Introducing Carrier Security
Carrier Security was specifically designed for wireless operators and combines Check Point's patented Stateful Inspection technology with full GPRS![]() General Packet Radio System, a non-voice value-added service for faster data transactions over a mobile telephone network, designed for deployment on GSM and TDMA-based mobile networks. GPRS overlays a packet-based air interface on the existing switched network. Tunneling Protocol (GTP
General Packet Radio System, a non-voice value-added service for faster data transactions over a mobile telephone network, designed for deployment on GSM and TDMA-based mobile networks. GPRS overlays a packet-based air interface on the existing switched network. Tunneling Protocol (GTP![]() GPRS Tunnel Protocol.) awareness. Carrier Security inspects all GTP tunnel fields in the context of both the packet and the tunnel. This enables granular security policies
GPRS Tunnel Protocol.) awareness. Carrier Security inspects all GTP tunnel fields in the context of both the packet and the tunnel. This enables granular security policies![]() Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. that deliver the highest level of security for these wireless infrastructures.
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. that deliver the highest level of security for these wireless infrastructures.
The Need for Security on GPRS/UMTS Networks
As networks undergo the transition from proprietary, closed networks to the open world of IP, both the MS![]() Mobile Station - a portable device that connects subscribers to a wireless network, for example a cellular phone or a laptop with a cellular modem. and the network itself become exposed to the full range of security threats that plague the Internet, as well as to threats that specifically target wireless mobile networks. IP-based signals expose UMTS
Mobile Station - a portable device that connects subscribers to a wireless network, for example a cellular phone or a laptop with a cellular modem. and the network itself become exposed to the full range of security threats that plague the Internet, as well as to threats that specifically target wireless mobile networks. IP-based signals expose UMTS![]() Universal Mobile Telephone System, a third generation service (part of the IMT-2000 vision) that is expected to enable cellular service providers to deliver high-value broadband information, commerce and entertainment services to mobile users via fixed, wireless and satellite networks./LTE
Universal Mobile Telephone System, a third generation service (part of the IMT-2000 vision) that is expected to enable cellular service providers to deliver high-value broadband information, commerce and entertainment services to mobile users via fixed, wireless and satellite networks./LTE![]() Long Term Evolution - a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA technologies. It increases the capacity and speed using a different radio interface together with core network improvements. networks to a wide range of attacks: Denial of Service, IP spoofing, Overbilling, tunnel hijacking, flooding, DNS cache poisoning, and many other attacks. Any hacker with the will to do so can compromise security and disrupt communications.
Long Term Evolution - a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA technologies. It increases the capacity and speed using a different radio interface together with core network improvements. networks to a wide range of attacks: Denial of Service, IP spoofing, Overbilling, tunnel hijacking, flooding, DNS cache poisoning, and many other attacks. Any hacker with the will to do so can compromise security and disrupt communications.
GTP - Insecure By Design
GTP, the key protocol used in delivering mobile data services, offers no solution. The GTP specification specifically states:
No security is provided in GTP to protect the communication between different GPRS networks. The security is provided, if needed, between the Border Gateways in different GPRS networks by operator agreements. A security mechanism that may be considered is for example IP Security.
The UMTS/LTE network is at risk from both its own subscribers and its partner networks. Despite years of development and deployment, new security vulnerabilities are constantly being found in IP software, and evolving UMTS/LTE software will be no different. The lesson: don't depend on the network to provide your security - provide your own security.
Check Point Protects UMTS/LTE Networks
Check Point Carrier Security (formally known as Firewall-1 GX) has been protecting GPRS, UMTS and LTE (also known as 2.5, 3rd and 4th Generation) networks worldwide since 2001 by providing a GTP-level security solution that blocks illegitimate traffic "at the door." Only Carrier Security provides cellular operators, enterprises and end users with an integrated, open, end-to-end security solution. Carrier Security enables operators to define and enforce customized, granular "GTP-aware" security policies for all GTP protocol versions.
