The Check Point Solution for DLP
The Check Point Data Loss Prevention![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that detects and prevents the unauthorized transmission of confidential information outside the organization. Acronym: DLP. Software Blade
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that detects and prevents the unauthorized transmission of confidential information outside the organization. Acronym: DLP. Software Blade![]() Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities. provides the ability for you to quickly configure realistic out-of-the-box detection capabilities based on expert heuristics.
Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities. provides the ability for you to quickly configure realistic out-of-the-box detection capabilities based on expert heuristics.
However, optimal DLP must take time. To specify data prevented from transmission, you must take into account many variables, different in the context of the particular transmission, for example:
-
What type of data is it?
-
Who owns it?
-
Who is sending it?
-
Who is the intended receiver?
-
When is it being sent?
-
What is the cost if tasks are disrupted because the policy is stricter than needed?
Data Loss Prevention Features
Check Point solves the complexity of Data Loss Prevention with unique features.
-
UserCheck™ - Provides rapid response for incident handling with automated user notification and the unique Ask User mode. Each person in your organization learns best practices as needed, preventing future unintentional leaks - the vast majority of DLP incidents - and quickly handling immediate incidents. The user handles these incidents either through the DLP Self Incident Handling Portal , or through the UserCheck client.
Without UserCheck, a security administrator, or even a security team, would have to check every email and data movement in real time and approve or reject each. For this reason, other products offer only detection of suspicious incidents. With UserCheck, the decision-making is distributed to the users. They are presented with the reason for the data capture and must provide a reason for letting it pass (if the notification did not change their minds about sending it on). User decisions (send or discard) and reasons for sending are logged. With the original message and user decisions and reasons, you can develop an effective prevention policy based on actual use.
-
MultiSpect™ - Provides unmatched accuracy in identifying and preventing incidents through multi-parameter correlation with Compound Data Types and customizable Data Types with CPcode.
-
Out of the Box Security - A rich set of pre-specified Data Types recognizes sensitive forms, templates, and data to be protected. The Data Types are enforced in an effective out-of-the-box policy.
-
Data Owner Auditing - The Data Owner is the person responsible for controlling the information and files of his or her own area in the corporation. Data Owners get timely and relevant information through automated notifications and reports that show exactly how their data is being moved. Check Point DLP gives Data Owners the information they need to handle usage issues directly related to their areas of responsibility. Without Data Owner control, the security administrator would often be placed in an awkward position between managers and employees.
-
CPcode - DLP supports fully customized data identification through the use of CPcode. You specify how data is to be matched by DLP, with the greatest flexibility possible. See the R77 versions CPcode DLP Reference Guide. .
Data Loss Prevention Benefits
Check Point DLP saves time and significantly improves ROI. Its innovative technologies provide automation that negates the need for long and costly analysis and a team for incident handling. You can now move from a detection-only policy to an accurate and effective prevention policy without bringing in outside consultants or hiring a security team.
All of this functionality is easy to manage through the SmartConsole![]() Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on., in an interface similar to other Software Blades. You are not expected to be a DLP expert from the day of configuration. Check Point Data Loss Prevention guides you on how to customize and improve your DLP policy - with the Improve Accuracy flag, for example. The DLP Software Blade comes with a large number of built-in Data Types that can be quickly applied as a default policy. You can fine-tune the out-of-the-box policy to easily convert the confidentiality and integrity guidelines of your organization into automated rules. And later, you can create your own Data Types. This cycle of updating the policy, moving from a detection policy to a preventative policy, is close with the Check Point Logs & Monitor tool.
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on., in an interface similar to other Software Blades. You are not expected to be a DLP expert from the day of configuration. Check Point Data Loss Prevention guides you on how to customize and improve your DLP policy - with the Improve Accuracy flag, for example. The DLP Software Blade comes with a large number of built-in Data Types that can be quickly applied as a default policy. You can fine-tune the out-of-the-box policy to easily convert the confidentiality and integrity guidelines of your organization into automated rules. And later, you can create your own Data Types. This cycle of updating the policy, moving from a detection policy to a preventative policy, is close with the Check Point Logs & Monitor tool.
Content Awareness Software Blade
Content Awareness![]() Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides data visibility and enforcement. Acronym: CTNT. and Data Loss Prevention both use Data Type
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides data visibility and enforcement. Acronym: CTNT. and Data Loss Prevention both use Data Type![]() Classification of data in a Check Point Security Policy for the Content Awareness Software Blade.. However, they have different features and capabilities. They work independently, and the Security Gateway
Classification of data in a Check Point Security Policy for the Content Awareness Software Blade.. However, they have different features and capabilities. They work independently, and the Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. enforces them separately.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. enforces them separately.
For more information on the Content Awareness Software Blade see the R81 Quantum Security Gateway Guide.
How DLP Works
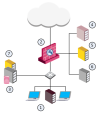
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Internal network |
|
2 |
Data Loss Prevention Software Blade enabled on a Security Gateway |
|
3 |
|
|
4 |
HTTP proxy |
|
5 |
Mail server |
|
6 |
Active Directory or LDAP server |
|
7 |
Logs & Monitor view |
DLP Workflow:
-
The Data Loss Prevention Software Blade is enabled on a Security Gateway (2) (or ClusterXL Security Cluster
 Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing.). This makes it a DLP Gateway (or a DLP security cluster). In other way, you can install a dedicated DLP Gateway behind a protecting Security Gateway.
