AD Query
AD Query![]() Check Point clientless identity acquisition tool. It is based on Active Directory integration and it is completely transparent to the user.
The technology is based on querying the Active Directory Security Event Logs and extracting the user and computer mapping to the network address from them. It is based on Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), a standard Microsoft protocol.
The Check Point Security Gateway communicates directly with the Active Directory domain controllers and does not require a separate server.
No installation is necessary on the clients, or on the Active Directory server. is an easy to configure, clientless tool to get identities. Its function is based on Active Directory integration, and it is fully transparent to the user.
Check Point clientless identity acquisition tool. It is based on Active Directory integration and it is completely transparent to the user.
The technology is based on querying the Active Directory Security Event Logs and extracting the user and computer mapping to the network address from them. It is based on Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), a standard Microsoft protocol.
The Check Point Security Gateway communicates directly with the Active Directory domain controllers and does not require a separate server.
No installation is necessary on the clients, or on the Active Directory server. is an easy to configure, clientless tool to get identities. Its function is based on Active Directory integration, and it is fully transparent to the user.
AD Query works when:
-
An identified user or computer tries to get an access to a resource that creates an authentication request. For example, when a user logs in, unlocks a screen, shares a network drive, reads emails through Exchange, or uses an Intranet portal.
-
You select AD Query to get identities.
In this technology, you make a query for the Active Directory Security Event Logs and extract the user and computer mapping to the network address from them. It works because of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), a standard Microsoft protocol. The Identity Awareness![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that enforces network access and audits data based on network location, the identity of the user, and the identity of the computer. Acronym: IDA. Gateway communicates directly with the Active Directory domain controllers and does not need a special server.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that enforces network access and audits data based on network location, the identity of the user, and the identity of the computer. Acronym: IDA. Gateway communicates directly with the Active Directory domain controllers and does not need a special server.
No installation is necessary on the clients, or on the Active Directory server.
AD Query extracts user and computer identity information from the Active Directory Security Event Logs. The system generates a Security Event Log entry when a user or a computer connects to a network resource. For example, this occurs when a user logs in, unlocks a screen, or connects to a network drive. Security Event Logs are not generated when a user logs out because Active Directory cannot detect this action.
These are limitations of AD Query:
-
User/IP association timeout -After a default period of network inactivity, a user session closes automatically. The user must log in again with the Captive Portal
 A Check Point Identity Awareness web portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate, when using Browser-Based Authentication..
A Check Point Identity Awareness web portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate, when using Browser-Based Authentication.. -
Many user accounts connected from the same IP address - AD Query cannot detect when a user logs out. Therefore, more than one user can have open sessions from the same IP address. When this occurs, the permissions for each account stay active until their User/IP association timeout occurs. In this scenario, there is a risk that currently connected users can get access to network resources, for which they do not have permissions.
How AD Query Works - Firewall Rule Base
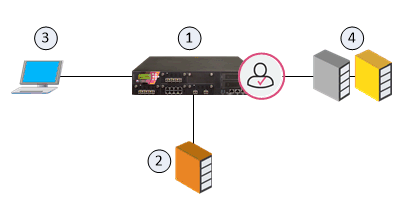
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Identity Awareness Gateway |
|
2 |
Active Directory Domain Controller |
|
3 |
User with Active Directory credentials |
|
4 |
Network resources |
Flow of events:
-
The Identity Awareness Gateway (1) gets security event logs from the Active Directory Domain Controllers (2).
-
A user logs in to a computer with Active Directory credentials (3).
-
The Active Directory Domain Controller (2) sends the security event log to the Identity Awareness Gateway (1).
-
The Identity Awareness Gateway gets the user name (
@domain), computer name and source IP address). -
The user opens a connection to the network resource (4).
-
The Identity Awareness Gateway confirms the user identity and allows or blocks access to the resource that works because of the policy.
