CloudGuard Controller Monitoring
CloudGuard Controller Logs and Events
To monitor the CloudGuard Controller![]() Provisions SDDC services as Virtual Data Centers that provide virtualized computer networking, storage, and security., use any of these options:
Provisions SDDC services as Virtual Data Centers that provide virtualized computer networking, storage, and security., use any of these options:
-
Filter the logs in SmartConsole
 Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. with this query syntax:
Check Point GUI application used to manage a Check Point environment - configure Security Policies, configure devices, monitor products and events, install updates, and so on. with this query syntax:blade:"CloudGuard IaaS" AND severity:Critical -
Create a User Defined Event based on logs and severity, see Creating a User Defined Event and Sending Alerts.
-
Connect the Event to an Automatic Reaction such as emails or scripts.
See the R81.10 Logging and Monitoring Administration Guide > Section Automatic Reactions.
-
|
|
Note - As the CloudGuard Controller uses Identity Awareness You can monitor and get a notification for this issue in SmartLog. For details, refer to sk113833. |
CloudGuard Controller Status
Options for checking the CloudGuard Controller status
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Follow these steps:
|
|
|
In SmartConsole |
Follow these steps:
|
|
SNMP Traps |
See sk124532. |
Output table columns:
-
Imported objects - Shows objects that are updated in the CPM process or in SmartConsole.
-
Controller Updates -Shows the number of updates sent about imported objects since the last CloudGuard Controller restart.
Note: The cpstat vsec tool does not monitor Data Center Query Objects.
Data Center Updates
CloudGuard Controller requires reliable connectivity to the Security Gateways to continuously update the Security Gateways with changes to the Data Center![]() Virtual centralized repository, or a group of physical networked hosts, Virtual Machines, and datastores. They are collected in a group for secured remote storage, management, and distribution of data. objects.
Virtual centralized repository, or a group of physical networked hosts, Virtual Machines, and datastores. They are collected in a group for secured remote storage, management, and distribution of data. objects.
The updates of Data Center objects include:
-
Adding new IP addresses to the rule base
 All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase..
All rules configured in a given Security Policy. Synonym: Rulebase.. -
Removing redundant IP addresses from the rule
 Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. base.
Set of traffic parameters and other conditions in a Rule Base (Security Policy) that cause specified actions to be taken for a communication session. base. -
Extending the expiration time on existing objects in the rule base so they do not expire and automatically erase.
If the Security Gateway stops receiving updates for a Data Center Object, the Gateway has no way to verify that the object is still a valid object on the Data Center.
To create a balance between security and connectivity, each IP address of a Data Center object has a built-in expiration timer (aka Time To Live – TTL).
The CloudGuard Controller updates the IP addresses of the Data Center objects TTL on the Security Gateway to avoid TTL expiration.
However, if the Security Gateway(s) update fails continuously (for example, because of lack of connectivity between the Management and the Security Gateway), the TTL of the IP address is not updated.
When the full TTL of the IP address is reached, the IP address expires, and security policy![]() Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. rules that use this IP of that Data Center object are no longer enforceable.
Collection of rules that control network traffic and enforce organization guidelines for data protection and access to resources with packet inspection. rules that use this IP of that Data Center object are no longer enforceable.
Due to the critical nature of Data Center Objects, it is highly recommended to monitor CloudGuard Controller status.
You can configure the TTL from 5 minutes to 30 days.
For more information see the enforcementSessionTimeoutInMinutes parameter in the Configuration Parameters section.
SNMP Traps
To configure custom SNMP traps, refer to sk124532.
Creating a User Defined Event and Sending Alerts
The CloudGuard Controller is very critical component for the security of an organization.
If the CloudGuard Controller loses connection with a data center, for some reason, then there are no updates to the Gateways.
This a serious situation for any security administrator.
While administrators can monitor the SmartConsole logs in the office, there is also option to send critical CloudGuard Controller Events to an administrator's smartphone or email.
