Basic Site to Site VPN Configuration
It is more complex to configure VPN with external Security Gateways (those managed by a different Security Management Server![]() Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server.) than to configure VPN with internal Security Gateways (managed by the same Security Management Server
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to manage the objects and policies in a Check Point environment within a single management Domain. Synonym: Single-Domain Security Management Server.) than to configure VPN with internal Security Gateways (managed by the same Security Management Server![]() Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server.) because:
Check Point Single-Domain Security Management Server or a Multi-Domain Security Management Server.) because:
-
There are two systems to configure separately.
-
Administrators of the peer VPN Security Gateways must coordinate with each other and agree on all details. The administrators must manually supply details such as the IP address and the VPN domain topology. These details cannot be detected automatically.
Configuring a Star or Meshed Community Between Internally Managed Security Gateways
See VPN Communities.
-
Install and configure the Security Gateways as described in the R81.10 Installation and Upgrade Guide.
-
From the left navigation panel, click Gateways & Servers.
-
On the General Properties page, click the Network Security tab, and select IPsec VPN.
-
Configure the VPN Domain:
-
From the left tree, click Network Management > VPN Domain.
-
Select one of these:
-
All IP Addresses behind the Gateway based on Topology information
-
User-defined - select the applicable object (Network, Address Range, Group).
-

Note - There is nothing to configure on the IPsec VPN page for certificates. This is because Security Gateways that this Management Server manages automatically receive a certificate from this Management Server's Internal Certificate Authority.
-
-
Click OK.
-
From the top toolbar, click Objects > Object Explorer.
-
From the left tree, click VPN Communities.
-
Create a new VPN Community
 A named collection of VPN domains, each protected by a VPN gateway. object.
A named collection of VPN domains, each protected by a VPN gateway. object. To create a Star community
To create a Star community
Click New > VPN Community > Star Community.
The New Star Community window opens.
-
Enter the name for this VPN Community.
-
On the Gateways page:
-
In the Center Gateways section, select the applicable Security Gateway / Cluster
 Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. objects.
Two or more Security Gateways that work together in a redundant configuration - High Availability, or Load Sharing. objects.
Important - This field does not support:
-
Maestro Security Groups.
-
Quantum Spark appliances that run Gaia
 Check Point security operating system that combines the strengths of both SecurePlatform and IPSO operating systems. Embedded OS.
Check Point security operating system that combines the strengths of both SecurePlatform and IPSO operating systems. Embedded OS.
Select Mesh center gateways for the center Security Gateways to connect with each other.
-
In the Satellite Gateways section, select the applicable Security Gateway objects.
-
-
On the Encrypted Traffic page:
Select Accept all encrypted traffic, if it is necessary to encrypt all traffic between the Security Gateways.
Select the applicable option:
-
Both center and satellite gateways
-
Satellite gateways only
If you do not need to encrypt all traffic between the Security Gateways, then create the applicable Access Control rules in the Security Policy
 Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. (see the next step).
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. (see the next step). -
-
On the VPN Routing page , select To center only.
-
Click OK.
-
Close the Object Explorer window.
For information on other options, such as Encryption, Shared Secret, and Advanced, see IPsec and IKE.
For information on the MEP option, see Multiple Entry Point (MEP) VPNs.
 To create a Meshed comminity
To create a Meshed comminity
Click New > VPN Community > Meshed Community.
The New Meshed Community window opens.
-
Enter the name for this VPN Community.
-
On the Gateways page:
Add the applicable Security Gateway objects.
-
On the Encrypted Traffic page:
Select Accept all encrypted traffic, if it is necessary to encrypt all traffic between the Security Gateways.
If you do not need to encrypt all traffic between the Security Gateways, then create the applicable Access Control rules in the Security Policy (see the next step).
-
Click OK.
-
Close the Object Explorer window.
For information on other options, such as Encryption, Shared Secret, and Advanced, see IPsec and IKE.
-
-
If you did not select Accept all encrypted traffic on the Encrypted Traffic page of the VPN Community, configure the applicable Access Control rules.
For example:
-
Install the Access Control Policy on these Security Gateways.