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing.). This makes it a DLP Gateway (or a DLP security cluster). In other way, you can install a dedicated DLP Gateway behind a protecting Security Gateway. -
You use the SmartConsole and the Security Management Server
 Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. to install the DLP Policy on the DLP Gateway.
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server. to install the DLP Policy on the DLP Gateway. -
The DLP gateway (2) uses the built-in Data Types and rules to provide out-of-the-box Data Loss Prevention. It may use the Active Directory or LDAP server (6) to identify the internal organization.
It catches all traffic that contains data and goes through supported protocols. When users send data that goes to an HTTP proxy (4) or a mail server (5), for example, the DLP Gateway catches the data before it goes outside the organization.
It scans the traffic, with email attachments, to find data that must not go outside the organization. To recognize this data, it uses protocol, source, destination, and complex Data Type representations.
It can also scan internal traffic between Microsoft Exchange clients within the organization. The installation of the Exchange Security Agent on the Microsoft Exchange server is necessary for this. The agent forwards internal emails to the DLP Gateway which then scans them. If the organization only uses Exchange servers for managing emails (internal and external), you can use this setup to also scan emails that are sent outside of the organization.
If the data does not match any of the rules of the DLP policy, the traffic is allowed to pass.
-
Use Logs & Monitor view (7) to effectively log, track, analyze events, and report of incidents that the DLP Gateway captures.
Integrated DLP Security Gateway Configuration
In an Integrated DLP Security Gateway configuration, the Data Loss Prevention Software Blade is enabled on a Security Gateway (or a cluster). This makes it the DLP Gateway (or DLP Security Cluster). The Firewall Software Blade, and optionally, other Network Security Software Blades, are also enabled on the gateway.
If the DLP Gateway is on the perimeter, the SMTP server forwards only transmissions with destinations outside of the organization to DLP. Internal and external transmissions can be inspected by DLP if they are forwarded to DLP by the Exchange Security Agent on the Exchange Server. For external transmissions through the Exchange Security Agent the Exchange Server must have an accessible IP address to the DLP Gateway.
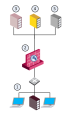
Dedicated DLP Gateway Configuration
In a Dedicated DLP Gateway configuration, a separate gateway (2) (or cluster) is installed in addition to the protecting gateway (3) (or cluster). The Data Loss Prevention Software Blade is enabled on that separate gateway.
Install the dedicated DLP Gateway behind the protecting Security Gateway to ensure its protection. We recommend that you enable only the Data Loss Prevention Software Blade to maximize the use of available hardware resources.
|
|
Best Practice - When you set up a dedicated DLP Gateway, configure it in Bridge Mode |
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Internal network |
|
2 |
Data Loss Prevention Software Blade enabled on a Security Gateway |
|
3 |
Security Gateway |
|
4 |
Security Management Server |
|
5 |
HTTP proxy |
|
6 |
Mail server |
|
7 |
Active Directory or LDAP server |
|
8 |
Logs & Monitor view |
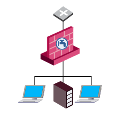
Alternative Gateway Configurations
As an alternative to putting the DLP Gateway on the network perimeter, you can put the DLP Gateway between the user networks and the servers, to allow DLP to inspect traffic before it goes to the servers. This configuration is the necessary configuration if you want to use a DLP rule![]() Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. that inspects data transmissions between departments.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. that inspects data transmissions between departments.
For example, you can create a DLP rule that checks emails between internal groups: Source is a specific network, Destination is Outside Source (anything outside of this Source). This rule applies only for this configuration.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Internal network |
|
2 |
Data Loss Prevention Software Blade enabled on a Security Gateway |
|
3 |
HTTP proxy |
|
4 |
Mail server |
|
5 |
Active Directory or LDAP server |
You can put the DLP Gateway between the users and the switch, to directly protect a subnet.
What Happens on Rule Match
The DLP Gateway captures traffic and scans it against the Data Loss Prevention policy.
-
Incident is logged.
-
The data is stored in a safe repository on a log server or Security Management Server that stores DLP logs.
-
The DLP Gateway logs an incident with the Logs & Monitor view.
-
-
Action of rule is performed.
-
If the matched rule is set to Detect, the user gets no notification. A DLP log incident is created, and the actual data is stored.
Action of rule is performed.
-
Detect - The user gets no notification. A DLP log incident is created, and the actual data is stored.
-
Inform User - DLP notifies the user that the captured traffic violates DLP rules. The traffic is passed.
-
Ask User - DLP notifies the user that the message stays, and sends a link to the DLP Portal, where the user decides whether the transmission goes through or not. User decisions, and reasons to send, are kept for your analysis.
-
Prevent - The traffic is blocked. You can notify the user and the Data Owner.
-
-
If the matched rule is set to Inform User, DLP notifies the user that the captured traffic violates DLP rules. The traffic is passed.
-
If the matched rule is set to Ask User, DLP notifies the user that the message is being held and contains a link to the DLP Portal, where the user decides whether the transmission should go through or be dropped. User decisions, and reasons for sending, are logged for your analysis.
-
If the matched rule is set to Prevent, the traffic is blocked. The user and the Data Owner may be notified.
-
-
Optionally, Data Owners, and other users configured for notifications get a notification about the incident.

 >
>