auto-Scaling events, refer to sk162592. |
Check Point CloudGuard Network Security Management Server Configuration:
|
Parameter Name |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
True |
Specify False to use an existing Security Management Server, or True to deploy a new Security Management Server. If you select False, ignore the other parameters in this section. |
|
|
m5.xlarge |
Select the EC2 instance type for the Security Management Server. |
|
|
R81.20-BYOL |
Select the version and license type for the Security Management Server. |
|
|
Optional |
(Optional) Provide the admin user's password hash (use the command " |
|
|
Optional |
(Optional) Check Point recommends to set the admin user's password and maintenance-mode password for recovery purposes (use the command |
|
|
Standard |
Specify the name of the Security Policy |
|
|
Requires input |
Specify the network allowed to connect to the Security Management Server through web, SSH, and graphical clients. |
|
|
Locally managed |
Select between local management or management over the Internet based on Security Gateway accessibility. If, at minimum, one of the Security Gateways that you want to manage is not directly accessed through its private IP address, select Over the internet. |
|
|
Requires input |
Specify the network allowed for communication of Security Gateways with the Security Management Server. |
|
|
Important - The External Load Balancer sends health probes to TCP port 8117 to determine the health of the CloudGuard Network Security Gateways, so port 8117 must be open on the Security Gateways. |
Step5: Deploying the AWS Transit Gateway
Follow the AWS instructions to deploy Transit Gateways.
When you create the Transit Gateway, set these options in the Amazon VPC console:
-
Disable the Default route table association.
-
Disable the Default route table propagation.
-
For cross-account spokes, enable the Auto accept shared attachments.
|
|
Note - If you did not disable the Default route table association and the Default route table propagation settings, you must remove the existing Transit Gateway and create a new one. If you do not remove the existing Transit Gateway, AWS connects all attachments to the Transit Gateway to the same default Transit Gateway route table. This causes traffic to move directly between spokes instead of flowing through the CloudGuard Security Gateways. To change this, move the association and propagation to the correct Transit Gateway route table. |
Step 6: Configure the Check Point Security Management Server
|
|
Important - If you deployed your Security Management Server as part of the GWLB Security VPC deployment (Step 4), the Cloud Management Extension (CME) was also initialized in that step. There is no need to re-initialize CME, and you can proceed to Step 7. |
Install and Configure Cloud Management Extension
Follow these steps to set up the Cloud Management Extension (CME).
|
|
Important - If you have existing configurations for other Check Point CloudGuard Network solutions, do not initialize your configuration. Instead, add the Controller or Template for the GWLB solution with the applicable configuration |
-
Install CME on the Security Management Server.
Install the latest CME tool on your Security Management Server. See sk157492.
For more details, see the "Structure and Configuration" section in the Cloud Management Extension Administration Guide.
-
Configure the Security Management Server using the "autoprov_cfg" tool.
The autoprov_cfg tool configures the Security Management Server with all the settings needed for GWLB.
Follow these steps:
-
Connect to the CLI on the Security Management Server.
-
Log in to the Expert mode.
-
Run each of the commands below.
Commands and their options:
-
To initialize the autoprov_cfg configuration with IAM credentials, run:
autoprov_cfg init AWS -mn "<MANAGEMENT-NAME>" -tn "<TEMPLATE-NAME>" -otp "<SIC-KEY>" -ver R81.20 -po "<POLICY-NAME>" -cn "<CONTROLLER-NAME>" -r "<REGIONS>" -iam
Options:
-
-mn- Security Management Server name -
-tn- Template name -
-otp- One-time SIC password -
-ver- Security Gateway version -
-po- Policy package name -
-cn- Controller name -
-r- Comma-separated list of regions -
-iam- Use IAM to connect to AWS
-
-
To display autoprov_cfg configuration and make sure all the configurations are correct, run:
autoprov_cfg show all
-
To test the configuration and make sure it is correct, run:
service cme test