Configuring a VPN with External Security Gateways Using Certificates
This section applies to typical configurations of a VPN with External Security Gateways, and assumes that the peers work with certificates. If this is not the case, see Configuring a VPN with External Security Gateways Using Pre-Shared Secret.
To configure a VPN with an externally managed peer, you and the peer administrator must choose the same Certificate Authority (CA) for communication between the two peers.
Even if each of the peer VPN Security Gateways uses a Check Point Internal CA (ICA![]() Internal Certificate Authority. A component on Check Point Management Server that issues certificates for authentication.), if they are not managed by the same Security Management Server then their ICAs are different.
Internal Certificate Authority. A component on Check Point Management Server that issues certificates for authentication.), if they are not managed by the same Security Management Server then their ICAs are different.
Example - A Check Point Security Gateway located at a headquarters office and a peer Check Point Security Gateway located at a branch office are managed separately. Each peer Security Gateway uses a different Check Point ICA and has different parameters for encryption. The administrators of the two networks must agree on a CA for communication between the two peers.
Note - Configuring a VPN with PKI and certificates is more secure than with pre-shared secrets.
-
Get the certificate of the CA that issued the certificate for the peer VPN Security Gateways. Request this from the peer administrator.
If the peer Security Gateway uses the Internal Certificate Authority, then to obtain the Certificate Authority certificate file, connect with a web browser to this portal:
-
In R81.10 and higher:
http://<IP address of Management Server that manages the peer Security Gateway>:18268 -
In R81 and lower:
http://<IP address of Management Server that manages the peer Security Gateway>:18265
-
-
In SmartConsole
 Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on., configure the Certificate Authority object for the Certificate Authority that issued the certificate for the peer. See Enrolling with a Certificate Authority.
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on., configure the Certificate Authority object for the Certificate Authority that issued the certificate for the peer. See Enrolling with a Certificate Authority. -
Configure a Certificate Authority to issue certificates for your side in case the Certificate issued by ICA is not applicable for the required VPN tunnel.
You may have to export the CA certificate and supply it to the peer administrator.
-
Define the Network Object
 Logical object that represents different parts of corporate topology - computers, IP addresses, traffic protocols, and so on. Administrators use these objects in Security Policies.(s) of the Security Gateway(s) that are internally managed:
Logical object that represents different parts of corporate topology - computers, IP addresses, traffic protocols, and so on. Administrators use these objects in Security Policies.(s) of the Security Gateway(s) that are internally managed:-
In the General Properties page of the Security Gateway object, select IPsec VPN.
-
In the Network Management page, define the Topology.
-
In the VPN Domain page, define the VPN Domain.
If the VPN domain does not contain all the IP addresses behind the Security Gateway,then configure the VPN domain manually by defining a group or network of machines and setting them as the VPN Domain.
-
-
If the ICA certificate is not applicable for this VPN tunnel, then generate a certificate from the applicable Certificate Authority on the IPsec VPN page.
-
Define the Network Object(s) of the externally managed Security Gateway(s).
-
If it is not a Check Point Security Gateway, define an Interoperable Device:
In Object Explorer, click New > Network Object > More > Interoperable Device.
-
If it is a Check Point Security Gateway, define an Externally Managed VPN Gateway:
In Object Explorer, click New > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > More > Externally Managed VPN Gateway.
-
-
Set the attributes of the peer Security Gateway.
-
For an externally managed Check PointSecurity Gateway:
In the General Properties page of the Security Gateway object, select IPsec VPN.
-
Define the Topology.
-
Define the VPN Domain with the VPN Domain information obtained from the peer administrator. If the VPN Domain does not contain all the IP addresses behind the Security Gateway, define the VPN domain manually by defining a group or network of machines and setting them as the VPN Domain.
-
For an Externally Managed Check Point Security Gateway:
On the IPsec VPN
 Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides a Site to Site VPN and Remote Access VPN access. page, define the Matching Criteria. Specify that the peer must present a certificate signed by its own Certificate Authority. If possible, enforce details that appear in the certificate.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that provides a Site to Site VPN and Remote Access VPN access. page, define the Matching Criteria. Specify that the peer must present a certificate signed by its own Certificate Authority. If possible, enforce details that appear in the certificate.
