Browser-Based Authentication
Browser-Based Authentication![]() Authentication of users in Check Point Identity Awareness web portal - Captive Portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate. gets identities and authenticates users with one of these acquisition methods:
Authentication of users in Check Point Identity Awareness web portal - Captive Portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate. gets identities and authenticates users with one of these acquisition methods:
-
 Captive Portal
Captive Portal

Important - Internal Users and Administrators who authenticate in Multi-Portals on the Security Gateway
 Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. must have different passwords.
Dedicated Check Point server that runs Check Point software to inspect traffic and enforce Security Policies for connected network resources. must have different passwords.This applies to:
-
Identity Awareness
 Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that enforces network access and audits data based on network location, the identity of the user, and the identity of the computer. Acronym: IDA. Captive Portal
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that enforces network access and audits data based on network location, the identity of the user, and the identity of the computer. Acronym: IDA. Captive Portal A Check Point Identity Awareness web portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate, when using Browser-Based Authentication.
A Check Point Identity Awareness web portal, to which users connect with their web browser to log in and authenticate, when using Browser-Based Authentication.
Captive Portal authenticates users with a web interface. When users try to access to a protected web resource, they enter authentication information in a form that shows in their web browser.
The Captive Portal shows when a user tries to get an access to a web resource and all of these conditions apply:
-
Captive Portal is enabled.
-
The Redirect option enabled for the applicable policy rule
 Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session..
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session.. -
Firewall or Application & URL Filtering
 Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that allows granular control over which web sites can be accessed by a given group of users, computers or networks. Acronym: URLF. rules stop access by unidentified users to resources that only identified users can get access to.
Check Point Software Blade on a Security Gateway that allows granular control over which web sites can be accessed by a given group of users, computers or networks. Acronym: URLF. rules stop access by unidentified users to resources that only identified users can get access to.
In addition, the Captive Portal shows when Transparent Kerberos
 An authentication server for Microsoft Windows Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS). Authentication is enabled but authentication fails.
An authentication server for Microsoft Windows Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS). Authentication is enabled but authentication fails.From the Captive Portal, users:
-
Enter their user name and password (which are configured in the Identity Awareness Gateway object > Identity Awareness page > near the Browser-Based Authentication, click Settings > refer to the Users Access section).
-
Enter guest user credentials (which are configured in the Identity Awareness Gateway object > Identity Awareness page > near the Browser-Based Authentication, click Settings > refer to the Users Access section).
-
Click a link to download an Identity Agent
 Check Point dedicated client agent installed on Windows-based user endpoint computers. This Identity Agent acquires and reports identities to the Check Point Identity Awareness Security Gateway. The administrator configures the Identity Agents (not the end users). There are two types of Identity Agents - Full and Light. You can download the Full and Light Identity Agent package from the Captive Portal - 'https://<Gateway_IP_Address>/connect' or from Support Center. (which is configured in the Identity Awareness Gateway object > Identity Awareness page > near the Browser-Based Authentication, click Settings > refer to the Identity Agent Deployment from the Portal section).
Check Point dedicated client agent installed on Windows-based user endpoint computers. This Identity Agent acquires and reports identities to the Check Point Identity Awareness Security Gateway. The administrator configures the Identity Agents (not the end users). There are two types of Identity Agents - Full and Light. You can download the Full and Light Identity Agent package from the Captive Portal - 'https://<Gateway_IP_Address>/connect' or from Support Center. (which is configured in the Identity Awareness Gateway object > Identity Awareness page > near the Browser-Based Authentication, click Settings > refer to the Identity Agent Deployment from the Portal section).
Browser-Based Authentication with Captive Portal
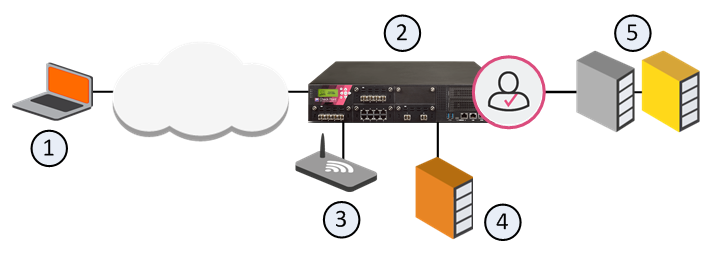
Item
Description
1
User
2
Identity Awareness Gateway
3
Captive Portal
4
Active Directory Domain Controller
5
Internal Data Center
Flow of events for Browser-Based Authentication with Captive Portal:
-
A user (1) wants to get an access to the Internal Data Center (5).
-
Identity Awareness Gateway (2) does not recognize the user and redirects the user's web browser to the Captive Portal (3).
-
The user enters regular office credentials, for example, AD, or other Check Point supported authentication methods, for example, LDAP, Check Point internal credentials, or RADIUS.
-
The credentials go to the Identity Awareness Gateway, which finds them in the AD server (4).
-
The user gets an access to the requested URL in the Data Center (5).
-
-
 Transparent Kerberos Authentication
Transparent Kerberos Authentication
To authenticate users, Transparent Kerberos Authentication gets authentication data from the web browser without user input. If authentication is successful, the user goes directly to the specified destination. If authentication fails, the user must enter credentials in the Captive Portal.
Flow of events for Browser-Based Authentication with Transparent Kerberos Authentication:
-
A user wants to get an access to the Internal Data Center.
-
Identity Awareness Gateway does not recognize the user and redirects the user's web browser to the Transparent Authentication page.
-
The Transparent Authentication page asks the web browser to authenticate itself.
-
The web browser gets a Kerberos ticket from Active Directory and presents it to the Transparent Authentication page.
-
The Transparent Authentication page sends the ticket to the Identity Awareness Gateway, which authenticates the user and redirects the user's web browser to the originally requested URL.
-
If Kerberos authentication fails for some reason, Identity Awareness Gateway redirects the user's web browser to the Captive Portal.
-