Important - Make sure there are no errors in the test results.
-
Step 7: Post Deployment - Attach the Security VPC to the Transit Gateway
Create a Security Gateway VPC Attachment with the Security VPC:
-
In the AWS Web Console, open the VPC service and go to Transit Gateway Attachments.
-
Create a new VPC attachment:
-
Select your Transit Gateway and the Security VPC.
-
Set attachments for all relevant Availability Zones to use Attachment Subnet (1 and 2) created by the CFT in the Security VPC.
For more information, see the Amazon documentation.
-
Create and configure the Transit Gateway Route Table:
-
In the AWS Web Console, open the VPC service and go to Transit Gateway Route Tables.
-
Create a new route table for the Transit Gateway to handle traffic from the Security VPC. Name it:
Check-Point-rtb. -
In the
Check-Point-rtb, create a route table association to the Security VPC attachment. -
In the
Check-Point-rtb, create a route table propagation to all your Spoke VPC attachments. -
Use an existing route table or create a new one for the Transit Gateway to handle traffic from the Spoke VPCs. Name it:
Spoke-rtb. -
In the
Spoke-rtb, create a route table association to the Spoke VPCs attachment. -
In the
Spoke-rtb, create a static route 0.0.0.0/0 > Security VPC attachment. This directs all traffic through the Security VPC for inspection.
Step 8: Post Deployment- Add Routes to Spoke VPCs CIDRs
The CloudFormation Templates manage default routing and Security VPC-specific routing, but not consumer-specific environment (Spoke) routing. Each consumer environment is unique. Consumers must add their own routing information into the Security VPC route tables in two specific locations. It is necessary for TGW VPC to VPC inspection, VPC to ground inspection, or any other Inter-VPC inspection.
The consumer must add consumer-specific routes to:
-
GWLBe subnet's route tables
-
NAT Gateways subnet's route tables
Add consumer-specific routes for any Inter-VPC routing, or VPC-ground routing done by DirectConnect or other VPN connectivity.
-
For each Spoke VPC CIDR, add these routes to all GWLBe Subnets Route Tables:
Destination
Next Hop
Spoke VPC-1 CIDR
Transit Gateway
Spoke VPC-2 CIDR
Transit Gateway
...
...
Spoke VPC-N CIDR
Transit Gateway
-
For each Spoke VPC CIDR, add the route(s) that follow to all NAT Gateway Subnets Route Tables that directs to the GWLBe (
vpc-id) in the corresponding Availability Zone:-
To NAT Gateway 1 in AZ-A Route Table, add:
Destination
Next Hop
Spoke VPC-1 CIDR
GWLBe-AZ-A
Spoke VPC-2 CIDR
GWLBe-AZ-A
...
...
Spoke VPC-N CIDR
GWLBe-AZ-A
-
To NAT Gateway 2 in AZ-B Route Table, add: GWLBe-AZ-B
Destination
Next Hop
Spoke VPC-1 CIDR
GWLBe-AZ-B
Spoke VPC-2 CIDR
GWLBe-AZ-B
...
...
Spoke VPC-N CIDR
GWLBe-AZ-B
-
|
|
Best Practice - Manage the route tables with care. Group similar subnets into supernet routes when possible. Example: Group subnets |
Step 9: Enable Transit Gateway Appliance Mode
The Transit Gateway Appliance Mode allows traffic inspection to occur in different Availability Zones (AZs) than the source or destination of the traffic.
With the AWS Transit Gateway Appliance Mode, you can specify attachments that forward network flows out of the same AZ, regardless of the flow's direction and origin AZ. This mode ensures that network flows route symmetrically to the same AZ and network appliance. For more information on AWS Transit Gateway Appliance Mode, see this example: Appliance in a shared services VPC.
To set Transit Gateway Appliance Mode on the Security VPC attachment, use this AWS CLI command with the latest version of AWS CLI v2:
|
aws ec2 modify-transit-gateway-vpc-attachment --transit-gateway-attachment-id <tgw-attach-xyx> --options ApplianceModeSupport="enable" |
Follow these steps to set Transit Gateway Appliance Mode on the Security VPC attachment from the AWS console:
-
Log in to the AWS Management Console.
-
From the primary menu bar, select VPC > Transit Gateway attachments.
-
Select the Security VPC attachment.
-
Click Actions > Modify transit gateway attachment.
-
Check Appliance Mode support.
-
Click Modify transit gateway attachment.
(Optional) Configure Inbound Traffic to Spoke VPCs
The architecture described in the Introduction "Solution 2 – A GWLB Security VPC for Transit Gateway" handles outbound and east-west (Spoke-to-Spoke) traffic only.
Prerequisites:
-
The Application instances in the Spoke VPC must be targets of an External Load Balancer.
-
Place the Load Balancer in separate subnets from the Application instances subnets.
To allow inbound traffic inspection to pass through the GWLB, do these steps:
-
Create a separate subnet in the Spoke VPC dedicated to the Gateway Load Balancer Endpoint (GWLBe). Set the default route through the AWS Internet Gateway (IGW).
-
Create the GWLBe in the subnet you created in step 1. Use this AWS CLI command:
aws ec2 create-vpc-endpoint --vpc-endpoint-type GatewayLoadBalancer --service-name com.amazonaws.vpce.us-east-2.vpce-svc-12345678901234567 --vpc-id spoke-vpc-id --subnet-ids gwlbe-subnet-id

Note - Find the Service Name in the CloudFormation outputs
‘GWLBServiceName'parameter.For more information about Gateway Load Balancer Endpoints, see the AWS VPC Gateway Load Balancer documentation.
-
Configure Ingress Routing through the GWLBe on the Load Balancer subnets' Route Table and the Internet Gateway Route Table.
For more information about ingress routing and edge routing tables, see New VPC Ingress Routing Simplifying Integration of Third-Party Appliances.

Note - The Load Balancer subnets' Route Table must be separate from the Application instances' Route Table.
Termination
To stop the environment:
-
Remove the TGW VPC association from every place that uses it.
-
Remove the Security VPC CFT Stack from your AWS account.