Planning your Deployment
This section includes best practices and other suggestions to help make your Multi-Domain Security Management deployment work efficiently.
Multi-Site High Availability Deployment
Large enterprises use Multi-Domain Security Management in a multi-site, High Availability deployment, with many Multi-Domain Servers located at remote sites, often in different countries. Each Multi-Domain Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to host virtual Security Management Servers called Domain Management Servers. Synonym: Multi-Domain Security Management Server. Acronym: MDS. and Multi-Domain Log Server
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to host virtual Security Management Servers called Domain Management Servers. Synonym: Multi-Domain Security Management Server. Acronym: MDS. and Multi-Domain Log Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to store and process logs in a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. The Multi-Domain Log Server consists of Domain Log Servers that store and process logs from Security Gateways that are managed by the corresponding Domain Management Servers. Acronym: MDLS. continuously synchronizes with its remote peers.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to store and process logs in a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. The Multi-Domain Log Server consists of Domain Log Servers that store and process logs from Security Gateways that are managed by the corresponding Domain Management Servers. Acronym: MDLS. continuously synchronizes with its remote peers.
The advantages of this type of deployment are:
-
Full Multi-Domain Server, Multi-Domain Log Server
 Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to store and process logs., and Domain Management Server
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to store and process logs., and Domain Management Server Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. redundancy
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. redundancy -
Domain Management Server
 Virtual Security Management Server that manages Security Gateways for one Domain, as part of a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. Acronym: DMS. load sharing that can balance traffic based on geographic location
Virtual Security Management Server that manages Security Gateways for one Domain, as part of a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. Acronym: DMS. load sharing that can balance traffic based on geographic location -
Many administrators can connect to different Multi-Domain Servers to manage Security Policies
 Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. and system configuration from different locations
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. and system configuration from different locations
|
|
Note - The system automatically creates the Global Domain when you install Multi-Domain Security Management. |
Single Site Deployments
Small organizations, with moderate traffic volumes can use a single-site deployment, with one Multi-Domain Server that manages a set of Domains.
|
|
Best Practice - For this type of deployment, use a backup solution that periodically saves the system databases and settings to another device. |
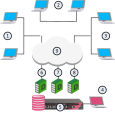
This example shows a single-site Multi-Domain Server deployment with three Domains at remote locations. Each Domain has many Security Gateways to protect the internal networks and resources. This example has only one Multi-Domain Server and does not use High Availability.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
London Domain and networks |
|
2 |
New York (Headquarters) Domain and networks |
|
3 |
Tokyo Domain and networks |
|
4 |
SmartConsole |
|
5 |
Multi-Domain Server |
|
6 |
London Domain Management Server |
|
7 |
New York Domain Management Server |
|
8 |
Tokyo Domain Management Server |
|
9 |
Internet |
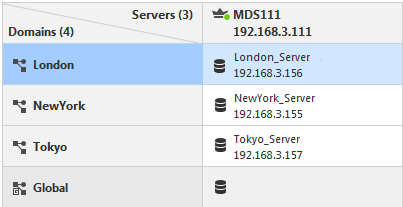
This illustration shows the configuration grid in the SmartConsole Multi Domain view for the example deployment:
Platform & Performance Issues
Make sure that your Multi-Domain Security Management system hardware is compliant with the system requirements for this release. If your Multi-Domain Server has more than one interface, make sure that the total traffic load complies with the performance load recommendations for that Multi-Domain Server.
Topology, IP Addresses, and Routing
All Multi-Domain Servers must have at least one interface with a routable IP address.
You must configure these Multi-Domain Servers to run DNS server queries and to resolve the IP addresses and host names.
Configure your network routing for IP communication between:
-
All Multi-Domain Servers, Domain Management Servers, and Multi-Domain Log Servers
-
Different Domains, if necessary
-
Domain Management Servers, Domain Log Servers, and Security Gateways in a Domain
-
A Domain Management Server and its Domain High Availability peers
-
SmartConsole and Multi-Domain Servers, Domain Management Servers and Domain Log Servers
Make sure that IP addresses and routing configuration can handle special issues, such as Multi-Domain Servers in different physical locations.
Configuring an IPv6 Address on a Multi-Domain Server
Starting in R82, it is possible to use IPv6 addresses for the internal Check Point communication:
-
Between a Multi-Domain Security Management Server
 Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server., its Domain Management Servers, and their managed Security Gateways.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server., its Domain Management Servers, and their managed Security Gateways.This internal Check Point communication includes Secure Internal Communication (SIC
 Secure Internal Communication. The Check Point proprietary mechanism with which Check Point computers that run Check Point software authenticate each other over SSL, for secure communication. This authentication is based on the certificates issued by the ICA on a Check Point Management Server.), policy installation, and logging.
