Firewall Control Connections in VPN Communities
Overview
Check Point Security Gateways communicate with other Check Point Nodes through control connections. For example a Security Management Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. and a Security Gateway
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. and a Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. use a control connection when the Security Policy
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. use a control connection when the Security Policy![]() Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. is installed from the Security Management Server
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. is installed from the Security Management Server![]() Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. to the Security Gateway. In addition, Security Gateways send logs to the Security Management Server across control connections. Control connections use Secure Internal Communication (SIC
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. to the Security Gateway. In addition, Security Gateways send logs to the Security Management Server across control connections. Control connections use Secure Internal Communication (SIC![]() Secure Internal Communication. The Check Point proprietary mechanism with which Check Point computers that run Check Point software authenticate each other over SSL, for secure communication. This authentication is based on the certificates issued by the ICA on a Check Point Management Server.).
Secure Internal Communication. The Check Point proprietary mechanism with which Check Point computers that run Check Point software authenticate each other over SSL, for secure communication. This authentication is based on the certificates issued by the ICA on a Check Point Management Server.).
Implied Rules in the Access Control Rule Base![]() All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase. allow the Control connections. The Management Server adds and removes the Implied Rules in the Access Control Rule
All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase. allow the Control connections. The Management Server adds and removes the Implied Rules in the Access Control Rule![]() Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. Base when you select or clear options in the SmartConsole
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. Base when you select or clear options in the SmartConsole![]() Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. > > Global properties > Firewall page.
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. > > Global properties > Firewall page.
Some administrators do not rely on implied rules, and instead define explicit rules in the Access Control Rule Base.
Why Disabling Implied Rules Blocks Firewall Control Connections
If you disable implicit rules, you may not be able to install an Access Control Policy on a remote Security Gateway.
Even if you configure explicit rules rather than implied rules, you may still not be able to install the policy:
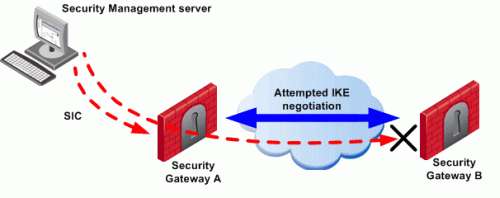
To configure a VPN between the Security Gateway "A" and the Security Gateway "B" through SmartConsole, the administrator must install a Policy from the Security Management Server to the Security Gateways.
-
The Security Management Server successfully installs the Policy on Security Gateway "A". Security Gateway "A" recognizes that Security Gateways "A" and "B" now belong to the same VPN Community
 A named collection of VPN domains, each protected by a VPN gateway.. However, Security Gateway "B" does not yet have the Policy.
A named collection of VPN domains, each protected by a VPN gateway.. However, Security Gateway "B" does not yet have the Policy. -
The Security Management Server opens a connection to Security Gateway B to install the Policy.
-
Security Gateway "A" allows the connection because of the explicit rules that allow the control connections. Security Gateway "A" starts IKE negotiation with Security Gateway "B" to build a VPN tunnel for the control connection.
-
Security Gateway "B" cannot negotiate with Security Gateway "A" because it does not yet have the Policy. Therefore, Policy installation on Security Gateway "B" fails.
Make sure that control connections do not have to pass through a VPN tunnel.
Allowing Firewall Control Connections Inside a VPN
If you disable implied rules, then you must follow sk179346 - Configuring Explicit Rules instead of Implied Rules.
Note - Although control connections between the Security Management Server and the Security Gateway are not encrypted by the community, they are still encrypted and authenticated with Secure Internal Communication (SIC).