-
-
Define the VPN Community.
If you are configuring a meshed community rather than a star community, ignore the difference between the Central Security Gateways and the Satellite Security Gateways.
-
Agree with the peer administrator about the various IKE properties and set them in the Encryption page and the Advanced page of the community object.
-
Define the Central Security Gateways. In most cases these are internal. If no other Community is defined for them, decide whether to mesh the central Security Gateways. If they are already in a Community, do not mesh the Central Security Gateways.
-
Define the Satellite Security Gateways. In most cases these are external.
-
-
Click OK.
-
Publish the SmartConsole session.
-
Define the applicable Access Control rules.
-
Add the Community in the VPN column, the services in the Service & Applications column, the Action, and the applicable Track option.
-
Install the Access Control Policy.
Configuring a VPN with External Security Gateways Using Pre-Shared Secret
Administrators of the peer VPN Security Gateways must coordinate with each other and agree on all details. The administrators must manually supply details such as the IP address and the VPN domain topology. These details cannot be detected automatically.
There are many possible scenarios for VPN with external Security Gateways. The next procedure is meant for typical cases and assumes that the peers work with pre-shared secrets. If the peers do not work with pre-shared secrets, see Configuring a VPN with External Security Gateways Using Certificates".
|
|
Note - It is more secure to configure a VPN with public key infrastructure (PKI) and certificates than with pre-shared secrets. |
-
Define the Network Object(s) of the Security Gateways that are internally managed.
-
In the General Properties page of the Security Gateway object, in the Network Security tab, select IPsec VPN.
-
In the Network Management page, define the Topology.
-
In the Network Management > VPN Domain page, define the VPN Domain. If the VPN domain does not contain all IP addresses behind the Security Gateway, define the VPN Domain manually by defining a group or network of machines and setting them as the VPN Domain.
-
-
Define the Network Object(s) of the externally managed Security Gateway(s).
-
If it is not a Check Point Security Gateway, define an Interoperable Device:
In Object Explorer, click New > Network Object > More > Interoperable Device.
-
If it is a Check Point Security Gateway, define an Externally Managed VPN Gateway:
In Object Explorer, click New > Network Object > Gateways and Servers > More > Externally Managed VPN Gateway.
-
-
Set the attributes of the peer Security Gateway.
-
In the Topology page, define the Topology and the VPN Domain with the VPN Domain information obtained from the peer administrator.
-
If the VPN Domain does not contain all the IP addresses behind the Security Gateway, configure the VPN Domain manually by defining a group or network of machines and setting them as the VPN Domain.
-
-
Define the Community.
If you are configuring a Mesh Community rather than a Star Community, ignore the difference between the Central Security Gateways and the Satellite Security Gateways.
-
Agree with the peer administrator about the IKE properties. Set the IKE properties in the Encryption page and the Advanced page of the community object.
-
Define the Central Security Gateways. These are usually the internally managed Security Gateways. If there is not another Community defined for them, decide whether to mesh the central Security Gateways. If the Central Security Gateways are already in a Community, do not mesh them.
-
Define the Satellite Security Gateways. These are usually the external Security Gateways.
-
-
Publish the changes in SmartConsole.
-
Agree on a pre-shared secret with the administrator of the external Community members. Then, in the Shared Secret page of the Community, select Use only Shared Secret for all external members. For each external member, enter the pre-shared secret.
-
Define the applicable Access Control rules in the Access Control Policy. Add the Community in the VPN column, the services in the Services & Applications column, the desired Action, and the applicable Track option.
-
Install the Access Control Policy.
Firewall Control Connections in VPN Communities
Check Point Nodes communicate with other Check Point Nodes through control connections. For example a Security Management Server and a Security Gateway use a control connection when the Security Policy is installed from the Security Management Server to the Security Gateway. In addition, Security Gateways send logs to the Security Management Server across control connections. Control connections use Secure Internal Communication (SIC![]() Secure Internal Communication. The Check Point proprietary mechanism with which Check Point computers that run Check Point software authenticate each other over SSL, for secure communication. This authentication is based on the certificates issued by the ICA on a Check Point Management Server.).