Secure Internal Communication. The Check Point proprietary mechanism with which Check Point computers that run Check Point software authenticate each other over SSL, for secure communication. This authentication is based on the certificates issued by the ICA on a Check Point Management Server.), policy installation, and logging. -
Between a Multi-Domain Log Server, its Domain Log Servers, and the managed Security Gateways.
This internal Check Point communication includes Secure Internal Communication (SIC) and logging.
-
Between a Multi-Domain Security Management Server and a Multi-Domain Log Server.
This internal Check Point communication includes Secure Internal Communication (SIC) and logging.
Part 1 - Configuring the Multi-Domain Server
-
Enable IPv6 support in the Gaia
 Check Point security operating system that combines the strengths of both SecurePlatform and IPSO operating systems. OS on the Multi-Domain Server.
Check Point security operating system that combines the strengths of both SecurePlatform and IPSO operating systems. OS on the Multi-Domain Server.See the R82 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter System Management > Section System Configuration.
-
Reboot the Multi-Domain Server.
See the R82 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter Maintenance > Section Shut Down.
-
On the Leading Interface of the Multi-Domain Server, configure the required IPv6 address.
See the R82 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter Network Management > Section Network Interfaces > Section Physical Interfaces.
-
Configure the applicable IPv6 static routes on the Multi-Domain Server.
See the R82 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter Network Management > Section IPv6 Static Routes.
-
Add the same IPv6 address you configured on the Leading Interface to the Multi-Domain Server database with the API command "
set-mds":-
In the Management API Reference:
-
Open the chapter "Multi-Domain".
-
Open the section "Multi-Domain Server (MDS)".
See one of these Management API references:
-
The online Check Point Management API Reference.
-
The local Management API Reference (first, you must follow sk174606 to allow access to this local Management API reference):
https://<IP Address or Gaia Management Interface>/api_docs/#introduction
-
-
Run the API command "
set-mds":(The syntax below is for the CLI command "
mgmt_cli".)mgmt_cli --domain 'System Data' set-mds name <Name of Multi-Domain Server Object> ipv6-address "IPv6 Address Configured on Leading Interface>"
Notes:
-
In the "
name" parameter, you must enter the name of the Multi-Domain Server object as it appears in SmartConsole. -
If you run command in the CLI on the Primary Multi-Domain Server, then in the "
name" parameter you can specify the name of the Secondary Multi-Domain Server object.
-
-
-
Restart the Check Point services on the Multi-Domain Server with these commands in the CLI (Gaia Clish
 The name of the default command line shell in Check Point Gaia operating system. This is a restricted shell (role-based administration controls the number of commands available in the shell). or the Expert mode):
The name of the default command line shell in Check Point Gaia operating system. This is a restricted shell (role-based administration controls the number of commands available in the shell). or the Expert mode):-
Stop the Check Point services:
mdsstop -
Start the Check Point services:
mdsstart
-
-
Make sure all the required processes are running on the Multi-Domain Server with this command in the CLI (Gaia Clish or the Expert mode):
mdsstat -
Configure the required IPv6 address in the Domain Management Server / Domain Log Server with the applicable API command.
You can update and existing object or create a new object.
(The syntax below is for the CLI command "
mgmt_cli".)-
To update an existing Domain Management Server / Domain Log Server object and restart it:
mgmt_cli set domain name "<Name of Domain Object>" servers.update.multi-domain-server "Name of Multi-Domain Server Object" servers.update.name "Name of Domain Management Server or Domain Log Server Object" servers.update.ipv6-address "<IPv6 Address of Domain Management Server or Domain Log Server Object>" servers.update.restart-domain-server true -
To create a new Domain Management Server / Domain Log Server object with both an IPv4 and an IPv6 addresses:
-
To create a new Domain Management Server and start it:
mgmt_cli add domain name "Name of Domain Object" servers.1.multi-domain-server "<Name of Multi-Domain Security Management Server Object>" servers.1.name "<Name of Domain Management Server Object>" servers.1.type "management server" servers.1.ipv4-address "<IPv4 Address of Domain Management Server Object>" servers.1.ipv6-address "<IPv6 Address of Domain Management Server Object>"
Note - Digit "
1" in the syntax "servers.1." means the first Domain Management Server on this Multi-Domain Security Management Server. If there are already configured Domain Management Servers, then enter the next subsequent number. -
To create a new Domain Log Server and start it:
mgmt_cli add domain name "Name of Domain Object" servers.1.multi-domain-server "<Name of Multi-Domain Log Server Object>" servers.1.name "<Name of Domain Log Server Object>" servers.1.type "log server" servers.1.ipv4-address "<IPv4 Address of Domain Log Server Object>" servers.1.ipv6-address "<IPv6 Address of Domain Log Server Object>"
Note - Digit "
1" in the syntax "servers.1." means the first Domain Log Server on this Multi-Domain Log Server. If there are already configured Domain Log Servers, then enter the next subsequent number.
