Working with Link Aggregation
Link Aggregation Overview
Link aggregation, also known as interface bonding, joins multiple physical interfaces together into a virtual interface, known as a bond interface. A bond interface can be configured for High Availability redundancy or for load sharing, which increases connection throughput above that which is possible using one physical interface.
For more about Bond Interfaces (Link Aggregation), see the R81 Gaia Administration Guide and R81 ClusterXL Administration Guide.
Bonding (Link Aggregation) Terminology
-
Link Aggregation (Interface Bonding): Networking technology that binds multiple physical interfaces together into one virtual interface.
-
Bond: A group of physical interfaces that operate together as one virtual interface and share an IP address and MAC address. A bond is identified by the cluster
 Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. by its Bond ID (for example:
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. by its Bond ID (for example: bond0). -
Bond Interface: The logical representation of the bond.
-
Subordinate Interface: A physical interface that is a member of a bond. Subordinate interfaces do not have an IP Address and in some cases share the same MAC address.
How Link Aggregation Works
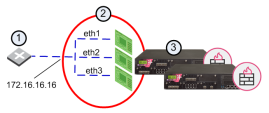
A bond contains a minimum of one and may contain up to eight subordinate interfaces. All subordinate interfaces contained in a bond share a common IP address and may share the same MAC address. We recommend that each cluster member![]() Security Gateway that is part of a cluster. contain the same quantity of identical subordinate interfaces.
Security Gateway that is part of a cluster. contain the same quantity of identical subordinate interfaces.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Switch |
|
2 |
bond 0 |
|
3 |
Cluster |
You can configure Link Aggregation using one of the following strategies:
-
High Availability (Active/Backup): Ensures redundancy in the event of interface or link failure. This option also provides switch redundancy.
-
Load Sharing (Active/Active): All interfaces are active, but handle different connections simultaneously. Traffic is balanced between subordinate interfaces to maximize throughput. The Load Sharing option does not support switch redundancy.
Link Aggregation High Availability
Clusters, by definition, provide redundancy and high availability at the VSX Gateway![]() Physical server that hosts VSX virtual networks, including all Virtual Devices that provide the functionality of physical network devices. It holds at least one Virtual System, which is called VS0. level.
Physical server that hosts VSX virtual networks, including all Virtual Devices that provide the functionality of physical network devices. It holds at least one Virtual System, which is called VS0. level.
Link Aggregation, however, adds interface and switch redundancy by providing automatic failover to a standby interface card within the same VSX![]() Virtual System Extension. Check Point virtual networking solution, hosted on a computer or cluster with virtual abstractions of Check Point Security Gateways and other network devices. These Virtual Devices provide the same functionality as their physical counterparts. Gateway.
Virtual System Extension. Check Point virtual networking solution, hosted on a computer or cluster with virtual abstractions of Check Point Security Gateways and other network devices. These Virtual Devices provide the same functionality as their physical counterparts. Gateway.
In a High Availability deployment, only one interface is active at a time. If an interface or connection fails, the bond fails over to a standby subordinate interface.
Bonding High Availability failover occurs in one of these cases:
-
An active interface detects a link state failure in a monitored interface.
-
ClusterXL detects a failure in sending or receiving Cluster Control Protocol (CCP) keep-alive packets.
Fully Meshed Redundancy through Interface Bonding
The Link Aggregation High Availability mode, when deployed with ClusterXL, enables a higher level of reliability by providing granular redundancy in the network.
This granular redundancy is achieved by using a fully meshed topology, which provides for independent backups for both NICs and switches.
In this scenario - VSX Cluster Members 1 and 2 are configured in the High Availability mode.
Link Aggregation Load Sharing
Load Sharing provides the ability to spread traffic over multiple subordinate interfaces, in addition to providing interface redundancy.
All interfaces are always active.
Traffic is balanced between interfaces in a manner similar to the way load sharing balances traffic between VSX Cluster Members.
Link Aggregation Load Sharing operates according to either the IEEE 802.3ad or the XOR standard.
In Load Sharing mode, each individual connection is assigned to a specific subordinate interface.
For a specific connection, only the designated subordinate interface is active.
If the designated subordinate interface fails, then the traffic fails over to another interface, which also continues to handle its existing traffic.
Bond Interface Limitations
-
You can define a maximum of 4096 interfaces on a Gaia
 Check Point security operating system that combines the strengths of both SecurePlatform and IPSO operating systems. server or appliance.
Check Point security operating system that combines the strengths of both SecurePlatform and IPSO operating systems. server or appliance.The total number of bond interfaces in use is the sum of bonds plus the number of subordinate interfaces contained in each bond.
-
Up to eight interfaces can be defined in a Link Aggregation deployment for each bond interface.