The Threat Emulation Solution
Getting Started with Threat Emulation
-
 If you use a Threat Emulation appliance, prepare the network and the Threat Emulation appliance, for local or remote emulation in the internal network
If you use a Threat Emulation appliance, prepare the network and the Threat Emulation appliance, for local or remote emulation in the internal network
-
 Enable the Threat Emulation Software Blade on the Security Gateway
Enable the Threat Emulation Software Blade on the Security Gateway
Step
Instructions
1
In the Gateways & Servers view, double-click the Security Gateway / Cluster
 Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. object.
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. object.The Gateway Properties window opens.
2
In the General Properties > Network Security tab, select SandBlast Threat Emulation.
The Threat Emulation First Time Configuration Wizard opens and shows the Emulation Location page.
3
Select the Emulation Location:
-
ThreatCloud Emulation Service
-
Locally on this Threat Emulation appliance
-
Other Threat Emulation appliances - Click the + sign to add emulation appliances (you can select more than one appliance for the emulation).
4
Click Next.
The Activate Threat Extraction window opens, with this checkbox selected:
Clean potentially malicious parts from files (Threat Extraction)
-
To activate Threat Extraction
 Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that removes malicious content from files. Acronym: TEX., keep this checkbox selected:
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that removes malicious content from files. Acronym: TEX., keep this checkbox selected: -
If you do not want to activate Threat Extraction, clear this checkbox.
5
Click Next.
The Summary page opens.

Note - If you selected the Emulation Location as Locally on this Threat Emulation appliance or Other Threat Emulation appliances, and you want to share Threat Emulation information with ThreatCloud
 The cyber intelligence center of all of Check Point products. Dynamically updated based on an innovative global network of threat sensors and invites organizations to share threat data and collaborate in the fight against modern malware., select Share attack information with ThreatCloud.
The cyber intelligence center of all of Check Point products. Dynamically updated based on an innovative global network of threat sensors and invites organizations to share threat data and collaborate in the fight against modern malware., select Share attack information with ThreatCloud.6
Click Finish to enable Threat Emulation (and if selected, Threat Extraction), and then close the First Time Configuration Wizard.
7
Click OK.
The Gateway Properties window closes.

Note - When a trial license is installed on the Security Gateway, a green "V" incorrectly appears next to the Threat Emulation Software Blade
 Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities. (in SmartConsole, go to the Gateways & Servers view > right-click the Security Gateway / Cluster object > click Monitor) > the Device and License Information window opens > Device Status > Threat Emulation).
Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities. (in SmartConsole, go to the Gateways & Servers view > right-click the Security Gateway / Cluster object > click Monitor) > the Device and License Information window opens > Device Status > Threat Emulation).To see the correct license status, go to the License Status tab in the Device and License Information window.
Using Cloud Emulation
Files are sent to the Check Point ThreatCloud over a secure TLS connection for emulation. The emulation in the ThreatCloud is identical to emulation in the internal network, but it uses only a small amount of CPU, RAM, and disk space of the Security Gateway. The ThreatCloud is always up-to-date with all available operating system environments.

