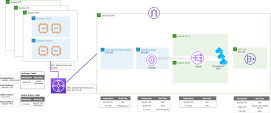
Overview of CloudGuard Network for AWS Centralized Gateway Load Balancer
The AWS![]() Amazon® Web Services. Public cloud platform that offers global compute, storage, database, application and other cloud services. Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) is a managed service. It allows AWS user to deploy, scale, and manage virtual appliances easily. These appliances include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and deep packet inspection systems. AWS customers can deploy these virtual appliances with high availability, scaling, and load balancing.
Amazon® Web Services. Public cloud platform that offers global compute, storage, database, application and other cloud services. Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) is a managed service. It allows AWS user to deploy, scale, and manage virtual appliances easily. These appliances include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and deep packet inspection systems. AWS customers can deploy these virtual appliances with high availability, scaling, and load balancing.
One example of such a virtual appliance is a CloudGuard Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources..
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources..
Cloud Network Security is one of the CloudGuard capabilities. It provides advanced Threat Prevention and automated network security through a virtual Security Gateway, with unified security management across all cloud and on-premises deployments. AWS customers use CloudGuard to securely migrate on-premises workloads to AWS and protect these assets with advanced security technologies, including Firewall, IPS![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that inspects and analyzes packets and data for numerous types of risks (Intrusion Prevention System)., Application Control
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that inspects and analyzes packets and data for numerous types of risks (Intrusion Prevention System)., Application Control![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that allows granular control over specific web-enabled applications by using deep packet inspection. Acronym: APPI., DLP, Anti-Virus
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that allows granular control over specific web-enabled applications by using deep packet inspection. Acronym: APPI., DLP, Anti-Virus![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that uses real-time virus signatures and anomaly-based protections from ThreatCloud to detect and block malware at the Security Gateway before users are affected. Acronym: AV., and Anti-Bot
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that uses real-time virus signatures and anomaly-based protections from ThreatCloud to detect and block malware at the Security Gateway before users are affected. Acronym: AV., and Anti-Bot![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that blocks botnet behavior and communication to Command and Control (C&C) centers. Acronyms: AB, ABOT.. Threat Extraction
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that blocks botnet behavior and communication to Command and Control (C&C) centers. Acronyms: AB, ABOT.. Threat Extraction![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that removes malicious content from files. Acronym: TEX. and Threat Emulation
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that removes malicious content from files. Acronym: TEX. and Threat Emulation![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that monitors the behavior of files in a sandbox to determine whether or not they are malicious. Acronym: TE. provide industry-leading protection from zero-day attacks.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that monitors the behavior of files in a sandbox to determine whether or not they are malicious. Acronym: TE. provide industry-leading protection from zero-day attacks.
For more information about the AWS Gateway Load Balancers, see the AWS documentation.
This guide explains how to deploy and configure Check Point's CloudGuard Network Gateway Load Balancer security protection.
|
|
Note - For the list of supported versions, refer to the Support Life Cycle Policy. |
How GWLB Works
A Gateway Load Balancer operates at Layer 3 of the OSI model (the network layer). It listens for all IP packets across all ports and forwards traffic to the target group specified in its listener rule![]() Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session.. The GWLB and its registered virtual appliance instances exchange application traffic through the GENEVE protocol on port 6081.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session.. The GWLB and its registered virtual appliance instances exchange application traffic through the GENEVE protocol on port 6081.
For more information, see the AWS Gateway Load Balancer documentation, and review AWS's detailed blog posts on GWLB.
Architecture Patterns
Solution 1 – A Centralized GWLB Security VPC
The diagram shows the GWLB architecture for Check Point CloudGuard AWS. This end-to-end solution includes:
-
Security VPC:
-
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB)
-
Auto Scaling Group of Security Gateways
-
-
Servers VPC
-
Gateway Load Balancer Endpoint (GWLBe)
-
Application Servers
-
The GWLBe is the Servers VPC Internet Gateway's (IGW's) next hop for ingress traffic and the servers' next hop for ingress and egress traffic. All traffic that reaches the GWLBe is automatically directed to the GWLB in the Security VPC. The GWLB forwards the packet to one of the Auto Scaling Group's (ASG) healthy instances over GENEVE protocol. The packet is then analyzed and processed based on the Security Gateway's policy. If the packet is accepted, it returns to the GWLB, and then to the corresponding GWLBe which redirects the packet to its original destination.
