Internal Communication with Overlapping Addresses
If two internal networks have overlapping (or partially overlapping) IP addresses, Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. enables:
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. enables:
-
Communication between the overlapping internal networks.
-
Communication between the overlapping internal networks and the outside world.
-
Enforcement of a different security policy
 Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. for each overlapping internal network.
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. for each overlapping internal network.
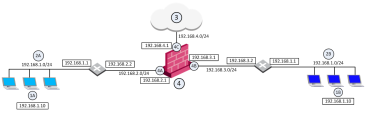
Example Network Configuration
Example topology:
For example, assume both Network 2A and Network 2B share the same address space (192.168.1.0/24).
Therefore, it is not possible to use standard NAT to enable communication between the two networks.
Instead, it is necessary to perform overlapping NAT on a per-interface basis.
-
Users in Network 2A, who want to communicate with users in Network 2B, must use the 192.168.30.0/24 network as a destination.
-
Users in Network 2B, who want to communicate with users in Network 2A, must use the 192.168.20.0/24 network as a destination.
The Security Gateway (4) translates the IP addresses in this way for each individual interface:
|
Interface |
IP Address Translation on the Interface |
|---|---|
|
4A |
|
|
4B |
|
|
4C |
Overlapping NAT is not configured for this interface. Instead, use NAT Hide in the normal way (not on a per-interface basis) to hide source addresses behind the interface's IP address (192.168.4.1). |
Communication Examples
If user 1A, at IP address 192.168.1.10 in Network 2A, wants to connect to user 1B, at IP address 192.168.1.10 (the same IP address) in Network 2B, user 1A opens a connection to the IP address 192.168.30.10.
User 1A, at IP address 192.168.1.10 in Network 2A, connects to IP address 192.0.2.10 on the Internet (3).
Routing Considerations
To allow routing from Network 2A to Network 2B (in our example above), you must configure the required routes on the Security Gateway:
|
Destination Network Address |
Default Gateway |
|---|---|
|
192.168.20.0 / 24 |
192.168.2.2 |
|
192.168.30.0 / 24 |
192.168.3.2 |
For configuration instructions, see the R81 Gaia Administration Guide > Chapter "Network Management" > Section "IPv4 Static Routes".
Object Database Configuration
To activate the overlapping NAT feature, use Database Tool (GuiDBEdit Tool) (see sk13009), or the dbedit command (see skI3301).
In our example network, the per-interface values for the interface 4A and the interface 4B are:
|
Parameter |
Value |
|---|---|
|
enable_overlapping_nat |
true |
|
overlap_nat_dst_ipaddr |
The overlapping IP addresses (before NAT). In our example, 192.168.1.0 for both interfaces. |
|
overlap_nat_src_ipaddr |
The IP addresses after NAT. In our example:
|
|
overlap_nat_netmask |
The net mask of the overlapping IP addresses. In our example, 255.255.255.0. |