Best Practice - For ThreatCloud emulation, it is necessary that the Security Gateway connects to the Internet. Make sure that the DNS and proxy settings are configured correctly in Global Properties.
-
-
Select deployment. See Selecting the Threat Emulation Deployment.
-
Configure Threat Emulation settings on the Threat Prevention profile. See Configuring Threat Emulation Settings on the Security Profile.
-
Optional: Configure Threat Emulation settings on the Security Gateway. See Configuring Threat Emulation on the Security Gateway - Custom Threat Prevention
-
Configure advanced Threat Emulation settings. See Configuring Advanced Threat Emulation Settings - Custom Threat Prevention.
-
Install the Threat Prevention policy on the Security Gateway. If you use a Threat Emulation appliance, install the Threat Prevention policy on the Threat Emulation appliance as well.
Threat Emulation Configuration Video
For information about Private ThreatCloud, see the following Secure Knowledge articles:
-
sk149692: Private ThreatCloud
-
sk113332: Private ThreatCloud - Engine Updates
-
sk161534: How to configure Private ThreatCloud (PTC) on Scalable Platform Appliances
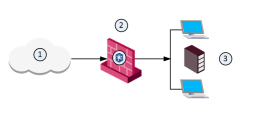
ThreatCloud Emulation
You can securely send files to the Check Point ThreatCloud for emulation. The ThreatCloud is always up-to-date with the latest Threat Emulation releases.
The new Threat Emulation engine uses Internet-connected sandboxes to prevent multi-stage attacks at the earliest stage. The full infection chain is analyzed and is presented in the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix visualization in the Threat Emulation report. The Internet-connected sandbox capability is supported on Threat Emulation AWS cloud platform and all Threat Emulation vectors: Web download, Mail Transfer Agent![]() Feature on a Security Gateway that intercepts SMTP traffic and forwards it to the applicable inspection component. Acronym: MTA., CloudGuard SaaS, SandBlast Agent and APIs.
Feature on a Security Gateway that intercepts SMTP traffic and forwards it to the applicable inspection component. Acronym: MTA., CloudGuard SaaS, SandBlast Agent and APIs.
-
The Security Gateway gets a file from the Internet or an external network.
-
The Security Gateway compares the cryptographic hash of the file with the database.
-
If the file is already in the database, no additional emulation is necessary
-
If the file is not in the database, it is necessary to run full emulation on the file
-
-
The file is sent over a TLS connection to the ThreatCloud.
-
The virtual computers in the ThreatCloud run emulation on the file.
-
The emulation results are sent securely to the Security Gateway for the applicable action.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Internet and external networks |
|
2 |
Perimeter Security Gateway |
|
3 |
Check Point ThreatCloud servers |
|
4 |
Computers and servers in the internal network |
Threat Emulation Analysis Locations
You can choose a location for the emulation analysis that best meets the requirements of your company.
-
ThreatCloud - You can send all files to the Check Point ThreatCloud for emulation. Network bandwidth is used to send the files and there is a minimal performance impact on the Security Gateway.
-
Threat Emulation Appliance in the Internal network - You can use a Threat Emulation appliance to run emulation on the files, whether locally or on a remote appliance.
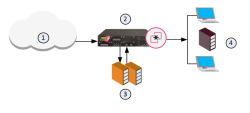
Local or Remote Emulation
You can install a Threat Emulation appliance in the internal network.
-
The Security Gateway receives the traffic, and aggregates the files.
-
The Security Gateway compares the cryptographic hash of the file with the database.
-
The file is already in the database, no emulation is needed.
-
If the file is not in the database, the virtual computers in the Security Gateway run full emulation on the file.
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Internet and external networks |
|
2 |
Security Gateway/Threat Emulation appliance |
|
3 |
Computers and servers in the internal network |
-
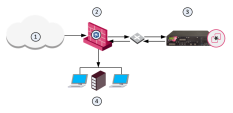
The Security Gateway aggregates the files, and the files are sent to the Threat Emulation appliance.
-
The Threat Emulation appliance compares the cryptographic hash of the file with the database. Files have unique cryptographic hashes. These file hashes are stored in a database after emulation is complete
-
If the file is already in the database, no emulation is needed.
-
If the file is not in the database, the virtual computers in the Threat Emulation appliance run full emulation on the file.
-
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Internet and external networks |
|
2 |
Perimeter Security Gateway |
|
3 |
Threat Emulation Appliance |
|
4 |
Computers and servers in the internal network |
Selecting the Threat Emulation Deployment
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Inline |
Traffic is sent for emulation before it is allowed to enter the internal network. You can use the Threat Prevention policy to block malware. |
|
Monitor (SPAN/TAP) |
You can use a mirror or TAP port to duplicate network traffic. Files are sent to the computer in the internal network. If Threat Emulation discovers that a file contains malware, the appropriate log action is done. |
|
MTA (see Configuring the Security Gateway as a Mail Transfer Agent) |
SMTP traffic goes to the Security Gateway, and is sent for emulation. The MTA acts as a mail proxy, and manages the SMTP connection with the source. The MTA sends email files to emulation after it closes the SMTP connection. When the file emulation is completed, the emails are sent to the mail server in the internal network. |
To switch between the Inline and Monitor modes, see the R81.20 Gaia Administration Guide
Inline Deployments
The ThreatCloud or Threat Emulation appliance gets a file from the Security Gateway. After emulation is done on the file, if the file is safe, it is sent to the computer in the internal network. If the file contains malware, it is quarantined and logged. The computer in the internal network is not changed.
Monitor (SPAN/TAP) Deployments
The Security Gateway gets a file from the Internet or an external network and lets it enter the internal network. The Threat Emulation appliance receives a copy of the file and the original file goes to the computer in the internal network. The Threat Emulation appliance compares the cryptographic the file with the database. If the file is already in the database, then no additional emulation is necessary. If the file is not in the database, the virtual computers in the Threat Emulation appliance do emulation of the file.
If the file is identified as malware, it is logged according to the Track action of the Threat Prevention rule![]() Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session.. Monitor deployments support only the Detect action.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session.. Monitor deployments support only the Detect action.
Threat Emulation Deployments with a Mail Transfer Agent
SMTP traffic goes to the Security Gateway, and is sent for emulation. The MTA acts as a mail proxy, and manages the SMTP connection with the source. The MTA sends email files to emulation after it closes the SMTP connection. When the file emulation is completed, the emails are sent to the mail server in the internal network.
For more information on how to work with the Mail Transfer Agent, see Configuring the Security Gateway as a Mail Transfer Agent.