The creation of a GWLBe in each servers VPC allows the user to protect multiple servers VPCs. All created GWLBe(s) must point to the centralized GWLB and be inspected by the same centralized Security VPC, such as the same Firewall appliances.
Solution 2 - A GWLB Security VPC for Transit Gateway (TGW)
The diagram shows the TGW GWLB architecture for Check Point CloudGuard's AWS end-to-end solution that includes:
-
Security VPC:
-
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB)
-
Auto Scaling Group of Security Gateways
-
Security Management Server
 Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. (Optional)
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. (Optional) -
GWLBe (for each Availability Zone)
-
Transit Gateway attachment subnets (for each Availability Zone)
-
NAT Gateways (for each Availability Zone)
-
-
Transit Gateway
-
Spoke VPCs
The TGW Solution Security VPC has 4 subnets for each AZ:
-
TGW attachment subnet
-
GWLBe subnet
-
Check Point's Firewall subnet
-
NAT Gateway subnet
This architecture allows the required management connectivity to the Check Point's EC2 instances.
For more architecture examples and traffic flows, refer to: Check Point CloudGuard Network Security - Integration with AWS Gateway Load Balancer workshop.
Benefits
The GWLB provides a simple native AWS solution to deploy and manage network appliances. This solution is horizontally scalable and fault-tolerant.
The GWLB operates in a transparent manner. It does not change packet headers or payloads. This means that the traffic source and destination software stacks do not need to change. Users and applications do not need to make any changes.
The GWLB integration with CloudGuard Network allows IT teams to maintain consistent security practices on cloud and on-premises deployments, use existing security skill sets, and build on existing investments and relationships with Check Point Security Solutions.
The GWLB provides:
-
Elastic scalability of managed Check Point CloudGuard Security Gateway fleets as traffic volumes change.
-
Resiliency for Check Point CloudGuard Network Security Gateways by automatically rerouting traffic to healthy Security Gateways.
-
Graceful failover among Auto Scaling Group Security Gateways for patching and maintenance (traffic always goes to one of the healthy appliances).
-
Reduced network complexity:
-
No traffic translation or source NAT (the packet keeps the original source and destination).
-
Transparent traffic inspection – bump-in-the-wire.
-
A single security VPC with the GWLB and Check Point CloudGuard Auto Scaling Group that can connect to multiple GWLB Endpoints across multiple VPCs and/or AWS accounts.
-
-
Ease of use:
-
Full deployment automation – uses CFT to deploy a security VPC to connect to multiple Endpoints (manual deployment of Endpoints).
-
Flexibility in the inspection enforcement with the use of subnets tags.
-
-
Support for multiple networking architectures:
-
The current architecture supports traffic inspection in a centralized security VPC for simple (single VPCs with GWLBe in each) and complex (TGW) scenarios.
-
Use Case
A typical use case involves customer AWS deployments with one or more VPCs. These deployments need to protect and inspect network traffic with Check Point's CloudGuard Network Security Gateways.
Check Point's CloudGuard Network Security integrates with GWLB to provide traffic inspection in a centralized security VPC.
-
Solution 1: Deploying a Centralized GWLB Security VPC
This solution provides ingress and egress traffic inspection in unconnected VPCs.
-
Solution 2: Deploying a GWLB Security VPC for Transit Gateway
This solution provides intra-VPC and egress traffic inspection for VPCs connected with AWS Transit Gateway.
Prerequisites
Before you use this solution, you must be familiar with these AWS terms and services:
-
VPC
-
EC2
-
Elastic Load Balancers (ELB)
-
Ingress Routing
-
VPC Endpoints Gateway Load Balancer (Endpoint)
-
Transit Gateway
-
NAT Gateway (see Deploying Solution 2 - A Check Point Gateway Load Balancer Transit Gateway Environment with CloudFormation Template)
If you are new to AWS, see the Getting Started with AWS guide.