Protecting the Multi-Domain Security Management Deployment
It is a security best practice to deploy a Check Point Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. that protects the Multi-Domain Servers, Multi-Domain Log Server
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. that protects the Multi-Domain Servers, Multi-Domain Log Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to store and process logs in a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. The Multi-Domain Log Server consists of Domain Log Servers that store and process logs from Security Gateways that are managed by the corresponding Domain Management Servers. Acronym: MDLS. and other components. You can manage this Security Gateway with a Domain Management Server
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to store and process logs in a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. The Multi-Domain Log Server consists of Domain Log Servers that store and process logs from Security Gateways that are managed by the corresponding Domain Management Servers. Acronym: MDLS. and other components. You can manage this Security Gateway with a Domain Management Server![]() Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. or a Security Management Server
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. or a Security Management Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. that is not part of a Multi-Domain Security Management environment.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server. that is not part of a Multi-Domain Security Management environment.
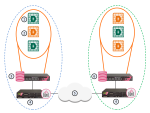
This simple use case shows a small High Availability deployment with a Security Gateway protecting each Multi-Domain Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to host virtual Security Management Servers called Domain Management Servers. Synonym: Multi-Domain Security Management Server. Acronym: MDS.. One of the Domain Management Servers
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to host virtual Security Management Servers called Domain Management Servers. Synonym: Multi-Domain Security Management Server. Acronym: MDS.. One of the Domain Management Servers![]() Virtual Security Management Server that manages Security Gateways for one Domain, as part of a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. Acronym: DMS. manages these Security Gateways.
Virtual Security Management Server that manages Security Gateways for one Domain, as part of a Multi-Domain Security Management environment. Acronym: DMS. manages these Security Gateways.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Active Domain Management Servers |
|
2 |
Standby Domain Management Servers |
|
3 |
Primary Multi-Domain Server with Active and Standby Domain Management Servers |
|
4 |
Security Gateways |
|
5 |
Internet |
|
6 |
Secondary Multi-Domain Server with Active and Standby Domain Management Servers |
Security Gateway Managed by a Domain Management Server
You can create a Domain and Domain Management Server to manage the Policies for Security Gateways that protect Multi-Domain Servers in your environment.
Workflow for this scenario:
-
Run SmartConsole
 Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. and log into the Multi-Domain Server.
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. and log into the Multi-Domain Server. -
Create a new Domain and Domain Management Server.
-
Connect to the new Domain SmartConsole and create a Security Gateway object.
-
Enable the Firewall and other Software Blades on this Security Gateway.
-
Create and install a Security Policy
 Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. for the Security Gateway.
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. for the Security Gateway.
Defining an Access Control Policy for Multi-Domain Server Components
communication between the different Multi-Domain Security Management components. You can define these rules in global configurations or in local Domain Policies.
Use this table as a guideline to allow connections between specified components:
|
Activity |
Source |
Destination |
|---|---|---|
|
Allow connections between SmartConsole and the Multi-Domain Server |
SmartConsole
|
Multi-Domain Server
|
|
Allow connections between Multi-Domain Servers |
Multi-Domain Servers |
Multi-Domain Servers |
|
Allow connections between Domain Management Servers and Security Gateways |
Domain Management Server
|
Security Gateway
|
|
Allow Domain Management Server status data and certificate exchange between Domain Management Server High Availability peers Allow Domain Management Server synchronization between peers |
Domain Management Server peer |
Domain Management Server peer |
See the R81 Security Management Administration Guide to learn how to create a Security Policy.
Using External Authentication Servers
Multi-Domain Security Management supports these external authentication solutions:
-
RADIUS
-
TACACS
-
RSA SecurID Authentication Manager
When an administrator logs in, an authentication requests goes to the external authentication server, which sends a reply to the Multi-Domain Server. TACACS and RADIUS use the Multi-Domain Server as a proxy between the Domain Management Server and the external authentication server. To make this work correctly, you must configure each Multi-Domain Server on the authentication server.
|
|
Note - If the Multi-Domain Server is DOWN, the Domain Management Server cannot authenticate administrators. |
Configuring External Authentication
To configure External Authentication:
-
Connect to the Multi-Domain Server with SmartConsole.
-
In the Domains view, select the Global Domain, and then click Connect.
-
Connect to the Global Domain with SmartConsole, and then create a host object for the authentication server.
-
Define the Multi-Domain Security Management administrators in the authentication server.
-
In SmartConsole, select Administrators.
-
Select an existing administrator or click New.
-
In the General tab, select the applicable Authentication Scheme.
-
If the selected authentication server is RADIUS or TACACS, select the server that you configured in the Global Domain SmartConsole.
-
If the authentication server is SecurID:
-
Close SmartConsole.
-
Generate the file
sdconf.recon the Authentication Manager, and configure the user to use Tokencode only. -
Copy
sdconf.recto/var/ace/on each Multi-Domain Server. -
Open
/etc/servicesin a text editor and add the following lines:securid 5500/udpsecuridprop 5510/tcp -
Reboot the Multi-Domain Server.
-
|
|
Note - The |