-
-
-
Make sure all the required processes are running on the Multi-Domain Server with this command in the CLI (Gaia Clish or the Expert mode):
mdsstat
Part 2 - Configuring the Security Gateways and Cluster Members
-
Enable IPv6 support in the Gaia OS on the applicable Security Gateways and each applicable Cluster Member
 Security Gateway that is part of a cluster..
Security Gateway that is part of a cluster..See the R82 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter System Management > Section System Configuration.
-
Reboot the Security Gateways and each Cluster
 Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. Member.
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. Member.See the R82 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter Maintenance > Section Shut Down.
-
Configure IPv6 addresses on the applicable interfaces.
See the R82 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter Network Management > Section Network Interfaces.
-
Configure the applicable IPv6 static routes.
See the R82 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter Network Management > Section IPv6 Static Routes.
Part 3 - Configuring the Security Gateways and Cluster objects in SmartConsole
Follow the R82 Security Management Administration Guide.
-
Connect to the command line on the Multi-Domain Security Management Server.
-
Log in to the Expert mode.
-
Disable the current IPv6 configuration:
mdsconfig -n disable_ipv6 <Name of Leading Interface> -
Restart the Check Point services on the Multi-Domain Server:
-
Stop the Check Point services:
mdsstop -
Start the Check Point services:
mdsstart
-
-
Make sure all the required processes are running on the Multi-Domain Server:
mdsstat -
Configure the new IPv6 address on the Leading Interface.
Follow steps 3-7 in Part 1 - Configuring the Multi-Domain Server.
-
Change the IPv6 addresses assigned Domain Management Servers / Domain Log Servers with the API command "
set domain":(The syntax below is for the CLI command "
mgmt_cli".)mgmt_cli set domain name "<Name of Domain Object>" servers.update.multi-domain-server "<Name of Multi-Domain Server Object>" servers.update.name "<Name of Domain Management Server or Domain Log Server Object>" servers.update.ipv6-address "<IPv6 Address of Domain Management Server or Domain Log Server Object>" servers.update.restart-domain-server true -
Make sure all the required processes are running on the Multi-Domain Server:
mdsstat
Using More than one Interface on a Multi-Domain Server
If there is more than one interface on a Multi-Domain Server, you must configure at least one interface to be the leading interface. Multi-Domain Servers (Primary and Secondary) and Multi-Domain Log Servers use the leading interface to communicate with each other for database synchronization.
Make sure that all Multi-Domain Server interfaces are routable. Domain Management Servers must be able to communicate with their Domain Security Gateways. Domain Log Servers must be able to communicate with their Domain Security Gateways.
Changing the Leading Interface
You define the leading interface during the installation procedure, but you can change it later. If you add a new interface to a Multi-Domain Server after installation, define the Leading Interface manually.
-
From the Multi-Domain Server command line, run:
mdsconfig -
Select Leading VIP Interfaces, and then select Add external IPv4 interface.
-
Enter the interface name and press Enter.
-
From the Multi-Domain Server command line, run:
mdsconfig -
Do steps 2-3, in the above procedure, to add new interface.
-
Select Leading VIP Interfaces.
-
Select Remove External IPv4 interface.
-
Enter the interface name to remove and press Enter.
Synchronizing Clocks
All Multi-Domain Server system clocks must synchronize to approximately one second. Before you create a new Multi-Domain Server or Multi-Domain Log Server, you must synchronize its clock with other system components.
Clock synchronization is important for these reasons:
-
SIC trust can fail if devices are not synchronized correctly
-
SmartEvent Correlation Unit uses time stamps, which must be accurate
-
Make sure that cron jobs run at the correct time
-
Certificate validation is based on the correct time
Use these resources to synchronize component system clocks:
-
Manually, using Gaia Portal
 Web interface for the Check Point Gaia operating system. or Gaia Clish
Web interface for the Check Point Gaia operating system. or Gaia Clish -
A third-party synchronization utility