-
Enable the SmartEvent Software Blade
 Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities. on the Management Server.
Specific security solution (module): (1) On a Security Gateway, each Software Blade inspects specific characteristics of the traffic (2) On a Management Server, each Software Blade enables different management capabilities. on the Management Server.See the R81.10 Logging and Monitoring Administration Guide > Section Deploying SmartEvent.
-
Open the Legacy SmartEvent GUI client:
-
From the left navigation panel, click Logs & Monitor.
-
At the top, click the + tab.
-
At the bottom, in the section External Apps, click SmartEvent Settings & Policy.
-
-
In the SmartEvent Policy tree, right-click Event policy.
The Event Definition wizard opens.
-
Step 1/6: In the Event Definition wizard window, below Create an event, select that is completely new > click Next.
-
Step 2/6: In the Name field, enter a name for the Event.
From the Severity list, select a severity for the event > click Next.
-
Step 3/6: Select a single log > click Next.
-
Step 4/6: Click Add product > select the checkbox for CloudGuard IaaS > click Next.
-
Step 5/6: Below the Define the condition that specifies which {your event name} logs are appropriate for this event:
-
Select Show more fields > Existing field.
The Select Log Fields window opens.
-
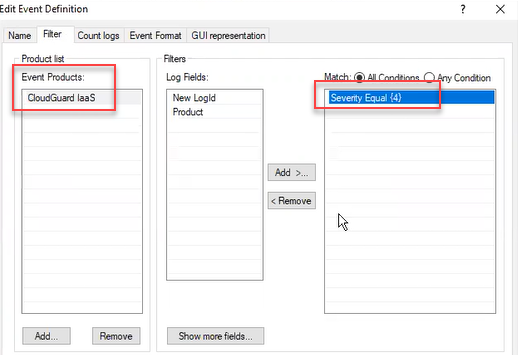
Below Log Fields, select Severity > click OK.
-
Below Available Log Fields, select Severity, click Add.
The Severity Filter window opens.
-
Click Add, in the Value field enter the number '4' for the value (four is the highest, referred to as "critical") > click OK.
-
Make sure that In the Event Definition wizard window, the right-side box now shows Severity Equal {x} > click Next.
-
Click Finish.
-
To install the policy, click Yes.
Note - In the SmartEvent window that opens, click Yes to install the policy.
There is now a User Defined Event, in this example "CloudGuard IaaS Critical", that you can connect to Automatic Reaction which you create.
-
-
Use SmartEvent to send push notifications to your mobile device or email account.
This allows you to get notification even when your not in front of SmartConsole, and even when your are not in the office.
In SmartEvent, this is called "Automatic Reaction."
For more information about how to edit an event, see the R81.10 Logging and Monitoring Administration Guide
-
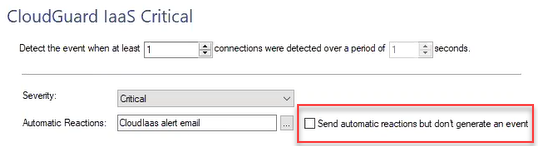
In the SmartEvent tree, right-click User Defined Events select the event.
-
In the top field, enter the parameters for detecting an Event.
Example, "Detect the event when at least 2 connections where detected over a period of 120 seconds".
-
Select the button to the right of the Automatic Reactions tab.
-
Select Add new > select Mail or External Script.
The Add Automatic Reaction window opens.
For more information about External scripts, see the R81.10 Logging and Monitoring Administration Guide > Section Creating an External Script Automatic Reaction.
-
In the Name field, delete the default name and enter a different name. For example, "CloudGuard IaaS alert email".
-
In the Command line field, enter the path and the name of the script. For example, "
/var/log/myscript.sh". -
Click Save.
-
In the Automatic Reactions window, click OK.
-
From the SmartEvent toolbar, click the save icon > click Yes.