Secure Internal Communication. The Check Point proprietary mechanism with which Check Point computers that run Check Point software authenticate each other over SSL, for secure communication. This authentication is based on the certificates issued by the ICA on a Check Point Management Server.).
Implied Rules in the Access Control Rule Base![]() All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase. allow the Control connections. The Management Server adds and removes the Implied Rules in the Access Control Rule
All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase. allow the Control connections. The Management Server adds and removes the Implied Rules in the Access Control Rule![]() Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. Base when you select or clear options in the SmartConsole > > Global properties > Firewall page.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. Base when you select or clear options in the SmartConsole > > Global properties > Firewall page.
Some administrators do not rely on implied rules, and instead define explicit rules in the Access Control Rule Base. Check Point does not support replacing implied rules with explicit rules. See sk43401.
Why Turning off Implied Rules Blocks Firewall Control Connections
If you turn off implicit rules, you may not be able to install an Access Control Policy on a remote Security Gateway. Even if you configure explicit rules rather than implied rules, you may still not be able to install the policy:
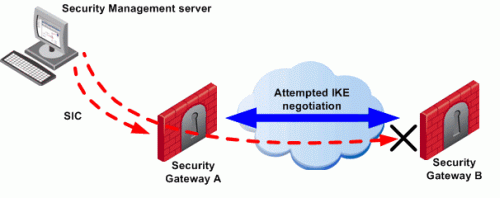
To configure a VPN between Security Gateways A and B through SmartConsole, the administrator must install a Policy from the Security Management Server to the Security Gateways.
-
The Security Management Server successfully installs the Policy on Security Gateway A. Security Gateway A recognizes that Security Gateways A and B now belong to the same VPN Community. However, Security Gateway B does not yet have the Policy.
-
The Security Management Server opens a connection to Security Gateway B to install the Policy.
-
Security Gateway A allows the connection because of the explicit rules that allow the control connections. Security Gateway A starts IKE negotiation with Security Gateway B to build a VPN tunnel for the control connection.
-
Security Gateway B cannot negotiate with Security Gateway A because it does not yet have the Policy. Therefore, Policy installation on Security Gateway B fails.
Make sure that control connections do not have to pass through a VPN tunnel.
Allowing Firewall Control Connections Inside a VPN
If you turn off implied rules, make sure that control connections are not changed by the Security Gateways. Add the services that are used for control connections to the Excluded Services page of the Community object. See sk42815 for details.
Note - Although control connections between the Security Management Server and the Security Gateway are not encrypted by the community, they are still encrypted and authenticated with Secure Internal Communication (SIC).
Discovering Which Services are Used for Control Connections
-
In SmartConsole, click > Global properties.
-
On the Firewall page, select Control Connections.
-
Click OK.
-
In SmartConsole, from the left panel, click Security Policies.
-
Select the applicable Access Control Policy.
-
From the toolbar above the policy, select Actions > Implied Rules.
The Implied Policy window opens.
-
Examine the Access Control Rule Base to see what Implied Rules are visible. Note the services used in the Implied Rules.
Simplified and Traditional Modes
By default, VPN configuration works with Simplified mode. Simplified mode uses VPN Communities for Site to Site VPN![]() An encrypted tunnel between two or more Security Gateways. Synonym: Site-to-Site VPN. Contractions: S2S VPN, S-to-S VPN. configuration, as described in this Administration Guide.
An encrypted tunnel between two or more Security Gateways. Synonym: Site-to-Site VPN. Contractions: S2S VPN, S-to-S VPN. configuration, as described in this Administration Guide.
Traditional mode is a different, legacy way to configure Site to Site VPN where one of the actions available in the Security Policy Rule Base is Encrypt. When Encrypt is selected, all traffic between the Security Gateways is encrypted. For details about Traditional Mode, see the R77 versions VPN Administration Guide.
In a policy package, all layers must use the same VPN mode.