Carrier Security is fully configurable, and produces GTP-specific detailed logs and alerts. It can be installed on the:
-
Gp
 Interface between two GSNs in different PLMNs. The Gp interface allows support of GPRS network services across areas served by the co-operating GPRS PLMNs./S8 interface (between the Home PLMN
Interface between two GSNs in different PLMNs. The Gp interface allows support of GPRS network services across areas served by the co-operating GPRS PLMNs./S8 interface (between the Home PLMN Public Land Mobile Network. and the GRX network)
Public Land Mobile Network. and the GRX network) -
Gn
 Interface between two GSNs within the same PLMN./S5 interface (between the nodes in the Home PLMN)
Interface between two GSNs within the same PLMN./S5 interface (between the nodes in the Home PLMN)
Working together with a standard Security Gateway![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. on the Gi
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. on the Gi![]() Reference point between GPRS and an external packet data network./SGi interface, Carrier Security provides UMTS/LTE networks with the highest level of security available today. Carrier Security provides protection from the following threats to the core network and mobile users:
Reference point between GPRS and an external packet data network./SGi interface, Carrier Security provides UMTS/LTE networks with the highest level of security available today. Carrier Security provides protection from the following threats to the core network and mobile users:
Carrier Security protections for cellular networks:
|
Attack Target |
Attack Source |
Deploy Carrier Security on: |
|---|---|---|
|
Core Network |
Partner network, or Partner of a Partner, or anyone with access to GRX |
Gp/S8 interface |
|
Core Network |
Mobile Users |
Gn/S5 interface |
|
Core Network |
Internet or enterprise connections |
Gn/S5 interface, with gateway on Gi/SGi interface |
|
Core Network |
Within core network |
Gn/S5 interface |
|
Mobile Users |
Mobile user to mobile user |
Gn/S5 interface |
The Check Point UMTS/LTE Commitment
Check Point maintains a dedicated R![]() Reference point between a non-ISDN compatible TE and MT. Typically this reference point supports a standard serial interface.&D and product management team specializing in UMTS/LTE security. Check Point is a member of the Global Systems Mobile communications Association (GSMA) security group, and is fully committed to keeping its products up-to-date with UMTS and LTE standards.
Reference point between a non-ISDN compatible TE and MT. Typically this reference point supports a standard serial interface.&D and product management team specializing in UMTS/LTE security. Check Point is a member of the Global Systems Mobile communications Association (GSMA) security group, and is fully committed to keeping its products up-to-date with UMTS and LTE standards.
Logging, Alerts, and Reporting
In addition to security enforcement, Carrier Security provides a rich set of GTP-specific log information, including granular logging details on tunnel creation, updates and deletions. Administrators can set a wide range of security alerts based on defined activity. And Carrier Security provides a GTP-enhanced reporting tool to give a bird's-eye view of network activity. See chapter 5, "Monitoring GPRS Network Security" for more information on logging, alerts and reports.
Licenses
All GTP features require carrier licenses installed on the Security Gateway. The management server does not require special licenses. If there is no Carrier license on a Security policy installation will fail.
Carrier license string: CPSG-CARR
Before Installing Carrier Security
Before installing Carrier Security, familiarize yourself with the following Check Point documentation:
-
Read the Release Notes and applicable Administration Guides on the R81 Home Page SK - sk166715.
-
Read the R81 Known Limitations SK for the information concerning LTE features - sk166717.
-
Read this Administration Guide, which describes the Carrier Security features.
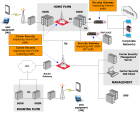
Deploying Carrier Security
For maximum security, a Carrier Security Gateway should be installed at all points in the network where the Home PLMN interfaces with other networks: at Border Gateways (Gp/S8) and Intra-PLMN interfaces (Gn/S5).
Suggested Carrier Security deployment:
In this example, two types of Check Point Gateways are deployed. The protections provided by each are described below:
Carrier Security Gateways
Carrier Security Gateways (Gateways with carrier license) are deployed at these interfaces:
|
Interface |
Located Between |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Gp/S8 |
Home PLMN and GRX |
Filters incoming roaming traffic and enforces a |
|
Gn/S5 |
GGSNs and the SSGNs in the HomePLMN |
Filters traffic between the Home PLMN GSNs, protecting them from malicious or erroneous traffic. |